|
Briquetting
A briquette (; also spelled briquet) is a compressed block of coal dust or other combustible biomass material (e.g. charcoal, sawdust, wood chips, peat, or paper) used for fuel and kindling to start a fire. The term derives from the French word ''brique'', meaning ''brick''. Coal briquettes Coal briquettes have long been produced as a means of using up 'small coal', the finely broken coal inevitably produced during the mining process. Otherwise this is difficult to burn as it is hard to arrange adequate airflow through a fire of these small pieces; also such fuel tends to be drawn up and out of the chimney by the draught, giving visible black smoke. The first briquettes were known as culm bombs and were hand-moulded with a little wet clay as a binder. These could be difficult to burn efficiently, as the unburned clay produced a large ash content, blocking airflow through a grate. With Victorian developments in engineering, particularly the hydraulic press, it became possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal Briquette
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern "charcoal" briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. This process happens naturally when combustion is incomplete, and is sometimes used in radiocarbon dating. It also happens inadvertently while burning wood, as in a fireplace or wood stove. The visible flame in these is due to combustion of the volatile gases exuded as the wood turns into charcoal. The soot and smoke commonly given off by wood fires result from incomplete combustion of those volatiles. Charcoal burns at a higher temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimney Draught
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the stack, or chimney effect. The space inside a chimney is called the ''flue''. Chimneys are adjacent to large industrial refineries, fossil fuel combustion facilities or part of buildings, steam locomotives and ships. In the United States, the term ''smokestack industry'' refers to the environmental impacts of burning fossil fuels by industrial society, including the electric industry during its earliest history. The term ''smokestack'' (colloquially, ''stack'') is also used when referring to locomotive chimneys or ship chimneys, and the term ''funnel'' can also be used. The height of a chimn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bituminous Coal
Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the seams. It is typically hard but friable. Its quality is ranked higher than lignite and sub-bituminous coal, but lesser than anthracite. It is the most abundant rank of coal, with deposits found around the world, often in rocks of Carboniferous age. Bituminous coal is formed from sub-bituminous coal that is buried deeply enough to be heated to or higher. Bituminous coal is used primarily for electrical power generation and in the steel industry. Bituminous coal suitable for smelting iron (''coking coal'' or ''metallurgical coal'' ) must be low in sulfur and phosphorus. It commands a higher price than other grades of bituminous coal (thermal coal) used for heating and power generation. Within the coal mining industry, this type of coal is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynheidre Colliery
Cynheidre Colliery was a coal mine located in the Gwendraeth valley, in Carmarthenshire, South Wales. Opened in 1954, it closed in 1989. Cynheidre was developed by the National Coal Board as one of the West Wales "super pits" alongside Abernant Colliery in the River Amman valley, a post-World War II investment intended to keep economic coal mining a viable industry in the area. Created to exploit of deep lying anthracite seams, it was envisaged to eventually encompass the working of the drift mines at the Great Mountain Colliery and Pentremawr. Between 1954 and 1956, shafts No.1 (upcast ) and No.2 (downcast ) were sunk south of Pentremawr, to give economic access to the deeper lying extents of the anthracite seams which couldn't be worked economically by slant mining. In 1955, shaft No.3 was created. Originally sunk for ventilating Glynhebog drift mine, it was extended to a depth of to meet the workings at Cynheidre, providing an upcast. By 1960, the colliery employed 650 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracite
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highest ranking of coals. Anthracite is the most metamorphosed type of coal (but still represents low-grade metamorphism), in which the carbon content is between 86% and 97%. The term is applied to those varieties of coal which do not give off tarry or other hydrocarbon vapours when heated below their point of ignition. Anthracite ignites with difficulty and burns with a short, blue, and smokeless flame. Anthracite is categorized into standard grade, which is used mainly in power generation, high grade (HG) and ultra high grade (UHG), the principal uses of which are in the metallurgy sector. Anthracite accounts for about 1% of global coal reserves, and is mined in only a few countries around the world. The Coal Region of northeastern Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary Of Welsh Biography
The ''Dictionary of Welsh Biography'' (DWB) (also ''The Dictionary of Welsh Biography Down to 1940'' and ''The Dictionary of Welsh Biography, 1941 to 1970'') is a biographical dictionary of Welsh people who have made a significant contribution to Welsh life over seventeen centuries. It was first published in 1959, and is now maintained as a free online resource. Origins Robert Thomas Jenkins was assistant editor, then joint editor, of ' and its English-language counterpart, the ''Dictionary of Welsh Biography'', writing over 600 entries. His joint editor was John Edward Lloyd, but the ''Dictionary'' was not published until 1959, twelve years after his death. It is properly known as ''The Dictionary of Welsh Biography Down to 1940'', and its supplementary volume as ''The Dictionary of Welsh Biography, 1941 to 1970'' (2001). Originally published by the Honourable Society of Cymmrodorion, recent editions have been published by the University of Wales Press. ''The Dictionary of Wels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powell Duffryn
Powell may refer to: People * Powell (surname) * Powell (given name) * Powell baronets, several baronetcies * Colonel Powell (other), several military officers *General Powell (other), several military leaders *Governor Powell (other), several governors *Justice Powell (other), several judges * Major Powell (other), several military officers *Secretary Powell (other), several officials *Senator Powell (other), several senators Places * Powell Butte (other), several hills * Powell County (other), several counties * Powell Creek (other), several watercourses * Mount Powell (other) or Powell Mountain, several mountains * Powell River (other), several watercourses * Powell Township (other), several townships Antarctica * Powell Island, South Orkney Islands Maldives * Powell Islands, Raa Atoll, Maldives United States * Powell, Alabama, a town in DeKalb County * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idris Jones (chemist)
Walter Idris Jones CBE (18 January 1900 – 5 July 1971) was a Welsh industrial chemist and international rugby union player. He captained the Wales national rugby union team on one occasion in 1925. Jones played his club rugby for Llanelli RFC. Private life and education Jones was born in Llanelli on 18 January 1900, the son of Frederick and Elizabeth Jones. His father worked in the tinplate industry. He was the brother of the politician Lord Elwyn-Jones. Jones won a scholarship to the University College of Wales, Aberystwyth, where he graduated in chemistry in 1921. He then studied at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, where in 1925 he obtained a PhD for research in organic chemistry. Idris Jones died in Llandaff on 5 July 1971 and was unmarried. Rugby union Jones captained Aberystwyth University Rugby Club (1919–1922) and played for Cambridge University (1923–1925). He played for London Welsh and Llanelli and for the Barbarians invitation team. He made four appearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
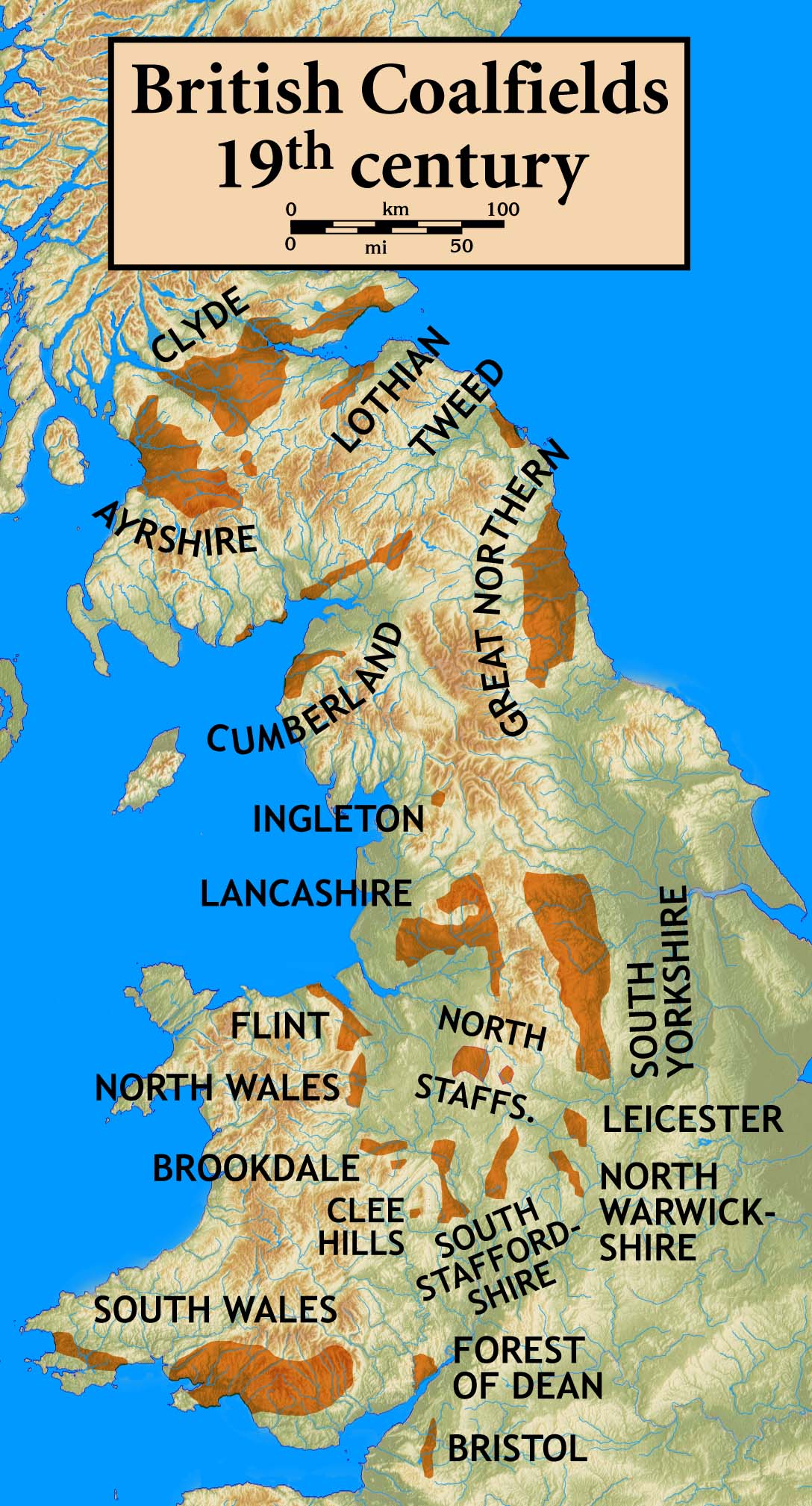
South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, especially in the South Wales Valleys. Description It comprises a fully exposed synclinorium with a varying thickness of coal measures (Upper Carboniferous/Pennsylvanian) with thick, workable seams in the lower parts and generally thinner and sparser seams in the upper parts, together with a development of sandstones (Pennant Sandstone). These sandstones have been much used in building construction (including the characteristic terraces of former miners' houses) and give rise to bleak uplands rising 300–600 metres above sea level between the steep-sided valleys in which most deep mines were developed. The coal generally increases in grade or "rank" from east to west, with bituminous coals in the east, and anthracite in the west, mostly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Gas
Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal and supplied to the user via a piped distribution system. It is produced when coal is heated strongly in the absence of air. Town gas is a more general term referring to manufactured gaseous fuels produced for sale to consumers and municipalities. The original coal gas was produced by the coal gasification reaction, and thus the burnable component consisted of a roughly equal molecular mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Thus, coal gas was highly toxic. Other compositions contain additional calorific gases such as methane, produced by the Fischer-Tropsch process, and volatile hydrocarbons together with small quantities of non-calorific gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Prior to the development of natural gas supply and transmission—during the 1940s and 1950s in the United States and during the late 1960s and 1970s in the United Kingdom and Australia—almost all gas for fuel and lighting was manufactured fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (resin)
Pitch is a viscoelastic polymer which can be natural or manufactured, derived from petroleum, coal tar, or plants. Various forms of pitch may also be called tar, bitumen, or asphalt. Pitch produced from plants is also known as resin. Some products made from plant resin are also known as rosin. Uses Pitch was traditionally used to help caulk the seams of wooden sailing vessels (see shipbuilding), and to coat earthenware vessels for the preservation of wine. Pitch may also be used to waterproof wooden containers and in the making of torches. Petroleum-derived pitch is black in colour, hence the adjectival phrase, "pitch-black". The viscoelastic properties of pitch make it well suited for the polishing of high-quality optical lenses and mirrors. In use, the pitch is formed into a lap or polishing surface, which is charged with iron oxide ( Jewelers' rouge) or cerium oxide. The surface to be polished is pressed into the pitch, then rubbed against the surface so formed. The ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |