|
Brace And Bit
A brace is a hand tool used with a bit (drill bit or auger (drill), auger) to wikt:drill#Verb, drill holes, usually in wood. Pressure is applied to the top and the tool is rotated with a U-shaped grip. Bits used come in a variety of types but the more commonly used Ridgeway- and Irwin- pattern bits also rely on a snail point (called the snail), which is a tapered screw point shaped the same as a wood screw thread, which helps to pull the bit into the wood as the user turns the brace handle and applies pressure The U-shaped part is a kind of crank (mechanism), crank. It gives the brace much greater torque than other kinds of hand-powered drills. A brace and bit can be used to drill much wider and deeper holes than can a geared hand-powered drill. The price of the greater torque is lower rotational speed; it is easy for a geared hand drill to achieve a rotational speed of several hundred revolutions per minute, but it requires considerable effort to achieve even 100 rpm with a bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hole Making
A hole is an opening in or through a particular medium, usually a solid body. Holes occur through natural and artificial processes, and may be useful for various purposes, or may represent a problem needing to be addressed in many fields of engineering. Depending on the material and the placement, a hole may be an indentation in a surface (such as a hole in the ground), or may pass completely through that surface (such as a hole created by a hole puncher in a piece of paper). Types Holes can occur for a number of reasons, including natural processes and intentional actions by humans or animals. Holes in the ground that are made intentionally, such as holes made while searching for food, for replanting trees, or postholes made for securing an object, are usually made through the process of digging. Unintentional holes in an object are often a sign of damage. Potholes and sinkholes can damage human settlements. Holes can occur in a wide variety of materials, and at a wide range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Adamson (publisher)
John Adamson (born 1949) is a British publisher, translator and writer. He specialises in illustrated books in the fine and decorative arts. Biography John Adamson was born in Devon, the younger son of George Worsley Adamson, illustrator and cartoonist and Mary Marguerita Renée (''née'' Diamond). After studying at the University of Edinburgh and the University of Geneva, he joined Cambridge University Press in 1974. He held various functions within the marketing department of the Press: first as European sales representative (1975); then publicity manager (1977); becoming export sales director in 1980. During the period of his directorship, Cambridge University Press won for the first time the Queen's Award for Export Achievement. While at Cambridge University Press he helped mount two exhibitions of humorous art in his spare time. For the first of these, "L’Humour Actuel franco-britannique. 200 dessins" [Franco-British Humour Today: 200 drawings], hosted by the Galerie M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Austin (photographer)
James Austin (born 4 June 1940) is an Australian Fine-art photography, fine-art and architectural photographer. Biography James Lucien Ashurst Austin was born in Melbourne, Australia, the eldest son of Lloyd James Austin (1915–1994) and of Jeanne-Françoise (''née'' Guérin). He is the older brother of the late Colin François Lloyd Austin, Colin Austin (1941–2010), the scholar of ancient Greek. After studying architecture and fine art at Jesus College, Cambridge, he continued his education at the Courtauld Institute, London. He then travelled widely in France and Italy as a freelance photographer building up a library of photographs now in use worldwide in art history archives and numerous publications. Among his early clients were the Bollingen Foundation in New York and Sir Nikolaus Pevsner, for whom he provided photographs for twenty volumes of the ''Pevsner Architectural Guides, Buildings of England'' series. He was Ben Nicholson's personal photographer for the last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David R
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, construction and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for miniature applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The earliest perforated artifacts, such as bone, ivory, shells, and antler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries. From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypres formed one of the most affluent regions in Europe. Up to 1477, the area under French suzerainty was west of the Scheldt and was called "Royal Flanders" (Dutch: ''Kroon-Vlaanderen'', French: ''Flandre royale''). Aside from this, the counts, from the 11th century onward, held land east of the river as a fief of the Holy Roman Empire: "Imperial Flanders" (''Rijks-Vlaanderen'' or ''Flandre impériale''). Part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1384, which had a complex relation with France, the whole county fell to the Empire after the Peace of Madrid in 1526 and the Peace of the Ladies in 1529. Having already regained much, by 1795, the rest – within the Austrian Netherlands – was acquired likewise by France under the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crank (mechanism)
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod). The term often refers to a human-powered crank which is used to manually turn an axle, as in a bicycle crankset or a brace and bit drill. In this case a person's arm or leg serves as the connecting rod, applying reciprocating force to the crank. There is usually a bar perpendicular to the other end of the arm, often with a freely rotatable handle or pedal attached. Examples Familiar examples include: Hand-powered cranks * Spinning Wheel * Mechanical pencil sharpener * Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc. *Starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood (known as " blood blisters") or with pus (for instance, if they become infected). The word "blister" entered English in the 14th century. It came from the Middle Dutch and was a modification of the Old French , which meant a leprous nodule—a rise in the skin due to leprosy. In dermatology today, the words ''vesicle'' and ''bulla'' refer to blisters of smaller or greater size, respectively. To heal properly, a blister should not be popped unless medically necessary. If popped, the bacteria can spread. The excess skin should not be removed because the skin underneath needs the top layer to heal properly. Causes A blister may form when the skin has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchet (device)
A ratchet (occasionally spelled rachet) is a mechanical device that allows continuous linear or rotary motion in only one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. Ratchets are widely used in machinery and tools. The word ''ratchet'' is also used informally to refer to a ratcheting socket wrench. __TOC__ Theory of operation A ratchet consists of a round gear or a linear rack with teeth, and a pivoting, spring-loaded finger called a '' pawl'' (or ''click'', in clocks and watches) that engages the teeth. The teeth are uniform but are usually asymmetrical, with each tooth having a moderate slope on one edge and a much steeper slope on the other edge. When the teeth are moving in the unrestricted (i.e. forward) direction, the pawl easily slides up and over the gently sloped edges of the teeth, with a spring forcing it (often with an audible 'click') into the depression between the teeth as it passes the tip of each tooth. When the teeth move in the opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
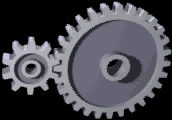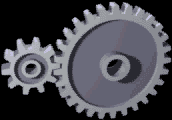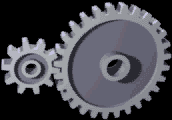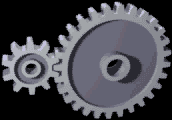
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)