|
Backward Speech
The trait of backward speech is described as an ability to spontaneously and accurately reverse words. Two strategies of word reversal were reported: reversal according to the phonetic structure of the words or reversal according to their spelling. In the 1980s Nelson Cowan hypothesized that this ability is afforded by an extraordinary working memory. Recent studies have provided evidence that the working memory is indeed involved in this ability and further suggested that genetic factors may contribute to this trait. Some cases * Patients of Nelson Cowan. * Italian-speaking patient that gained the ability to speak backwards after neurosurgery. * A patient that could talk backward after a head injury which resulted in conversion disorder. * Serbian Serbian may refer to: * someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe * someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people * Serbian language * Serbian names See also * * * Old Serbian (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. The field of phonetics is traditionally divided into three sub-disciplines based on the research questions involved such as how humans plan and execute movements to produce speech (articulatory phonetics), how various movements affect the properties of the resulting sound (acoustic phonetics), or how humans convert sound waves to linguistic information (auditory phonetics). Traditionally, the minimal linguistic unit of phonetics is the phone—a speech sound in a language which differs from the phonological unit of phoneme; the phoneme is an abstract categorization of phones. Phonetics deals with two aspects of human speech: production—the ways humans make sounds—and perception—the way speech is understood. The communicative modali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Words
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonological, grammatical or orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations. The concept of "word" is distinguished from that of a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of language that has a meaning, even if it cannot stand on its own. Words are made out of at least o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spelling
Spelling is a set of conventions that regulate the way of using graphemes (writing system) to represent a language in its written form. In other words, spelling is the rendering of speech sound (phoneme) into writing (grapheme). Spelling is one of the elements of orthography, and highly standardized spelling is a prescriptive element. Spellings originated as transcriptions of the sounds of spoken language according to the alphabetic principle. They remain largely reflective of the sounds, although fully phonemic spelling is an ideal that most languages' orthographies only approximate, some more closely than others. This is true for various reasons, including that pronunciation changes over time in all languages, yet spellings as visual norms may resist change. In addition, words from other languages may be adopted without being adapted to the spelling system, and different meanings of a word or homophones may be deliberately spelled in different ways to differentiate them visu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Cowan
Nelson Cowan is the Curators' Distinguished Professor of Psychological Sciences at the University of Missouri. He specializes in working memory, the small amount of information held in mind and used for language processing and various kinds of problem solving. To overcome conceptual difficulties that arise for models of information processing in which different functions occur in separate boxes, Cowan proposed a more organically organized "embedded processes" model. Within it, representations held in working memory comprise an activated subset of the representations held in long-term memory, with a smaller subset held in a more integrated form in the current focus of attention. Other work has been on the developmental growth of working memory capacity and the scientific method. His work, funded by the National Institutes of Health since 1984 (primarily NICHD), has been cited over 41,000 times according to Google Scholar. The work has resulted in over 250 peer-reviewed articles, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
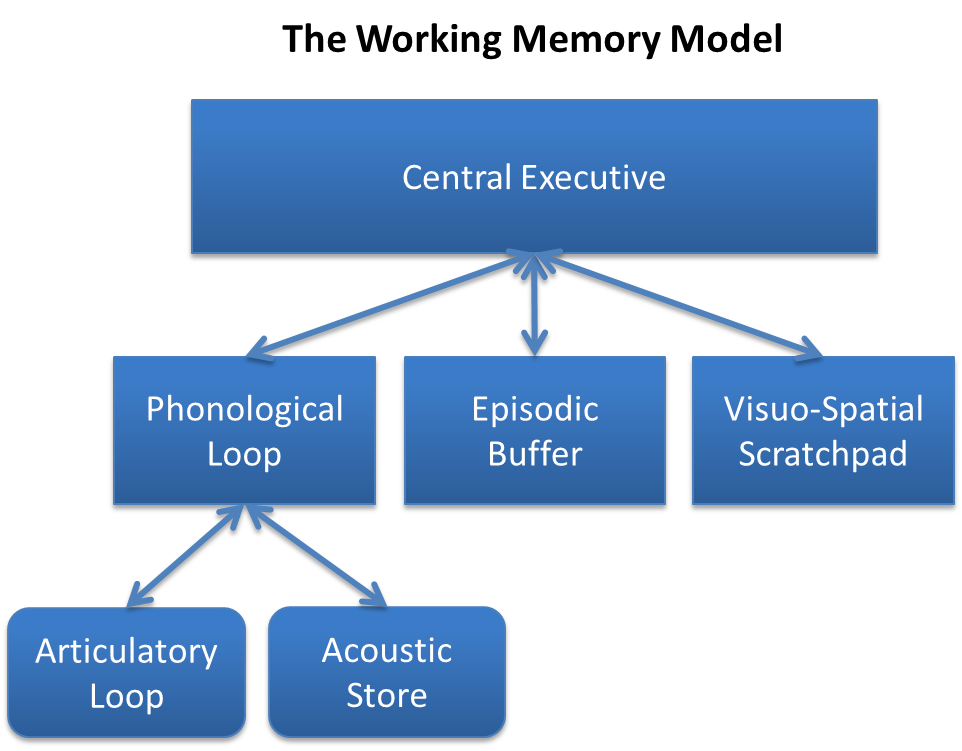
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 85 million people (2022), Italian is an official language in Italy, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), San Marino, and Vatican City. It has an official minority status in western Istria (Croatia and Slovenia). Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia.Ethnologue report for language code:ita (Italy) – Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United States In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school, and seven years of residency (PGY-1-7). Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue additional training in the form of a fellowship after residency, or, in some cases, as a senior resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of injuries, there are many causes—including accidents, falls, physical assault, or traffic accidents—that can cause head injuries. The number of new cases is 1.7 million in the United States each year, with about 3% of these incidents leading to death. Adults have head injuries more frequently than any age group resulting from falls, motor vehicle crashes, colliding or being struck by an object, or assaults. Children, however, may experience head injuries from accidental falls or intentional causes (such as being struck or shaken) leading to hospitalization. Acquired brain injury (ABI) is a term used to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder, or from a congenital disorder. Unlike a broken bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conversion Disorder
Conversion disorder (CD), or functional neurologic symptom disorder, is a diagnostic category used in some psychiatric classification systems. It is sometimes applied to patients who present with neurological symptoms, such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits, which are not consistent with a well-established organic cause, which cause significant distress, and can be traced back to a psychological trigger. It is thought that these symptoms arise in response to stressful situations affecting a patient's mental health or an ongoing mental health condition such as depression. Conversion disorder was retained in DSM-5, but given the subtitle functional neurological symptom disorder. The new criteria cover the same range of symptoms, but remove the requirements for a psychological stressor to be present and for feigning to be disproved. ICD-10 classifies conversion disorder as a dissociative disorder while DSM-IV classifies it as a somatoform disorder. Signs and symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbians
The term Serbians in English is a polysemic word, with two distinctive meanings, derived from morphological differences: * Morphology 1: Serb-ian- s, derived from the noun ''Serb'' and used interchangeably to refer to ethnic Serbs, thus having a synonymous ethnonymic use. * Morphology 2: Serbia- an- s, a demonym derived from the noun ''Serbia'', designating the population of Serbia, in general. In English, the use of term ''Serbians'' depends on the context, with demonymic use being more common, but not exclusive. Demonymic use The term ''Serbians'' is used in English as a demonym for all citizens of Serbia, regardless of their ethnic, linguistic, religious or other cultural distinctions. In Serbian, however, the term ''Srbijanci'' ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, link=no, Србијанци, Srbijanci) is also used for ethnic Serbs from Serbia, or in a narrower sense, Serbs from Central Serbia ( Serbia proper). The term thus excludes ethnic Serbs in the neighboring countries, such as Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Disorders
Language disorders or language impairments are disorders that involve the processing of linguistic information. Problems that may be experienced can involve grammar (syntax and/or morphology), semantics (meaning), or other aspects of language. These problems may be receptive (involving impaired language comprehension), expressive (involving language production), or a combination of both. Examples include specific language impairment, better defined as developmental language disorder, or DLD, and aphasia, among others. Language disorders can affect both spoken and written language, and can also affect sign language; typically, all forms of language will be impaired. Current data indicates that 7% of young children display language disorder, with boys being diagnosed twice as often as girls. Preliminary research on potential risk factors have suggested biological components, such as low birth weight, prematurity, general birth complications, and male gender, as well as family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)