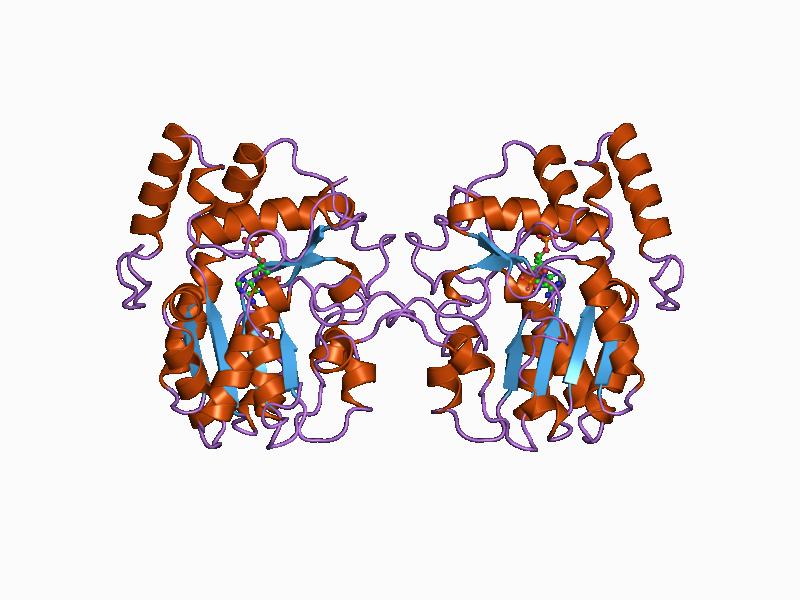
|
B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide B-1,4-galactosyltransferase
B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide b-1,4-galactosyltransferase is a galactosyltransferase Galactosyltransferase is a type of glycosyltransferase which catalyzes the transfer of galactose. An example is B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide b-1,4-galactosyltransferase. The biosynthesis of disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysacchar .... It is classified under . Genes * , , , , , References External links * Transferases EC 2.4.1 {{2.4-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactosyltransferase
Galactosyltransferase is a type of glycosyltransferase which catalyzes the transfer of galactose. An example is B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide b-1,4-galactosyltransferase. The biosynthesis of disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides involves the action of hundreds of different glycosyltransferases. These enzymes catalyse the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. A classification of glycosyltransferases using nucleotide diphospho-sugar, nucleotide monophospho-sugar and sugar phosphates () and related proteins into distinct sequence based families has been described. This classification is available on the CAZy (Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes) web site. The same three-dimensional fold is expected to occur within each of the families. Because 3-D structures are better conserved than sequences, several of the families defined on the basis of sequence similarities may have similar 3-D structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferases
A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes. Transferases are involved in myriad reactions in the cell. Three examples of these reactions are the activity of coenzyme A (CoA) transferase, which transfers thiol esters, the action of N-acetyltransferase, which is part of the pathway that metabolizes tryptophan, and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA. Transferases are also utilized during translation. In this case, an amino acid chain is the functional group transferred by a peptidyl transferase. The transfer involves the removal of the growing amino acid chain from the tRNA molecule in the A-site of the ribosome and its subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |