|
Beryllium Oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most metals. As an amorphous solid, beryllium oxide is white. Its high melting point leads to its use as a refractory material. It occurs in nature as the mineral bromellite. Historically and in materials science, beryllium oxide was called glucina or glucinium oxide, owing to its sweet taste. Preparation and chemical properties Beryllium oxide can be prepared by calcining (roasting) beryllium carbonate, dehydrating beryllium hydroxide, or igniting metallic beryllium: :BeCO3 → BeO + CO2 :Be(OH)2 → BeO + H2O :2 Be + O2 → 2 BeO Igniting beryllium in air gives a mixture of BeO and the nitride Be3N2. Unlike the oxides formed by the other Group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals), beryllium oxide is amphoteric rather than basic. Beryllium ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haynes
Haynes may refer to: People *Haynes (surname) Places Australia * Haynes, Western Australia Canada * Haynes, Alberta United Kingdom *Haynes, Bedfordshire **Haynes Church End United States *Haynes, Arkansas *Haynes, North Dakota *Haynes, Ohio *Haynes Township, Michigan Other uses *Haynes International, a US corporation specializing in corrosion-resistant metal alloys *Haynes Manuals, set of manuals for automobile repair and other do it yourself projects *Haynes Automobile Company, a defunct American automobile company *John C. Haynes & Co., a musical instrument maker *William S. Haynes Flute Company, American flute maker *Haynes v. United States, a United States Supreme Court decision *Haynes International Motor Museum, a motor museum in Sparkford, Somerset, England. See also *Haine *Hayne *Haines (other) *Hanes *Hayes (other), Hayes *Hawnes {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium Carbonate
Beryllium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . Structures There are three forms reported, anhydrous, tetrahydrate and basic beryllium carbonate. The anhydrous form is reported to be unstable, decomposing to BeO and carbon dioxide, and requiring storage under .Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier The tetrahydrate is said to be formed when is bubbled through a solution of and is also reported to be similarly unstable. Preparation Basic beryllium carbonate is a mixed salt, which can be prepared by the reaction of beryllium sulfate and ammonium carbonate Ammonium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is an ammonium salt of carbonic acid. It is composed of ammonium cations and carbonate anions . Since ammonium carbonate readily degrades to gaseous ammonia and carbon diox ..., and contains both carbonate and hydroxide ions, with formula .J.E. Macintyre, ''Dictionary of Inorganic Comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide (MgO), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions held together by ionic bonding. Magnesium hydroxide forms in the presence of water (MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2), but it can be reversed by heating it to remove moisture. Magnesium oxide was historically known as magnesia alba (literally, the white mineral from Magnesia), to differentiate it from '' magnesia nigra'', a black mineral containing what is now known as manganese. Related oxides While "magnesium oxide" normally refers to MgO, the compound magnesium peroxide MgO2 is also known. According to evolutionary crystal structure prediction, MgO2 is thermodynamically stable at pressures above 116 GPa (gigapascals), and a semiconducting suboxide Mg3O2 is thermodynamically stable above 500 GPa. Because of its stability, MgO is used as a mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectronicity
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in the structure. For example, , , and are isoelectronic, while and = are not. This definition is sometimes termed valence isoelectronicity. Definitions can sometimes be not as strict, sometimes requiring identity of the total electron count and with it the entire electronic configuration. More usually, definitions are broader, and may extend to allowing different numbers of atoms in the species being compared.A. A. Aradi & T. P. Fehlner, "Isoelectronic Organometallic Molecules", in F. G. A. Stone & Robert West (eds.) ''Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 30'' (1990), Chapter 5 (at p. 190google books link/ref> The importance of the concept lies in identifying significantly related species, as pairs or series. Isoelectronic specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
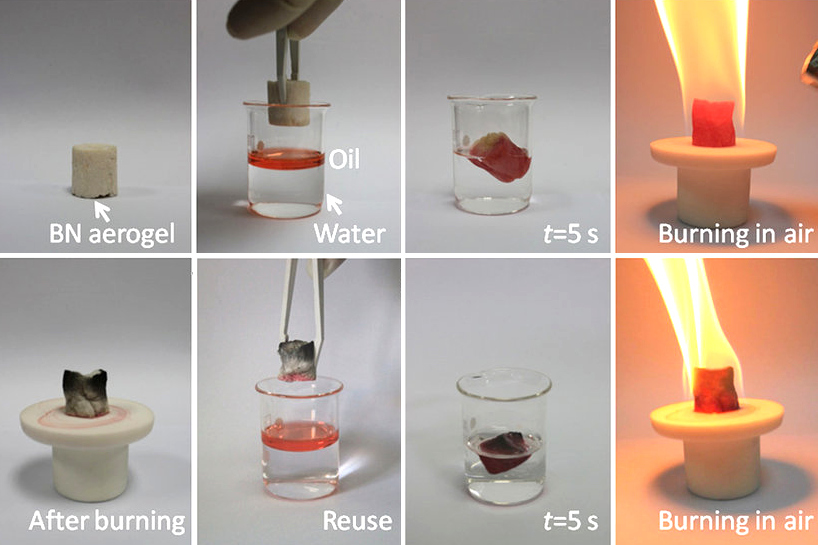
Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. History Boron nitride was discovered by chemistry teacher of the Liverpool Institute in 1842 via reduction of boric acid with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonsdaleite
Lonsdaleite (named in honour of Kathleen Lonsdale), also called hexagonal diamond in reference to the crystal structure, is an allotrope of carbon with a hexagonal lattice, as opposed to the cubical lattice of conventional diamond. It is found in nature in meteorite debris; when meteors containing graphite strike the Earth, the immense heat and stress of the impact transforms the graphite into diamond, but retains graphite's hexagonal crystal lattice. Lonsdaleite was first identified in 1967 from the Canyon Diablo meteorite, where it occurs as microscopic crystals associated with ordinary diamond. It is translucent and brownish-yellow and has an index of refraction of 2.40–2.41 and a specific gravity of 3.2–3.3. Its hardness is theoretically superior to that of cubic diamond (up to 58% more), according to computational simulations, but natural specimens exhibited somewhat lower hardness through a large range of values (from 7–8 on Mohs hardness scale). The cause is sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wurtzite Crystal Structure
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur. Uses Agriculture The primary use of ammonium sulfate is as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil, the ammonium ion is released and forms a small amount of acid, lowering the pH balance of the soil, while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth. One disadvantage to the use of ammonium sulfate is its low nitrogen content relative to ammonium nitrate, which elevates transportation costs. It is also used as an agricultural spray adjuvant for water-soluble insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. There, it functions to bind iron and calcium cations that are present in both well water and plant cells. It is particularly effective as an adjuvant for 2,4-D (amine), glyphosate, and glufosinate herbicides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Bifluoride
Ammonium bifluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula or . It is produced from ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. This colourless salt is a glass-industrial etching, etchant and an intermediate in a once-contemplated route to hydrofluoric acid. Structure Ammonium bifluoride, as its name indicates, contains an ammonium cation (), and a bifluoride (or hydrogen difluoride) anion (). The triatomic bifluoride anion features a strong three-center four-electron bond (specifically, a symmetrical hydrogen bond) with a bond energy greater than 155 kJ/mol, and an H-F length of 114 pm. In solid form (), ammonium biflouride is similar to other fluoride salts. Its crystal system is considered orthorhombic, with each cation coordinated with four anions in a tetrahedron (and vice versa). Hydrogen atoms in the ammonium ion form hydrogen bonds with the fluorine atoms, and in the resulting structure, N-H-F are roughly colinear. As a result of these hydrogen bonds, this crystal structure varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphoterism
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used. Etymology and terminology Amphoteric is derived from the Greek word () meaning "both". Related words in acid-base chemistry are amphichromatic and amphichroic, both describing substances such as acid-base indicators which give one colour on reaction with an acid and another colour on reaction with a base. Amphiprotism Amphiprotism is exhibited by compounds with both Brønsted acidic and basic properties. A prime example is H2O. Amphiprotic molecules can either donate or accept a proton (). Amino acids (and proteins) are amphiprotic molecules because of their amine () and carboxylic acid () groups. Ampholytes Ampholytes are zwitterions ‒ molecules or ions that contain both acidic and basic functional groups. Amino acids have both a basic group and an acidic group . Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactivity (chemistry), reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Together with helium, these elements have in common an outer atomic orbital, s orbital which is full —that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with electric charge, charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. Helium is grouped with the noble gases and not with the alkaline earth metals, but it is theorized to have some similarities to beryllium when forced into bonding and has sometimes been suggested to belong to group 2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |