|
Burr (metal)
A burr is a raised edge or small piece of material that remains attached to a workpiece after a modification process. It is usually an unwanted piece of material and is removed with a deburring tool in a process called 'deburring'. Burrs are most commonly created by machining operations, such as grinding, drilling, milling, engraving or turning. It may be present in the form of a fine wire on the edge of a freshly sharpened tool or as a raised portion of a surface; this type of burr is commonly formed when a hammer strikes a surface. Deburring accounts for a significant portion of manufacturing costs. In the printmaking technique of drypoint, burr, which gives a rich fuzzy quality to the engraved line, is highly desirable—the great problem with the drypoint medium is that the burr rapidly diminishes after as few as ten impressions are printed. Types There are three types of burrs that can be formed from machining operations: ''Poisson burr'', ''rollover burr'', and ''break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Burr
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electropolishing
Electropolishing, also known as electrochemical polishing, anodic polishing, or electrolytic polishing (especially in the metallography field), is an electrochemical process that removes material from a metallic workpiece, reducing the surface roughness by levelling micro-peaks and valleys, improving the surface finish. Electropolishing is often compared to, but distinctly different from, electrochemical machining. It is used to polish, passivate, and deburr metal parts. It is often described as the reverse of electroplating. It may be used in lieu of abrasive fine polishing in microstructural preparation. Mechanism Typically, the work-piece is immersed in a temperature-controlled bath of electrolyte and serves as the anode; it is connected to the positive terminal of a DC power supply, the negative terminal being attached to the cathode. A current passes from the anode, where metal on the surface is oxidised and dissolved in the electrolyte, to the cathode. At the cathode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
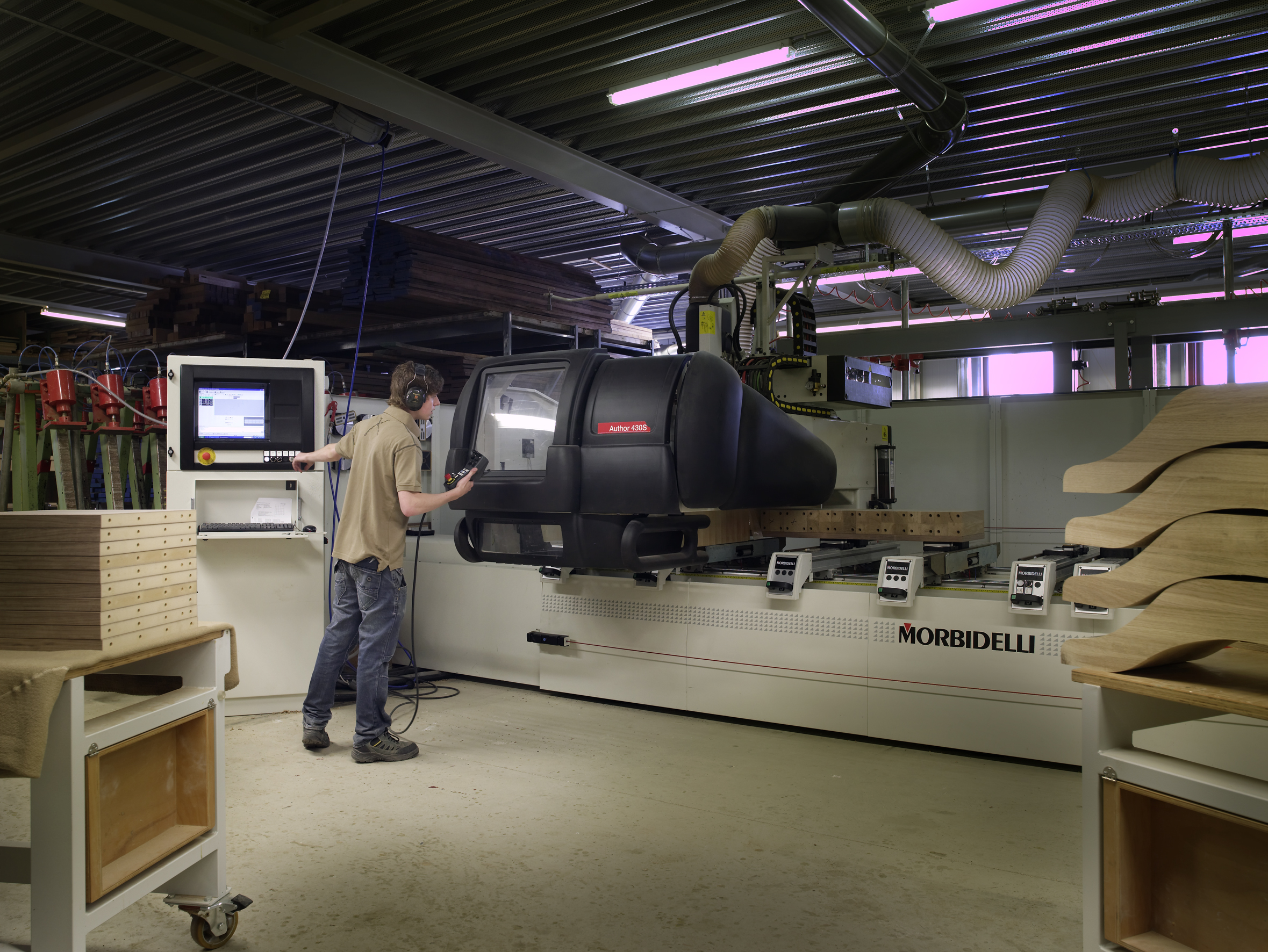
Numerical Control
Numerical control (also computer numerical control, and commonly called CNC) is the automated control of machining tools (such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers) by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a piece of material (metal, plastic, wood, ceramic, or composite) to meet specifications by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation. A CNC machine is a motorized maneuverable tool and often a motorized maneuverable platform, which are both controlled by a computer, according to specific input instructions. Instructions are delivered to a CNC machine in the form of a sequential program of machine control instructions such as G-code and M-code, and then executed. The program can be written by a person or, far more often, generated by graphical computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. In the case of 3D printers, the part to be print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Deburring Tool
Mechanical may refer to: Machine * Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement * Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic * Mechanical energy, the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy * Mechanical system, a system that manages the power of forces and movements to accomplish a task * Mechanism (engineering), a portion of a mechanical device Other * Mechanical (character), one of several characters in Shakespeare's ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' * A kind of typeface in the VOX-ATypI classification See also * Machine, especially in opposition to an electronic item * ''Mechanical Animals'', the third full-length studio release by Marilyn Manson * Manufactured or artificial, especially in opposition to a biological or natural component * Automation, using machine decisions and processing instead of human * Mechanization, using machine labor ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrittlement
Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such as temperature or environmental composition. This is oftentimes undesirable as brittle fracture occurs quicker and can much more easily propagate than ductile fracture, leading to complete failure of the equipment. Various materials have different mechanisms of embrittlement, therefore it can manifest in a variety of ways, from slow crack growth to a reduction of tensile ductility and toughness. Mechanisms Embrittlement is a series complex mechanism that is not completely understood. The mechanisms can be driven by temperature, stresses, grain boundaries, or material composition. However, by studying the embrittlement process, preventative measures can be put in place to mitigate the effects. There are several ways to study the mechanisms. During me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and sublimates directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily as a cooling agent, but is also used in fog machines at theatres for dramatic effects. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of water ice and not leaving any residue (other than incidental frost from moisture in the atmosphere). It is useful for preserving frozen foods (such as ice cream) where mechanical cooling is unavailable. Dry ice sublimates at at Earth atmospheric pressure. This extreme cold makes the solid dangerous to handle without protection from frostbite injury. While generally not very toxic, the outgassing from it can cause hypercapnia (abnormally elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood) due to buildup in confined locations. Properties Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO2), a molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic interaction, manifested in its very low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. This effect, known as the Leidenfrost effect, occurs when any liquid comes in contact with a surface which is significantly hotter than its b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
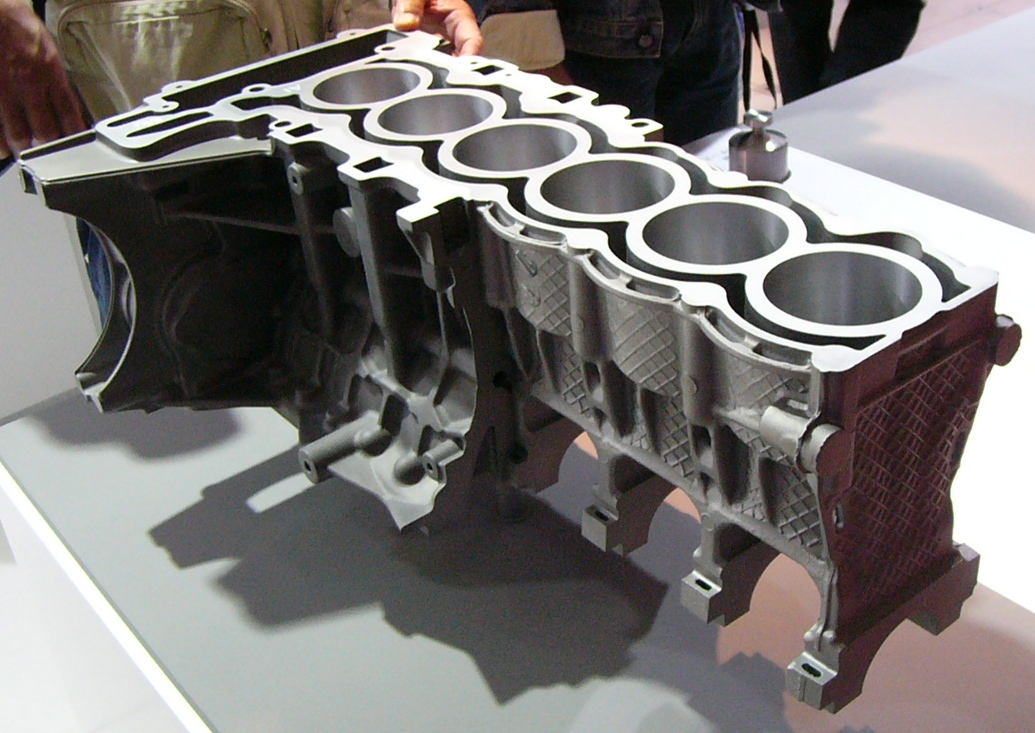
Die Cast
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1,1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash (manufacturing)
Flash, also known as flashing, is excess material attached to a molded, forged, or cast product, which must usually be removed. This is typically caused by leakage of the material between the two surfaces of a mold (beginning along the parting line) or between the base material and the mold in the case of overmolding. Details Molding flash is seen when the optimized parameter on cull height is not calibrated. Proper design of mold parting surfaces can reduce or eliminate flash. Molding flash can be caused from old or worn mold cavities that no longer fit tightly together. Other times, the complexity of the part requires so many mating pieces with such precise geometries that it is almost impossible to create a perfect fit on every impression. Most often, the type of material being molded, and its attendant viscosity in its liquid form, is the primary factor that leads to the creation of the unwanted mold flash.Bozzelli, Joh"An Expert Tells How to Stop Flash" ''Plastics Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |