|
Bronchial
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi. Structure The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchial Artery
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part of the respiratory system. Structure There are typically two left and one right bronchial arteries. The ''left bronchial arteries'' (superior and inferior) usually arise directly from the thoracic aorta. The single ''right bronchial artery'' usually arises from one of the following: * 1) the thoracic aorta at a common trunk with the right 3rd posterior intercostal artery * 2) the superior bronchial artery on the left side * 3) any number of the right intercostal arteries mostly the third right posterior. Function The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs. They travel with and branch with the bronchi, ending about at the level of the respiratory bronchioles. They anastomose with the branche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
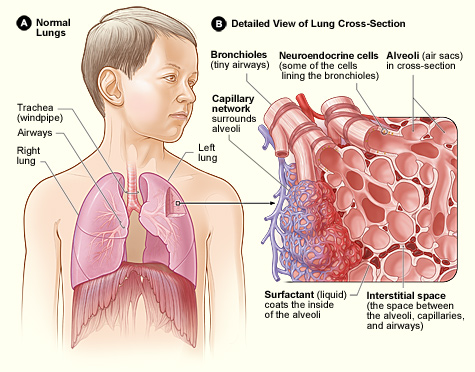
Human Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (anatomy), organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration (physiology), Respiration is driven by different muscle, muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, that branch into smaller airways called bronchioles that ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchial Vein
The bronchial veins are small vessels that return blood from the larger bronchi and structures at the roots of the lungs. The right side drains into the azygos vein, while the left side drains into the left superior intercostal vein or the accessory hemiazygos vein The accessory hemiazygos vein, also called the superior hemiazygous vein, is a vein on the left side of the vertebral column that generally drains the fourth through eighth intercostal spaces on the left side of the body. Structure The accessor .... Bronchial veins are thereby part of the bronchial circulation, carrying waste products away from the cell (biology), cells that constitute the human lungs, lungs. The bronchial veins are counterparts to the bronchial arteries. However, they only carry ~13% of the blood flow of the bronchial arteries. The remaining blood is returned to the heart via the pulmonary veins. See also * Bronchial arteries * Pulmonary arteries * Pulmonary veins References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Of The Lung
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back (posterior border) than the front (anterior border). The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura (covering the rib cage) and the visceral pleura (covering the lung) is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities. Location The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium, and below the azygos vein. That of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta; the phrenic nerve, pericardiacophrenic artery and vein, and the anterior pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying annular ligaments of trachea, ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. It is epithelium lined with columnar epithelium, column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Of The Lung
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back (posterior border) than the front (anterior border). The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura (covering the rib cage) and the visceral pleura (covering the lung) is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities. Location The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium, and below the azygos vein. That of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta; the phrenic nerve, pericardiacophrenic artery and vein, and the anterior pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carina Of Trachea
In anatomy, the carina or tracheal bifurcation is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi. Structure The carina occurs at the lower end of the trachea (usually at the level of the 4th to 5th thoracic vertebra). This is in line with the sternal angle, but the carina may raise or descend up to two vertebrae higher or lower with breathing. The carina lies to the left of the midline, and runs antero-posteriorly (front to back). The bronchial arteries supply the carina and the rest of the lower trachea. The carina is around the area posterior to where the aortic arch crosses to the left of the trachea. The azygos vein crosses right to the trachea above the carina. Clinical significance Foreign bodies that fall down the trachea are more likely to enter the right bronchus. The mucous membrane of the carina is the most sensitive area of the trachea and larynx for triggering a cough reflex. Widening and distortion of the carina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchopulmonary Segment
A bronchopulmonary segment is a portion of lung supplied by a specific segmental bronchus and its vessels. These arteries branch from the pulmonary and bronchial arteries, and run together through the center of the segment. Veins and lymphatic vessels drain along the edges of the segment. The segments are separated from each other by layers of connective tissue that forms them into discrete anatomical and functional units. This separation means that a bronchopulmonary segment can be surgically removed without affecting the function of the others. There are ten bronchopulmonary segments in the right lung: three in the superior lobe, two in the middle lobe, and five in the inferior lobe. Some of the segments may fuse in the left lung to form usually eight to nine segments (four to five in the upper lobe and four to five in the lower lobe. The delineation of the bronchopulmonary segments was made by Chevalier Jackson and John Franklin Huber at Temple University Hospital. Right lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carina Of Trachea
In anatomy, the carina or tracheal bifurcation is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi. Structure The carina occurs at the lower end of the trachea (usually at the level of the 4th to 5th thoracic vertebra). This is in line with the sternal angle, but the carina may raise or descend up to two vertebrae higher or lower with breathing. The carina lies to the left of the midline, and runs antero-posteriorly (front to back). The bronchial arteries supply the carina and the rest of the lower trachea. The carina is around the area posterior to where the aortic arch crosses to the left of the trachea. The azygos vein crosses right to the trachea above the carina. Clinical significance Foreign bodies that fall down the trachea are more likely to enter the right bronchus. The mucous membrane of the carina is the most sensitive area of the trachea and larynx for triggering a cough reflex. Widening and distortion of the carina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |