|
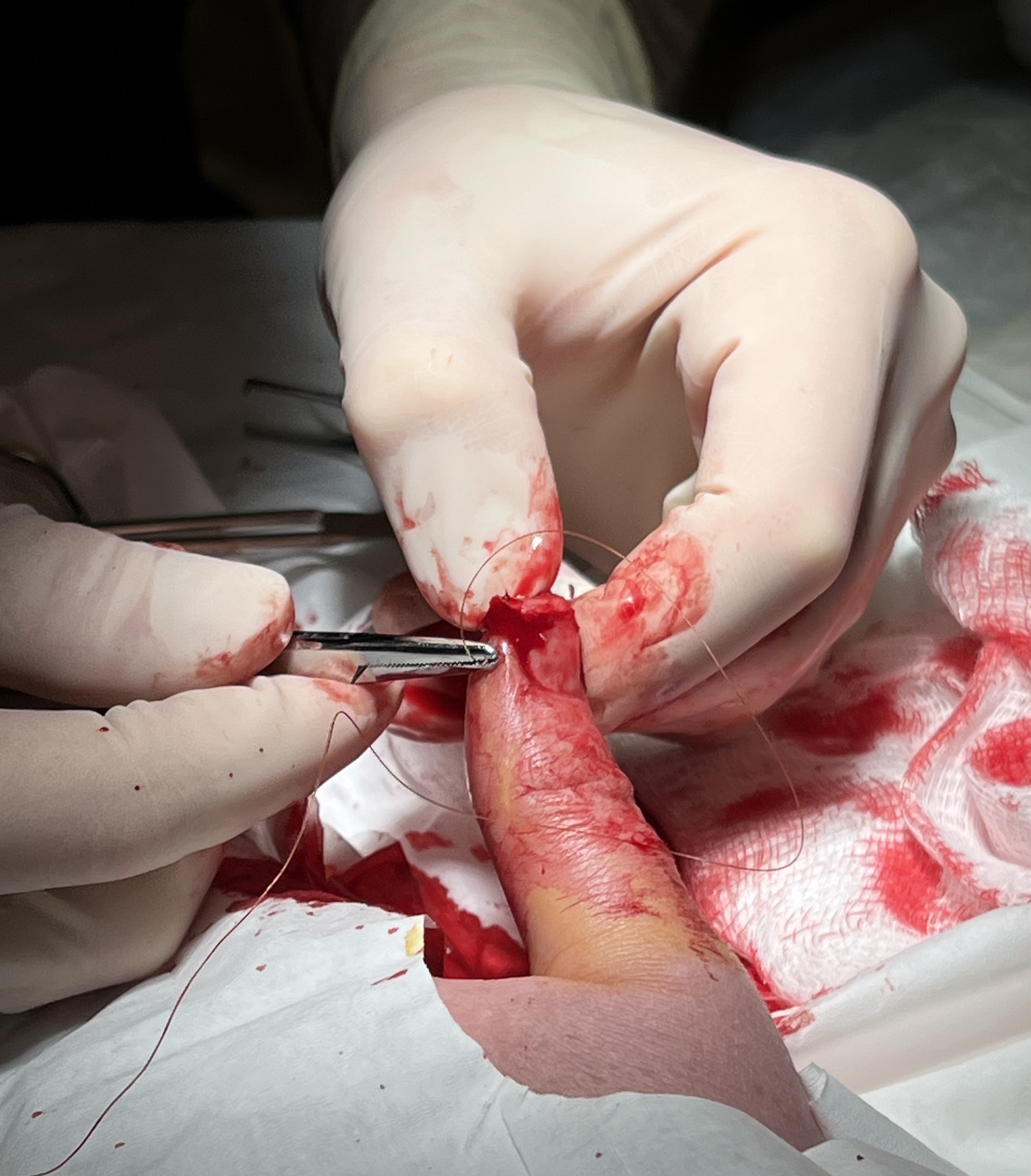
Barbed Suture
A barbed suture is a type of knotless surgical suture that has barbs on its surface. While suturing tissue, these barbs penetrate inside the tissue and lock them into place, eliminating the need for knots to tie the suture. Conventional sutures rely on a surgeon's ability to tie secure knots; barbed sutures provide a knotless alternative in some surgical situations. Barbed sutures are primarily used in cosmetic surgery. In recent years there has been an increasing uptake in the use of barbed sutures, particularly in minimally invasive and laparoscopic procedures where they may reduce operating time and improve surgical efficiency. However, little is known about the adverse events associated with these new materials and concerns have arisen regarding their safety in certain procedures. Although barbed sutures provide an attractive means to allow easier and faster laparoscopic suturing, they should be used carefully in inframesocolic surgery and the suture end cut and buried to avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
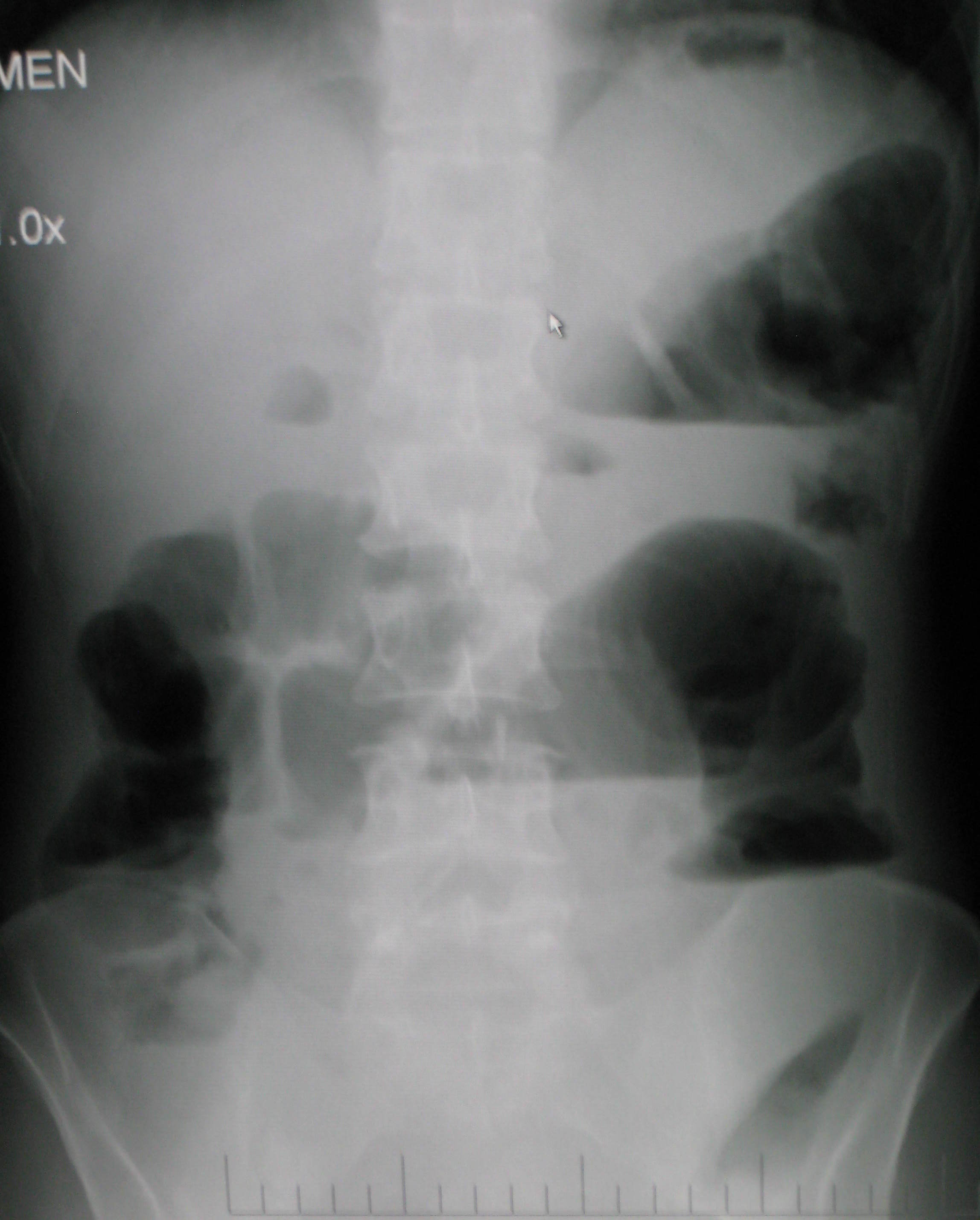
Small Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital. Causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often due to tumors and volvulus. The diagnosis may be made on plain X-rays; however, CT scan is more accurate. Ultrasound or MRI may help in the diagnosis of children or pregnant women. The condition may be treated conserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Staple
Surgical staples are specialized staples used in surgery in place of sutures to close skin wounds or connect or remove parts of the bowels or lungs. The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, and time it takes to close. A more recent development, from the 1990s, uses clips instead of staples for some applications; this does not require the staple to penetrate. History The technique was pioneered by "father of surgical stapling", Hungarian surgeon Hümér Hültl. Hultl's prototype stapler of 1908 weighed , and required two hours to assemble and load. The technology was refined in the 1950s in the Soviet Union, allowing for the first commercially produced re-usable stapling devices for creation of bowel and vascular anastomoses. Mark M. Ravitch brought a sample of stapling device after attending a surgical conference in USSR, and introduced it to entrepreneur Leon C. Hirsch, who founded the United States Surgical Corporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
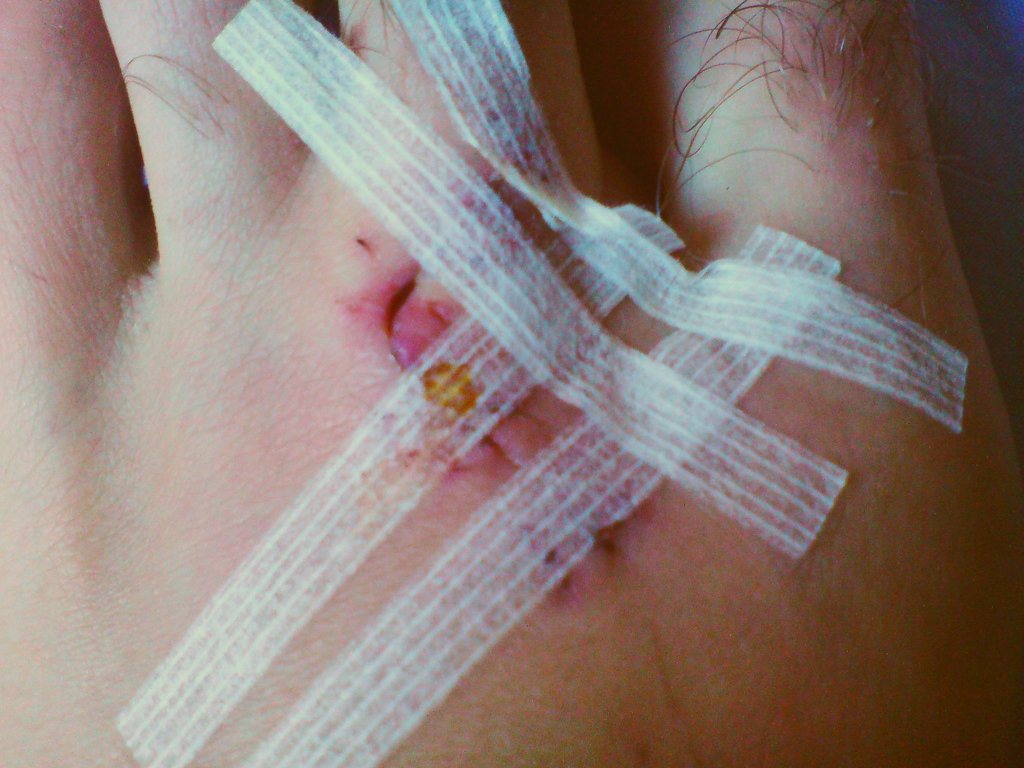
Steri Strip
Wound closure strips are porous surgical tape strips which can be used to close small wounds. They are applied across the laceration in a manner which pulls the skin on either side of the wound together. Wound closure strips may be used instead of sutures (stitches) in some injuries, because they lessen scarring and are easier to care for. Names Wound closure strips are often referred to using the genericized trademark ''Steri-Strips'', the brand name used by 3M's Nexcare. The precursor to the Steri-Strip was 3M's Micropore brand of microporous surgical tape. Usage Wound closure strips are ideal for use in highly contoured areas or areas of musculoskeletal movements, such as joints. They are also for use in areas where swelling, edema, hematomas, or bloating may occur. Additionally, they provide wound support following early suture or staple removal. Wound closure strips may also be applied together with special glue (e.g. 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate, also known as Dermabond) to sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanoacrylate
Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate and related esters. The cyanoacrylate group in the monomer rapidly polymerizes in the presence of water to form long, strong chains. They have some minor toxicity. Specific cyanoacrylates include methyl 2-cyanoacrylate (MCA), ethyl 2-cyanoacrylate (ECA, commonly sold under trade names such as "Super Glue" and "Krazy Glue", or Toagosei), ''n''-butyl cyanoacrylate (n-BCA), octyl cyanoacrylate, and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate (used in medical, veterinary and first aid applications). Octyl cyanoacrylate was developed to address toxicity concerns and to reduce skin irritation and allergic response. Cyanoacrylate adhesives are sometimes known generically as instant glues, power glues or superglues. The abbreviation "CA" is commonly used for industrial grade cyanoacrylate. Development The original patent for cyanoacrylate was filed in 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |