|
Atypical Localization Of Immature Precursors
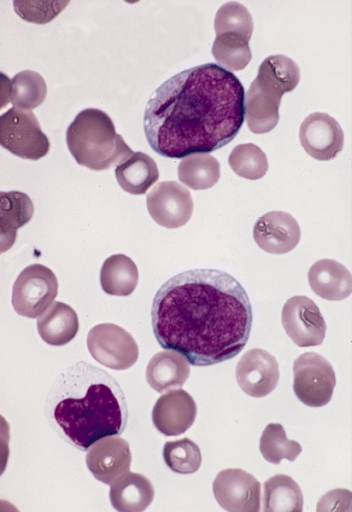
In haematology atypical localization of immature precursors (ALIP) refers to finding of atypically localized precursors (myeloblasts and promyelocytes) on bone marrow biopsy. In healthy humans, precursors are rare and are found localized near the endosteum, and consist of 1-2 cells. In some cases of myelodysplastic syndromes, immature precursors might be located in the intertrabecular region and occasionally aggregate as clusters of 3 ~ 5 cells. The presence of ALIPs is associated with worse prognosis of MDS . Recently, in bone marrow sections of patients with acute myeloid leukemia Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may includ ... cells similar to ALIPs were defined as ALIP-like clusters. The presence of ALIP-like clusters in AML patients within remission was reported to be associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character and is devoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocyte
A promyelocyte (or progranulocyte) is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12-20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a myeloblast but their cytoplasm is much more abundant. They also have less prominent nucleoli than myeloblasts and their chromatin is more coarse and clumped. The cytoplasm is basophilic and contains primary red/purple granules. Additional images File:Cytology of acute promyelocytic leukemia, annotated.png, Bone marrow smear from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia, showing characteristic abnormal promyelocytes.Image by Mikael Häggström, MD. Reference for findings: Last author update: 1 February 2013Source image: :File:Faggot cell in AML-M3.jpg froPEIR Digital Library (Pathology image database)(Public Domain) File:Hematopoiesis (human) diagram en.svg, Hematopoiesis File:Basophilic promyelocyte.png, Basophilic promyelocyte File: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
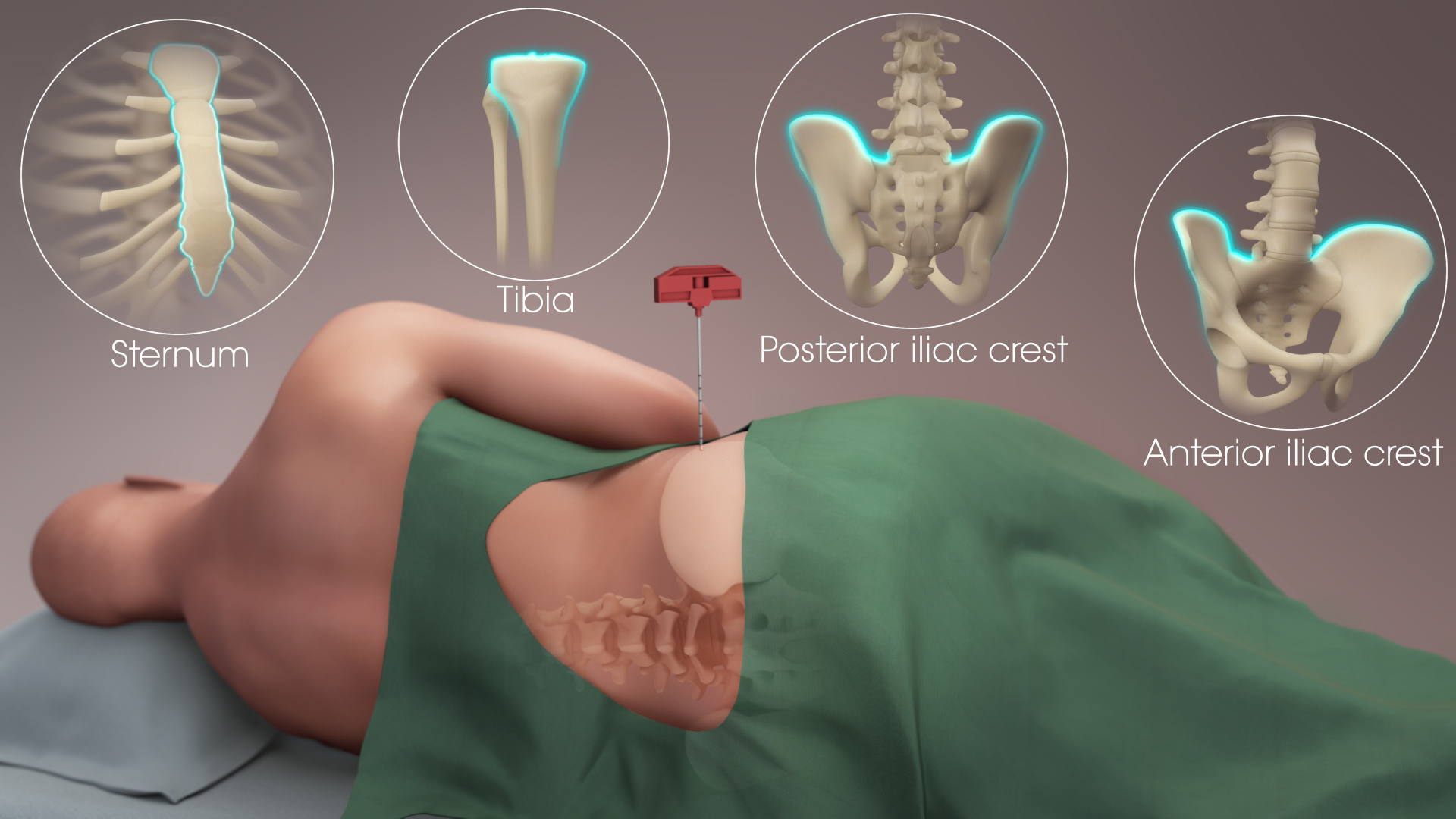
Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself (drawn from a vein by phlebotomy), it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. Components of the procedure Bone marrow samples can be obtained by aspiration and trephine biopsy. Sometimes, a bone marrow examination will include both an aspirate and a biopsy. The aspirate yields semi-liquid bone marrow, which can be examined by a pathol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia. Risk factors include previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, exposure to certain chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and benzene, and exposure to heavy metals such as mercury or lead. Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cell, platelet, and white blood cell counts. Some types have an increase in immature blood cells, called blasts, in the bone marrow or blood. The types of MDS are based on specific changes in the blood cells and bone marrow. Treatments may include supportive care, drug therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cells
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'', primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40-45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to squeeze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |