|
Avalanche Transistor
An avalanche transistor is a bipolar junction transistor designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector-to-emitter breakdown voltage, called ''avalanche breakdown region''. This region is characterized by avalanche breakdown, which is a phenomenon similar to Townsend discharge for gases, and negative differential resistance. Operation in the avalanche breakdown region is called avalanche-mode operation: it gives avalanche transistors the ability to switch very high currents with less than a nanosecond rise and fall times (transition times). Transistors not specifically designed for the purpose can have reasonably consistent avalanche properties; for example 82% of samples of the 15V high-speed switch 2N2369, manufactured over a 12-year period, were capable of generating avalanche breakdown pulses with rise time of 350 ps or less, using a 90V power supply as Jim Williams writes.V_: this is the expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the derivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametric Family
In mathematics and its applications, a parametric family or a parameterized family is a indexed family, family of objects (a set of related objects) whose differences depend only on the chosen values for a set of parameters. Common examples are parametrized (families of) Function (mathematics), functions, probability distributions, curves, shapes, etc. In probability and its applications For example, the probability density function of a random variable may depend on a parameter . In that case, the function may be denoted f_X( \cdot \, ; \theta) to indicate the dependence on the parameter . is not a formal argument of the function as it is considered to be fixed. However, each different value of the parameter gives a different probability density function. Then the ''parametric family'' of densities is the set of functions \ , where denotes the parameter space, the set of all possible values that the parameter can take. As an example, the normal distribution is a family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doping Profile
Doping may refer to: * Doping, adding a dopant to something * Doping (semiconductor), intentionally introducing impurities into an extremely pure semiconductor to change its electrical properties * Aircraft dope, a lacquer that is applied to fabric-covered aircraft * Link doping, in search engine optimization Sports * Doping in sport, the use of drugs or other methods to improve athletic performance * Abortion doping, the rumoured practice of purposely inducing pregnancy for performance-enhancing benefits, then aborting * Blood doping, boosting the number of red blood cells in the bloodstream * Boosting (doping), a method of inducing autonomic dysreflexia * Gene doping, the hypothetical non-therapeutic use of gene therapy by athletes * Stem cell doping * Technology doping * Doping in China * Doping in Russia See also * Dope (other) Dope may refer to: Chemistry Biochemistry * Dope, a slang word for a euphoria-producing drug, particularly: ** Cocaine ** Cannabis (dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirchhoff's Current Law
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. They were first described in 1845 by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. This generalized the work of Georg Ohm and preceded the work of James Clerk Maxwell. Widely used in electrical engineering, they are also called Kirchhoff's rules or simply Kirchhoff's laws. These laws can be applied in time and frequency domains and form the basis for network analysis. Both of Kirchhoff's laws can be understood as corollaries of Maxwell's equations in the low-frequency limit. They are accurate for DC circuits, and for AC circuits at frequencies where the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are very large compared to the circuits. Kirchhoff's current law This law, also called Kirchhoff's first law, or Kirchhoff's junction rule, states that, for any node (junction) in an electrical circuit, the sum of currents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
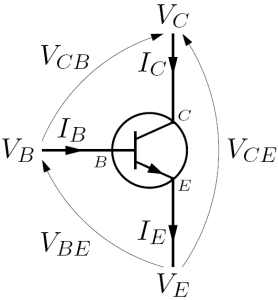
Bias Currents And Voltages For An NPN Bipolar Transistor
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, or a belief. In science and engineering, a bias is a systematic error. Statistical bias results from an unfair sampling of a population, or from an estimation process that does not give accurate results on average. Etymology The word appears to derive from Old Provençal into Old French ''biais'', "sideways, askance, against the grain". Whence comes French ''biais'', "a slant, a slope, an oblique". It seems to have entered English via the game of bowls, where it referred to balls made with a greater weight on one side. Which expanded to the figurative use, "a one-sided tendency of the mind", and, at first especially in law, "undue propensity or prejudice". Types of bias Cognitive biases A cognitive bias is a repeating or basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to electrons worth of charge moving past a point in a second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly C ( coulomb), which means an ampere is an electrical current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds or elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition the ampere was defined as the current that would need to be passed through 2 parallel wires 1 metre apart to produce a magnetic force of newtons per metre. The earlier CGS system had two definitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Current
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Semiconductor
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way. Because of their application in the computer and photovoltaic industry—in devices such as transistors, lasers, and solar cells—the search for new semiconductor materials and the improvement of existing materials is an important field of study in materials science. Most commonly used semiconductor materials are crystalline inorganic solids. These materials are classified according to the periodic table groups of their constituent atoms. Different semiconductor materials differ in their properties. Thus, in comparison with silicon, compound semiconductors have both advantages and disadvantages. For example, gallium arsenide (GaAs) has six times higher electron mobility than silicon, which allows faster operation; wider band gap, which allows op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)