|
Boogie-woogie Bass
Boogie-woogie is a Music genre, genre of blues music that became popular during the late 1920s, developed in African-American communities since 1870s.Paul, Elliot, ''That Crazy American Music'' (1957), Chapter 10, p. 229. It was eventually extended from piano, to piano duo and trio, guitar, big band, country music, country and western music, and Gospel music, gospel. While standard blues traditionally expresses a variety of emotions, boogie-woogie is mainly associated with dancing (although not the competitive dance known as boogie-woogie (dance), boogie-woogie, a term of convenience in that sport). The genre had a significant influence on rhythm and blues and rock and roll. Musical features Boogie-woogie is characterized by a regular left-hand bassline, bass figure, which is transposed following the chord changes. : : Boogie-woogie is not strictly a solo piano style; it can accompany singers and be featured in orchestras and small combos. It is sometimes called ''"eight to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the African-American culture. The blues form is ubiquitous in jazz, rhythm and blues, and rock and roll, and is characterized by the call-and-response pattern (the blues scale and specific chord progressions) of which the twelve-bar blues is the most common. Blue notes (or "worried notes"), usually thirds, fifths or sevenths flattened in pitch, are also an essential part of the sound. Blues shuffles or walking bass reinforce the trance-like rhythm and form a repetitive effect known as the groove. Blues as a genre is also characterized by its lyrics, bass lines, and instrumentation. Early traditional blues verses consisted of a single line repeated four times. It was only in the first decades of the 20th century that the most common current str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The South Bank Show
''The South Bank Show'' is a British television arts magazine series originally produced by London Weekend Television and broadcast on ITV between 1978 and 2010. A new version of the series began 27 May 2012 on Sky Arts. Conceived, written, and presented by former BBC arts broadcaster Melvyn Bragg, the show aims to bring both high art and popular culture to a mass audience. History ITV (1978–2010) The programme was a replacement for ''Aquarius'', the arts series which had been running since 1970. Presenter Melvyn Bragg was already well known for his arts broadcasting on BBC television, notably ''Monitor'' and BBC Two's ''The Lively Arts''. It first aired on 14 January 1978, covering many subjects, including Germaine Greer, Gerald Scarfe and Paul McCartney. It is the longest continuously running arts programme on UK television. From the beginning the series' intent was to mix high art and popular culture. This has remained, and the programme has always focused predominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka Language
The Mandinka language (; Ajami: ) or Mandingo, is a Mande language spoken by the Mandinka people of Guinea, northern Guinea-Bissau, the Casamance region of Senegal, and in The Gambia where it is one of the principal languages. Mandinka belongs to the Manding branch of Mande and is thus similar to Bambara and Maninka/Malinké but with only 5 instead of 7 vowels. In a majority of areas, it is a tonal language with two tones: low and high, although the particular variety spoken in the Gambia and Senegal borders on a pitch accent due to its proximity with non-tonal neighboring languages like Wolof. Phonology Mandinka is here represented by the variety spoken in Casamance. There is little dialectical diversity. Tone Mandinka has two tones, high and low. Unmodified nouns are either high tone on all syllables or low tone on all syllables. The definite suffix ''-o'' takes a low tone on high-tone nouns and a falling tone on low-tone nouns. It also assimilates any preceding sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
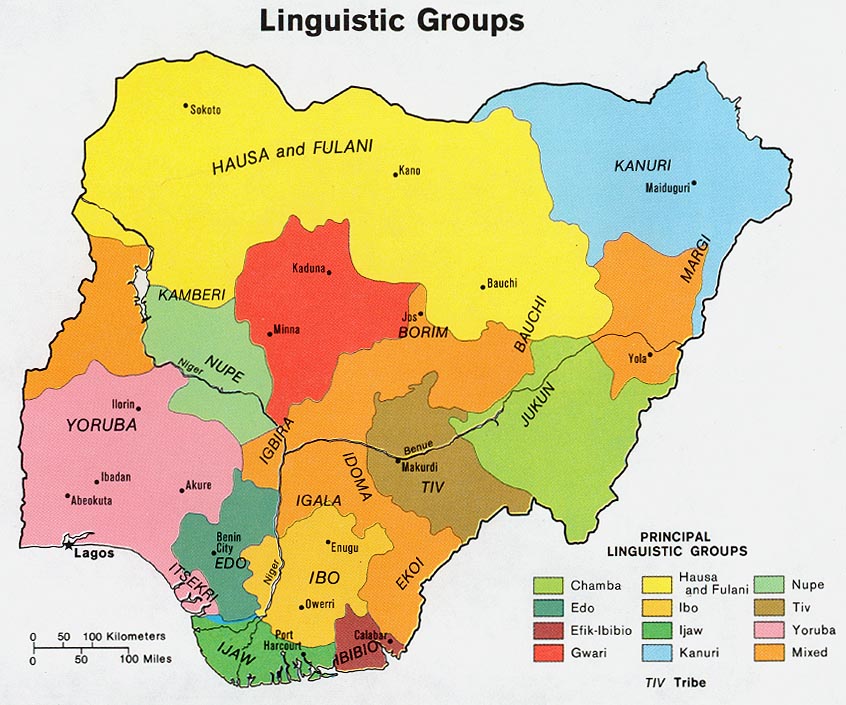
Hausa Language
Hausa (; /; Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic languages, Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologue estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa-speaking film industry is known as Hausa-language cinema, Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. Geographic distribution Native speakers of Hausa, the Hausa people, are mostly found in southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just A Closer Walk With Thee (song)
"Just a Closer Walk with Thee" is a traditional gospel song and jazz standard that has been performed and recorded by many artists. Performed as either an instrumental or vocal, "A Closer Walk" is perhaps the most frequently played number in the hymn and dirge section of traditional New Orleans jazz funerals. The title and lyrics of the song allude to the Biblical passage from 2 Corinthians 5:7 which states, "We walk by faith, not by sight" and James 4:8, "Come near to God and He will come near to you." History The precise author of "A Closer Walk" is unknown. Circumstantial evidence strongly suggested it dated back to southern African-American churches of the nineteenth century, possibly even prior to the Civil War, as some personal African American histories recall "slaves singing as they worked in the fields a song about walking by the Lord's side." Horace Boyer cites a story that repudiates this claim, stating, “On a train trip from Kansas City to Chicago, composer Kennet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Folks At Home
"Old Folks at Home" (also known as " Swanee River") is a minstrel song written by Stephen Foster in 1851. Since 1935, it has been the official state song of Florida, although in 2008 the original lyrics were revised. It is Roud Folk Song Index no. 13880. Composition "Old Folks at Home" was commissioned in 1851 by E. P. Christy for use by Christy's Minstrels, his minstrel troupe. Christy also asked to be credited as the song's creator, and was so credited on early sheet music printings. As a result, while the song was a success, Foster did not directly profit much from it, though he continued to receive royalties for the song. Foster had composed most of the lyrics but was struggling to name the river of the opening line, and asked his brother, Morrison, to suggest one. Morrison wrote, “One day in 1851, Stephen came into my office, on the bank of the Monongahela, Pittsburgh, and said to me, ‘What is a good name of two syllables for a Southern river? I want to use it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve-bar Blues
The 12-bar blues (or blues changes) is one of the most prominent chord progressions in popular music. The blues progression has a distinctive form in lyrics, phrase, chord structure, and duration. In its basic form, it is predominantly based on the I, IV, and V chords of a key. Mastery of the blues and rhythm changes are "critical elements for building a jazz repertoire". Background The blues originated from a combination of work songs, spirituals, and early southern country music. The music was passed down through oral tradition. It was first written down by W. C. Handy, an African American composer and band leader. Its popularity led to the creation of "race records" and the popularity of blues singers like Bessie Smith and Ma Rainy. The style of music heard on race records was later called "rhythm and blues" (R & B). As the music became more popular, more people wanted to perform it. General patterns that existed in the blues were formalized, one of these being the 12-bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord Progressions
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice era of Classical music to the 21st century. Chord progressions are the foundation of Western popular music styles (e.g., pop music, rock music), traditional music, as well as genres such as blues and jazz. In these genres, chord progressions are the defining feature on which melody and rhythm are built. In tonal music, chord progressions have the function of either establishing or otherwise contradicting a tonality, the technical name for what is commonly understood as the " key" of a song or piece. Chord progressions, such as the common chord progression I–vi–ii–V, are usually expressed by Roman numerals in Classical music theory. In many styles of popular and traditional music, chord progressions are expressed using the name a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Signature
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are contained in each measure (bar), and which note value is equivalent to a beat. In a music score, the time signature appears at the beginning as a time symbol or stacked numerals, such as or (read ''common time'' or ''four-four time'', respectively), immediately following the key signature (or immediately following the clef symbol if the key signature is empty). A mid-score time signature, usually immediately following a barline, indicates a change of meter. There are various types of time signatures, depending on whether the music follows regular (or symmetrical) beat patterns, including simple (e.g., and ), and compound (e.g., and ); or involves shifting beat patterns, including complex (e.g., or ), mixed (e.g., & or & ), additive (e.g., ), fractional (e.g., ), and irrational met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaver
180px, Figure 1. An eighth note with stem extending up, an eighth note with stem extending down, and an eighth rest. 180px, Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together. An eighth note (American) or a quaver (British) is a musical note played for one eighth the duration of a whole note (semibreve). Its length relative to other rhythmic values is as expected—e.g., half the duration of a quarter note (crotchet), one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), and twice the value of a sixteenth note. It is the equivalent of the ''fusa'' in mensural notation. Eighth notes are notated with an oval, filled-in note head and a straight note stem with one note flag (see Figure 1). The stem is on the right of the notehead extending upwards or on the left extending downwards, depending primarily on where the notehead lies relative to the middle line of the staff. A related symbol is the eighth rest (or quaver rest), which denotes a silence for the same duration. Eighth notes may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |