|
Attachment-based Psychotherapy
Attachment-based psychotherapy is a psychoanalytic psychotherapy that is informed by attachment theory.Slade, A. (1999) Attachment Theory and Research: Implications for the theory and practice of individual psychotherapy with adults. ''Handbook of Attachment: Theory, Research and Clinical Applications'' eds Cassidy, J. & Shaver, P. (1999) Guilford Press: New York and London. pp. 575–594Special Issue: Attachment-based psychoanalytic psychotherapy. ''Attachment & Human Development, 6, June 2004'', pp. 113–207. Attachment-based psychotherapy combines the epidemiological categories of attachment theory (including the identification of the attachment styles such as secure, anxious, ambivalent and disorganized/disoriented) with an analysis and understanding of how dysfunctional attachments get represented in the human inner world and subsequently re-enacted in adult life. Attachment-based psychotherapy is the framework of treating individuals with depression, anxiety, and childhoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might be considered an unfortunately abbreviated description, Freud said that anyone who recognizes transference and resistance is a psychoanalyst, even if he comes to conclusions other than his own.… I prefer to think of the analytic situation more broadly, as one in which someone seeking help tries to speak as freely as he can to someone who listens as carefully as he can with the aim of articulating what is going on between them and why. David Rapaport (1967a) once defined the analytic situation as carrying the method of interpersonal relationship to its last consequences." Gill, Merton M. 1999.Psychoanalysis, Part 1: Proposals for the Future" ''The Challenge for Psychoanalysis and Psychotherapy: Solutions for the Future''. New York: American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attachment Theory
Attachment theory is a psychological, evolutionary and ethological theory concerning relationships between humans. The most important tenet is that young children need to develop a relationship with at least one primary caregiver for normal social and emotional development. The theory was formulated by psychiatrist and psychoanalyst John Bowlby. Within attachment theory, infant behaviour associated with attachment is primarily the seeking of proximity to an attachment figure in stressful situations. Infants become attached to adults who are sensitive and responsive in social interactions with them, and who remain as consistent caregivers for some months during the period from about six months to two years of age. During the latter part of this period, children begin to use attachment figures (familiar people) as a secure base to explore from and return to. Parental responses lead to the development of patterns of attachment; these, in turn, lead to internal working models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Belief
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different from one's own states and include beliefs, desires, intentions, emotions, and thoughts. Possessing a functional theory of mind is considered crucial for success in everyday human social interactions. People use such a theory when analyzing, judging, and inferring others' behaviors. The discovery and development of theory of mind primarily came from studies done with animals and infants. Factors including drug and alcohol consumption, language development, cognitive delays, age, and culture can affect a person's capacity to display theory of mind. It has been proposed that deficits in theory of mind can occur in people with autism (although this is contentious), anorexia nervosa, schizophrenia, dysphoria, attention deficit hyperactivity d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attunement
Attunement was the early term adopted by practitioners of energy medicine, originally developed by Lloyd Arthur Meeker (1907 – 1954) and his colleagues. Meeker taught and practiced Attunement as a central feature of his spiritual teaching and ministry, Emissaries of Divine Light. Attunement is taught as a personal spiritual practice and as a healing modality offered through the hands. Emissaries of Divine Light believe that Attunement is a pivotal factor in the conscious evolution of humanity. Like Qigong, Reiki and Therapeutic touchbr>reikiattunement is a putative practice as defined by the United States National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), lacking published scientific study of its effectiveness. Attunement practitioners and clients rely on personal and anecdotal experience to promote it. History Beginnings Lloyd Arthur Meeker shared the first Attunement with Rudolph Plagge in Wichita, Kansas, in 1929, and developed the teaching and practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
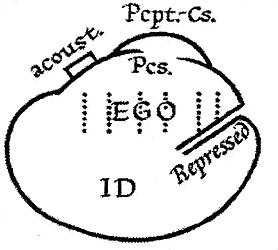
Id, Ego And Super-ego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |