|
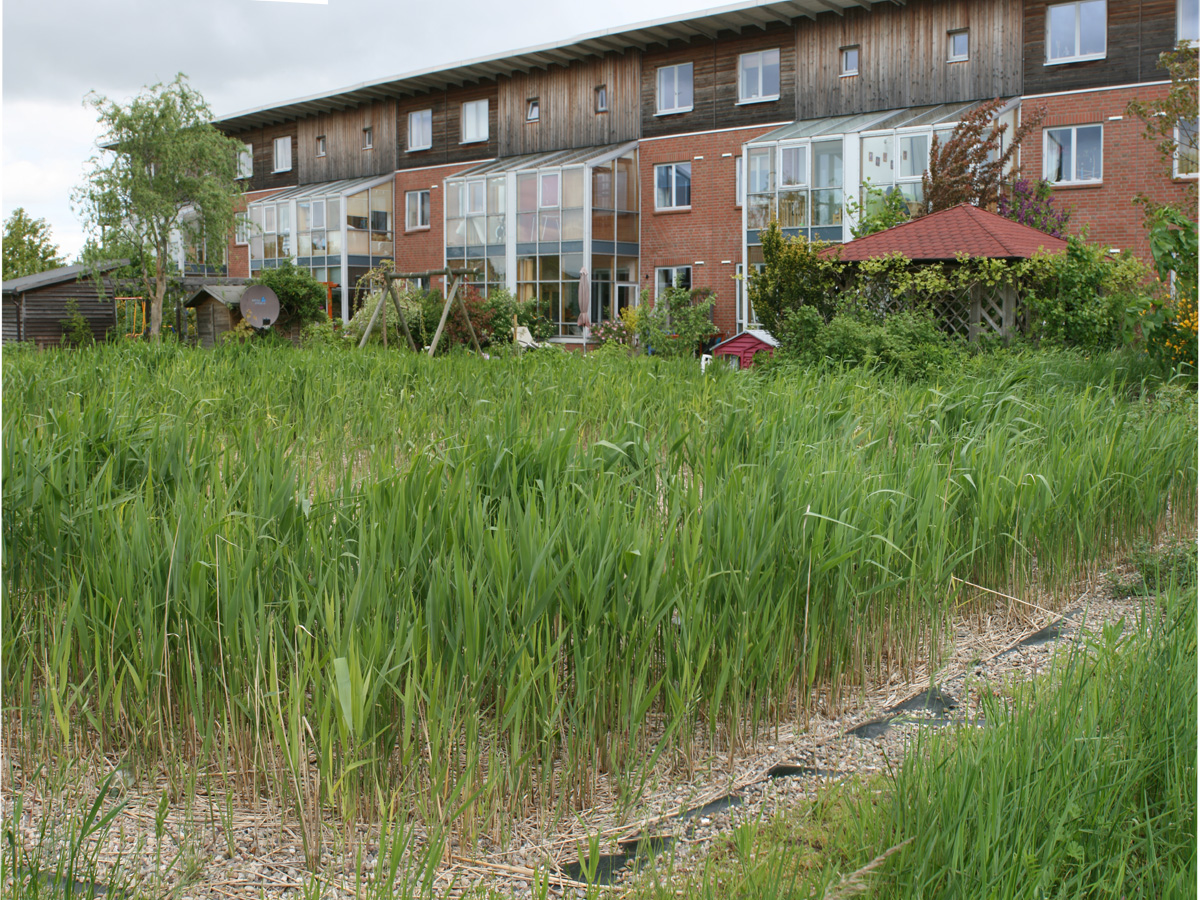
Biofilter
Biofiltration is a pollution control technique using a bioreactor containing living material to capture and biologically degrade pollutants. Common uses include processing waste water, capturing harmful chemicals or silt from surface runoff, and microbiotic oxidation of contaminants in air. Industrial biofiltration can be classified as the process of utilizing biological oxidation to remove volatile organic compounds, odors, and hydrocarbons. Examples of biofiltration Examples of biofiltration include: * Bioswales, biostrips, biobags, bioscrubbers, Vermifilters and trickling filters * Constructed wetlands and natural wetlands * Slow sand filters * Treatment ponds * Green belts * Green walls * Riparian zones, riparian forests, bosques * Bivalve bioaccumulation Control of air pollution When applied to air filtration and purification, biofilters use microorganisms to remove air pollution. The air flows through a packed bed and the pollutant transfers into a thin biofilm on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trickling Filter
A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward and causes a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to grow, covering the bed of media. Aerobic conditions are maintained by splashing, diffusion, and either by forced-air flowing through the bed or natural convection of air if the filter medium is porous. The treatment of sewage or other wastewater with trickling filters is among the oldest and most well characterized treatment technologies. The fundamental components of a complete trickling filter system are: * a bed of filter medium upon which a layer of microbial slime is promoted and developed; * an enclosure or a container which houses the bed of filter medium; * a system for distributing the flow of wastewater over the filter medium; and * a system for removing and disposing of any sludge fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructed Wetland
A constructed wetland is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a mitigation step for natural areas lost to land development. Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that use the natural functions of vegetation, soil, and organisms to provide secondary treatment to wastewater. The design of the constructed wetland has to be adjusted according to the type of wastewater to be treated. Constructed wetlands have been used in both centralized and decentralized wastewater systems. Primary treatment is recommended when there is a large amount of suspended solids or soluble organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand). Similar to natural wetlands, constructed wetlands also act as a biofilter and/or can remove a range of pollutants (such as organic matter, nutrients, pathogens, heavy metals) from the water. Constructed wetlands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermifilter
A vermifilter (also vermi-digester or lumbrifilter) is an aerobic treatment system, consisting of a biological reactor containing media that filters organic material from wastewater. The media also provides a habitat for aerobic bacteria and composting earthworms that purify the wastewater by removing pathogens and oxygen demand. The "trickling action" of the wastewater through the media dissolves oxygen into the wastewater, ensuring the treatment environment is aerobic for rapid decomposition of organic substances. Vermifilters are most commonly used for sewage treatment and for agro- industrial wastewater treatment. Vermifilters can be used for primary, secondary and tertiary treatment of sewage, including blackwater and greywater in on-site systems and municipal wastewater in large centralised systems. Vermifilters are used where wastewater requires treatment before being safely discharged into the environment. Treated effluent is disposed of to either surface or sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ... that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into Ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioswale
Bioswales are channels designed to concentrate and convey stormwater runoff while removing debris and pollution. Bioswales can also be beneficial in recharging groundwater. Bioswales are typically vegetated, mulched, or xeriscaped. They consist of a swaled drainage course with gently sloped sides (less than 6%). Construction Engineering Research Laboratory. Document no. ERDC/CERL TR-03-12. Bioswale design is intended to safely maximize the time water spends in the swale, which aids the collection and removal of pollutants, silt and debris. Depending on the site topography, the bioswale channel may be straight or meander. Check dams are also commonly added along the bioswale to increase stormwater infiltration. A bioswale's make-up can be influenced by many different variables, including climate, rainfall patterns, site size, budget, and vegetation suitability. It is important to maintain bioswales to ensure the best possible efficiency and effectiveness in removal of pollut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
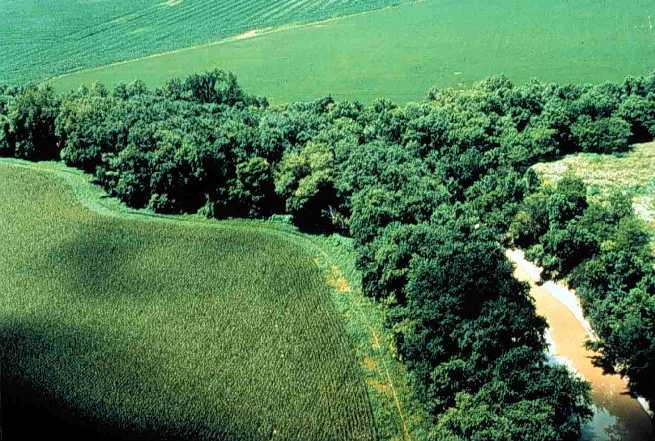
Riparian Zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, or even non-vegetative areas. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Characteristics Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zones are important natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosque
A bosque ( ) is a type of gallery forest habitat found along the riparian flood plains of stream and river banks in the southwestern United States. It derives its name from the Spanish word for 'woodlands'. Setting In the predominantly arid or semi-arid southwestern United States, a bosque is an oasis-like ribbon of green vegetation, often canopied, that only exists near rivers, streams, or other water courses. The most notable bosque is the -long ecosystem along the valley of the middle Rio Grande in New Mexico that extends from Santa Fe south to El Paso, Texas. One of the most famous and ecologically intact sections of the bosque is included in the Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge. Flora and fauna Common trees in the bosque habitat include mesquite, cottonwood, desert willow, and desert olive. Because there is often only a single canopy layer and because the tree species found in the bosque are generally deciduous, a wide variety of shrubs, grasses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. Thus, the longer the biological half-life of a toxic substance, the greater the risk of chronic poisoning, even if environmental levels of the toxin are not very high. Bioaccumulation, for example in fish, can be predicted by models. Hypothesis for molecular size cutoff criteria for use as bioaccumulation potential indicators are not supported by data. Biotransformation can strongly modify bioaccumulation of chemicals in an organism. Toxicity induced by metals is associated with bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Storage or uptake of metals faster than the rate at which an organism metabolizes and excretes lead to the accumulation of that metal. The presence of various chemicals and harmful substances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
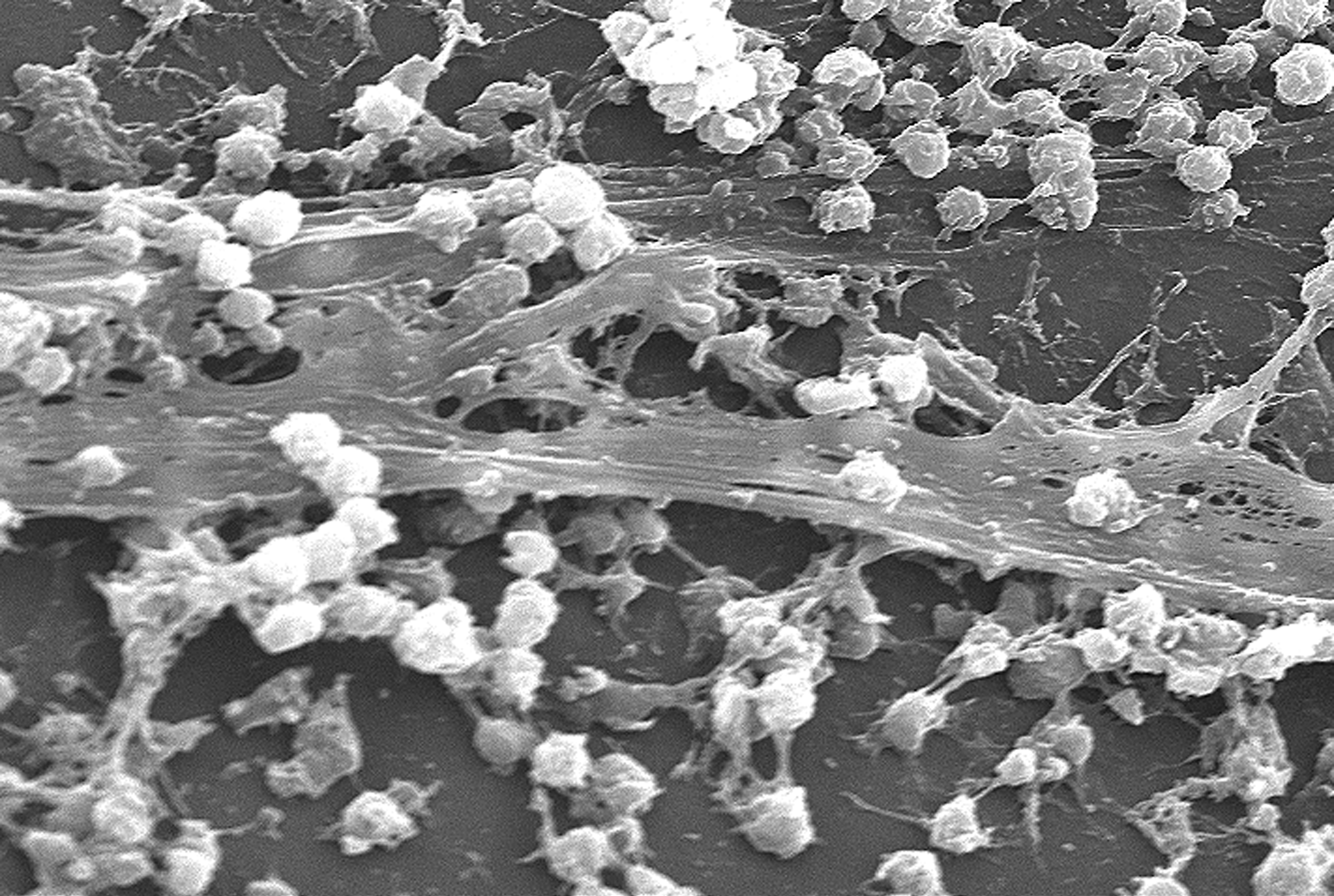
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |