|
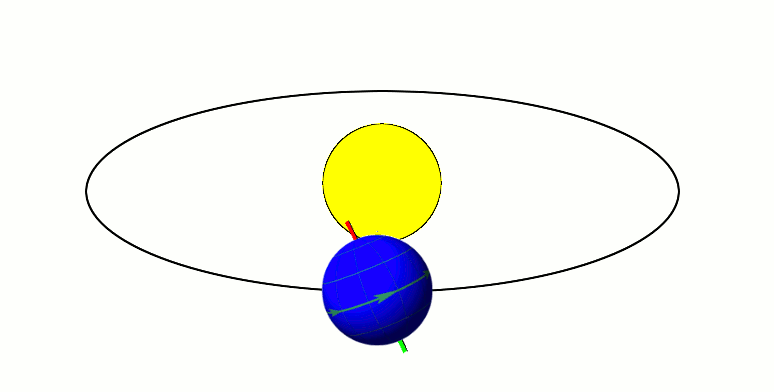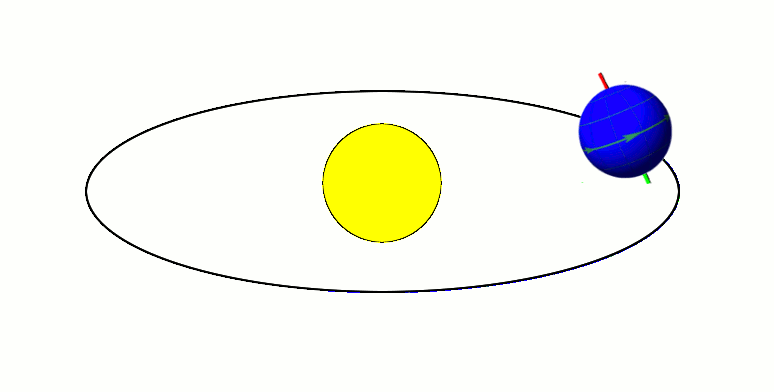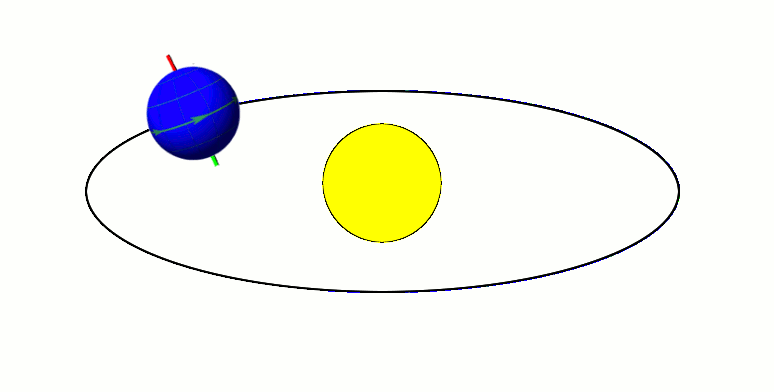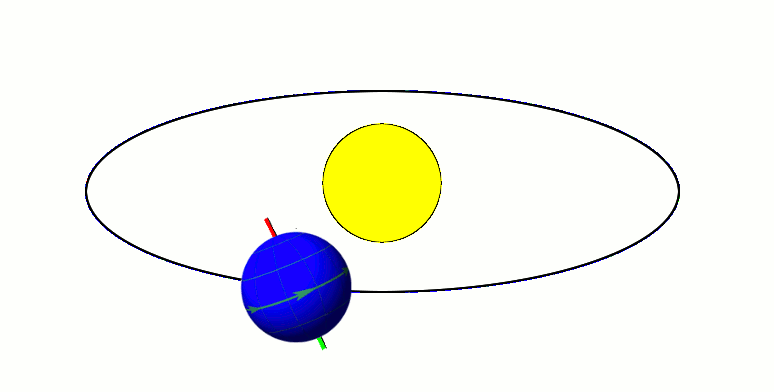
Axial Parallelism
Axial parallelism (also called gyroscopic stiffness, inertia or rigidity, or "rigidity in space") is the characteristic of a rotating body in which the direction of the axis of rotation around a fixed axis, rotation remains fixed as the object moves through space. In astronomy, this characteristic is found in astronomical bodies in orbit. It is the same effect that causes a gyroscope's axis of rotation to remain constant as Earth rotates, allowing the devices to measure Earth's rotation. Examples Earth's axial parallelism The Earth's orbit, with its Axial tilt, axis tilted at 23.5 degrees, exhibits approximate axial parallelism, maintaining its direction towards Polaris (the "North Star") year-round. Together with the Earth's axial tilt, this is one of the primary reasons for the Earth's seasons, as illustrated by the diagram to the right. It is also the reason that the Fixed stars, stars appear fixed in the night sky, such as a "fixed" pole star, throughout Earth's orbit around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Earth Tilt Animation
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Axial Precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particular, axial precession can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years.Hohenkerk, C.Y., Yallop, B.D., Smith, C.A., & Sinclair, A.T. "Celestial Reference Systems" in Seidelmann, P.K. (ed.) ''Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac''. Sausalito: University Science Books. p. 99. This is similar to the precession of a spinning top, with the axis tracing out a pair of cones joined at their apices. The term "precession" typically refers only to this largest part of the motion; other changes in the alignment of Earth's axis— nutation and polar motion—are much smaller in magnitude. Earth's precession was historically called the precession of the equinoxes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polar Motion
Polar motion of the Earth is the motion of the Earth's rotation, Earth's rotational axis relative to its Earth's crust, crust. This is measured with respect to a reference frame in which the solid Earth is fixed (a so-called ''Earth-centered, Earth-fixed'' or ECEF reference frame). This variation is a few meters on the surface of the Earth. Analysis Polar motion is defined relative to a conventionally defined reference axis, the CIO (Conventional International Origin), being the pole's average location over the year 1900. It consists of three major components: a free oscillation called Chandler wobble with a period of about 435 days, an annual oscillation, and an irregular drift in the direction of the 80th Meridian (geography), meridian west, which has lately been less extremely west. Causes The slow drift, about 20 m since 1900, is partly due to motions in the Earth's core and mantle, and partly to the redistribution of water mass as the Greenland ice sheet melts, and to iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gyroscopic Effect
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, due to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, achieved the Unification of theories in physics#Unification of gravity and astronomy, first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy, shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating calculus, infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz. Newton contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science. In the , Newton formulated the Newton's laws of motion, laws of motion and Newton's law of universal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David Gregory (mathematician)
David Gregory (originally spelt Gregorie) FRS (3 June 1659 – 10 October 1708) was a Scottish mathematician and astronomer. He was professor of mathematics at the University of Edinburgh, and later Savilian Professor of Astronomy at the University of Oxford, and a proponent of Isaac Newton's '' Principia''. Biography The fourth of the fifteen children of David Gregorie, a doctor from Kinnairdy, Banffshire, and Jean Walker of Orchiston, David was born in Upper Kirkgate, Aberdeen. The nephew of astronomer and mathematician James Gregory, David, like his influential uncle before him, studied at Aberdeen Grammar School and Marischal College (University of Aberdeen), from 1671 to 1675. The Gregorys were Jacobites and left Scotland to escape religious discrimination. Young David visited several countries on the continent, including the Netherlands (where he began studying medicine at Leiden University) and France, and did not return to Scotland until 1683. On 28 November 1683 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Foucault's Gyroscope Experiment
The Foucault gyroscope was a gyroscope created by French physicist Léon Foucault in 1852, conceived as a follow-up experiment to his pendulum in order to further demonstrate the Earth's rotation Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in progra .... Foucault felt that the results of his famous pendulum experiment had been misunderstood. He therefore endeavored to create an apparatus with a "body freely suspended by its center of gravity and rotating around one of its principal axes", allowing the study of a plane with "absolute directional stability".: "C'est faute d'avoir compris dans son acception véritable la fixité du plan d'oscillation, que beaucoup de personnes se sont fait, de la déviation, une idée inexacte, et ont méconnu sa valeur et son uniformité. Mais, si au plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rings Of Saturn
Saturn has the most extensive and complex ring system of any planet in the Solar System. The rings consist of particles in orbit around the planet made almost entirely of water ice, with a trace component of Rock (geology), rocky material. Particles range from micrometers to meters in size. There is no consensus as to what mechanism facilitated their formation: while investigations using theoretical models suggested they formed early in the Solar System's existence, newer data from ''Cassini–Huygens, Cassini'' suggests a more recent date of formation. In September 2023, astronomers reported studies suggesting that the rings of Saturn may have resulted from the collision of two moons "a few hundred million years ago". Though light reflected from the rings increases Saturn's apparent brightness, they are not themselves visible from Earth with the naked eye. In 1610, the year after Galileo Galilei's first observations with a telescope, he became the first person to observe Saturn' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saros (astronomy)
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, 18 years 11 days and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the solar eclipse, Sun and lunar eclipse, Moon. One saros period after an eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and Moon return to approximately the same relative geometry, a near straight line, and a nearly identical eclipse will occur, in what is referred to as an eclipse cycle. Every eclipse has an associated saros series and all succeeding or preceding eclipses have a different saros series associated with them - as the eclipse of the same series occurs or occurred with a gap of one saros only. Solar and lunar eclipses have different saros series. A series of eclipses that are separated by one saros is called a ''saros series''. It corresponds to: *6,585.321347 solar days *18.029 years *223 synodic months *241.999 draconic months *18.999 eclipse years (38 eclipse seasons of 173.31 days) *238.992 anomalistic months *241.029 sidereal months The 19 eclipse years means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a ''syzygy''. An eclipse is the result of either an '' occultation'' (completely hidden) or a ''transit'' (partially hidden). A "deep eclipse" (or "deep occultation") is when a small astronomical object is behind a bigger one. "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" The term ''eclipse'' is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
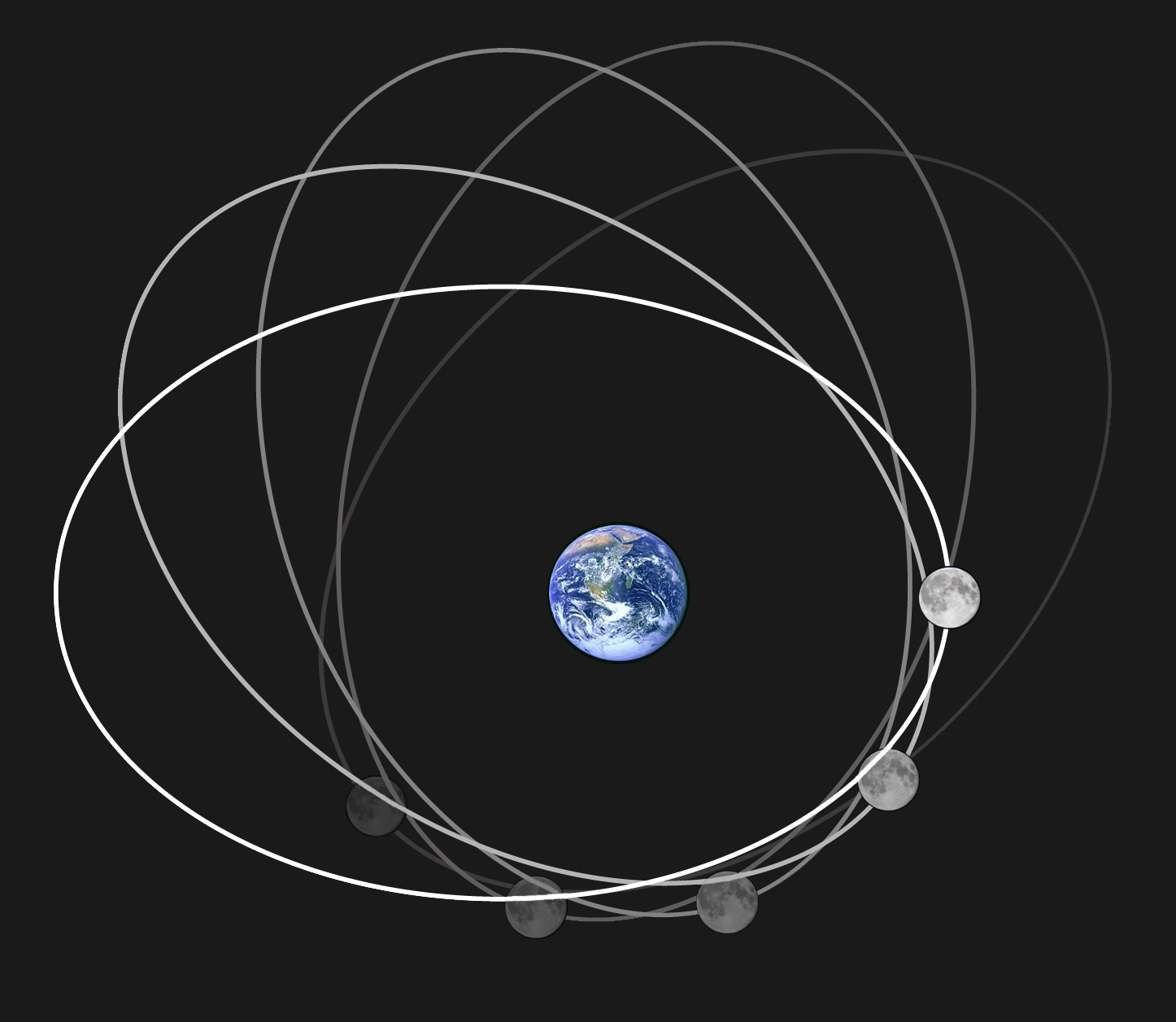
Orbit Of The Moon
The Moon orbits Earth in the retrograde and prograde motion, prograde direction and completes one orbital period, revolution relative to the March Equinox, Vernal Equinox and the fixed stars in about 27.3 days (a tropical month and sidereal month), and one revolution relative to the Sun in about 29.5 days (a synodic month). On average, the lunar distance, distance to the Moon is about from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.28 light-seconds. Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a satellite system called the Earth–Moon system. With a mean orbital speed around the barycentre of , the Moon covers a distance of approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most Regular moon, regular satellites of other planets in that its orbital plane (astronomy), orbital plane is closer to the ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |