|
Battle Of Rabaul (1942)
The Battle of Rabaul, also known by the Japanese as Operation R, an instigating action of the New Guinea campaign, was fought on the island of New Britain in the Australian Territory of New Guinea, from 23 January into February 1942. It was a strategically significant defeat of Allied forces by Japan in the Pacific campaign of World War II, with the Japanese invasion force quickly overwhelming the small Australian garrison, the majority of which was either killed or captured. Hostilities on the neighbouring island of New Ireland are usually considered to be part of the same battle. Rabaul was significant because of its proximity to the Japanese territory of the Caroline Islands, site of a major Imperial Japanese Navy base on Truk. Following the capture of the port of Rabaul, Japanese forces turned it into a major base and proceeded to land on mainland New Guinea, advancing toward Port Moresby. Heavy fighting followed along the Kokoda Track, and around Milne Bay, before the Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea Campaign
The New Guinea campaign of the Pacific War lasted from January 1942 until the end of the war in August 1945. During the initial phase in early 1942, the Empire of Japan invaded the Australian-administered Mandated Territory of New Guinea (23 January) and Territory of Papua, the Australian Territory of Papua (21 July) and overran Dutch New Guinea, western New Guinea (beginning 29/30 March), which was a part of the Netherlands East Indies. During the second phase, lasting from late 1942 until the Japanese surrender, the Allies of World War II, Allies—consisting primarily of Australian forces—cleared the Japanese first from Papua, then the Mandate and finally from the Dutch colony. The campaign resulted in a crushing defeat and heavy losses for the Empire of Japan. As in most Pacific War campaigns, disease and starvation claimed more Japanese lives than enemy action. Most Japanese troops never even came into contact with Allied forces, and were instead simply cut off and subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Moresby
(; Tok Pisin: ''Pot Mosbi''), also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific (along with Jayapura) outside of Australia and New Zealand. It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the south-western coast of the Papuan Peninsula of the island of New Guinea. The city emerged as a trade centre in the second half of the 19th century. During World War II, it was a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43 as a staging point and air base to cut off Australia from Southeast Asia and the Americas. As of the 2011 census, Port Moresby had 364,145 inhabitants. An unofficial 2020 estimate gives the population as 383,000. The place where the city was founded has been inhabited by the Motu-Koitabu people for centuries. The first Briton to see it was Royal Navy Captain John Moresby in 1873. It was named in honour of his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvation Army
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its consequences."Salvation." ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. 1989. "The saving of the soul; the deliverance from sin and its consequences." The academic study of salvation is called ''soteriology''. Meaning In Abrahamic religions and theology, ''salvation'' is the saving of the soul from sin and its consequences. It may also be called ''deliverance'' or ''redemption'' from sin and its effects. Depending on the religion or even denomination, salvation is considered to be caused either only by the grace of God (i.e. unmerited and unearned), or by faith, good deeds (works), or a combination thereof. Religions often emphasize that man is a sinner by nature and that the penalty of sin is death (physical death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Battery
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facilitate better battlefield communication and command and control, as well as to provide dispersion for its constituent gunnery crews and their systems. The term is also used in a naval context to describe groups of guns on warships. Land usage Historically the term "battery" referred to a cluster of cannon in action as a group, either in a temporary field position during a battle or at the siege of a fortress or a city. Such batteries could be a mixture of cannon, howitzer, or mortar types. A siege could involve many batteries at different sites around the besieged place. The term also came to be used for a group of cannon in a fixed fortification, for coastal or frontier defence. During the 18th century "battery" began to be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea Volunteer Rifles
The New Guinea Volunteer Rifles (NGVR) was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army. It was initially raised as a unit of the Militia from white Australian and European expatriates in New Guinea upon the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939, before being activated for full-time service following the Japanese landings in early 1942. NGVR personnel then helped rescue survivors of Lark Force from Rabaul in February and March 1942. Between March and May, the NGVR monitored the Japanese bases which had been established in the Huon Gulf region, being the only Allied force in the area until the arrival of Kanga Force at Wau in May. The battalion subsequently established observation posts overlooking the main approaches and reported on Japanese movements. Later, it inflicted significant casualties on the Japanese in a series of raids, and led them to believe that they faced a much larger opposing force. On 29 June, the NGVR and the newly arrived 2/5th Independent Company carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Army Reserve
The Australian Army Reserve is a collective name given to the reserve units of the Australian Army. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, the reserve military force has been known by many names, including the Citizens Forces, the Citizen Military Forces, the Militia and, unofficially, the Australian Military Forces. In 1980, however, the current name—Australian Army Reserve—was officially adopted, and it now consists of a number of components based around the level of commitment and training obligation that its members are required to meet. Overview For the first half of the 20th century, due to a widespread distrust of permanent military forces in Australia, the reserve military forces were the primary focus of Australian military planning.Grey 2008, pp. 66–83. Following the end of World War II, however, this focus gradually shifted due to the changing strategic environment, and the requirement for a higher readiness force available to support collective security go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lark Force
Larks are passerine birds of the family Alaudidae. Larks have a cosmopolitan distribution with the largest number of species occurring in Africa. Only a single species, the horned lark, occurs in North America, and only Horsfield's bush lark occurs in Australia. Habitats vary widely, but many species live in dry regions. When the word "lark" is used without specification, it often refers to the Eurasian skylark ''(Alauda arvensis)''. Taxonomy and systematics The family Alaudidae was introduced in 1825 by the Irish zoologist Nicholas Aylward Vigors as a subfamily Alaudina of the finch family Fringillidae. Larks are a well-defined family, partly because of the shape of their . They have multiple scutes on the hind side of their tarsi, rather than the single plate found in most songbirds. They also lack a pessulus, the bony central structure in the syrinx of songbirds. They were long placed at or near the beginning of the songbirds or oscines (now often called Passeri) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Australian Imperial Force
The Second Australian Imperial Force (2nd AIF, or Second AIF) was the name given to the volunteer expeditionary force of the Australian Army in the Second World War. It was formed following the declaration of war on Nazi Germany, with an initial strength of one infantry division and related auxiliary components. After considerable expansion of this force, three divisions were sent to the Middle East and North Africa, while the 8th Division was sent to garrison British Malaya and Singapore. Under the '' Defence Act 1903'', neither the part-time Militia nor the full-time Permanent Military Force (PMF) could serve outside Australia or its territories unless they volunteered to do so. The Second AIF fought against Nazi Germany, Italy, Vichy France and Japan. After the war, Australia's wartime military structures were demobilised and the 2nd AIF was disbanded, although a small cadre of its personnel became part of the Interim Army that was established in 1947, and from which the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2/22nd Battalion (Australia)
The 2/22nd Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army. Raised as part of the Second Australian Imperial Force for service during World War II, the battalion formed part of the 23rd Brigade, attached to the 8th Division. It was captured by the Japanese during the Battle of Rabaul in 1942. After being captured, the battalion was not re-raised and a large number of its personnel died in captivity; those that did not were returned to Australia at the end of the war in 1945. History Formation and training Formed on 1 July 1940 at Victoria Barracks, Melbourne, the 2/22nd Battalion formed part of the 23rd Brigade, attached to the 8th Division. The battalion's personnel were drawn from the state of Victoria, and included a number of veterans of the World War I. The colours chosen for the battalion's unit colour patch (UCP) were the same as those of the 22nd Battalion, a unit which had served during World War I before being raised as a Militia formation in 1921. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Army
The Australian Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army (Australia), Chief of Army (CA), who is subordinate to the Chief of the Defence Force (Australia), Chief of the Defence Force (CDF) who commands the ADF. The CA is also directly responsible to the Minister of Defence (Australia), Minister for Defence, with the Department of Defence (Australia), Department of Defence administering the ADF and the Army. Formed in 1901, as the Commonwealth Military Forces, through the amalgamation of the colonial forces of Australia following the Federation of Australia. Although Australian soldiers have been involved in a number of minor and major conflicts throughout Australia's history, only during the Second World War has Australian territory come under direct attack. The Australian Army was initially composed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
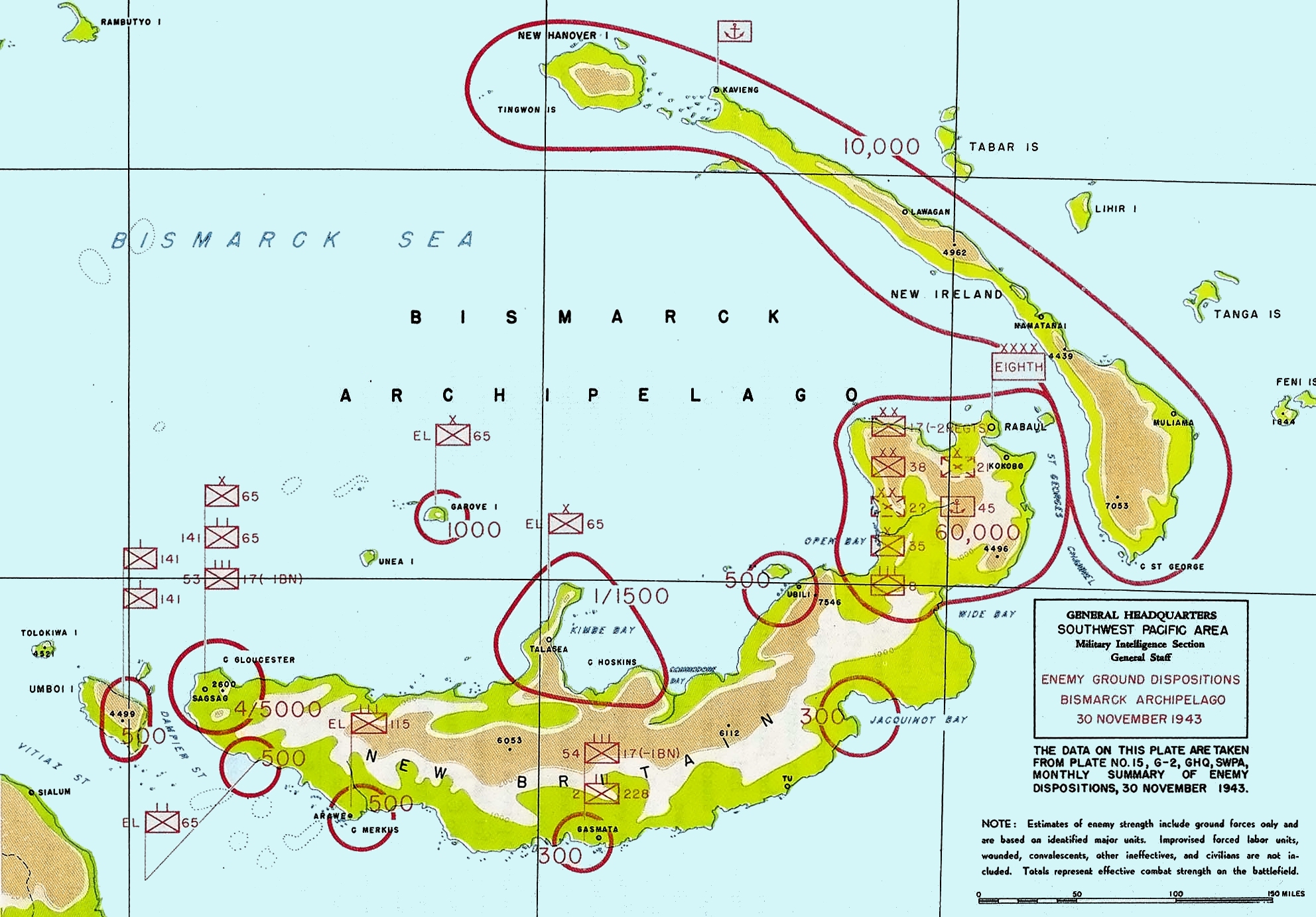
New Britain Campaign
The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945. Initial fighting on New Britain took place around the western end of the island in December 1943 and January 1944, with US forces landing and securing bases around Arawe and Cape Gloucester. This was followed by a further landing in March 1944 around Talasea, after which little fighting took place between the ground forces on the island. In October 1944, the Australian 5th Division took over from the US troops and undertook a Landing at Jacquinot Bay the following month, before beginning a limited offensive to secure a defensive line across the island between Wide Bay and Open Bay behind which they contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Cartwheel
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the South Pacific Area, under Admiral William Halsey, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US and various Pacific Islands. Background Japanese forces had captured Rabaul, on New Britain, in the Territory of New Guinea, from Australian forces in February 1942 and turned it into their major forward base in the South Pacific, and the main obstacle in the two Allied theatres. MacArthur formulated a strategic outline, the Elkton Plan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)