|
Asperities
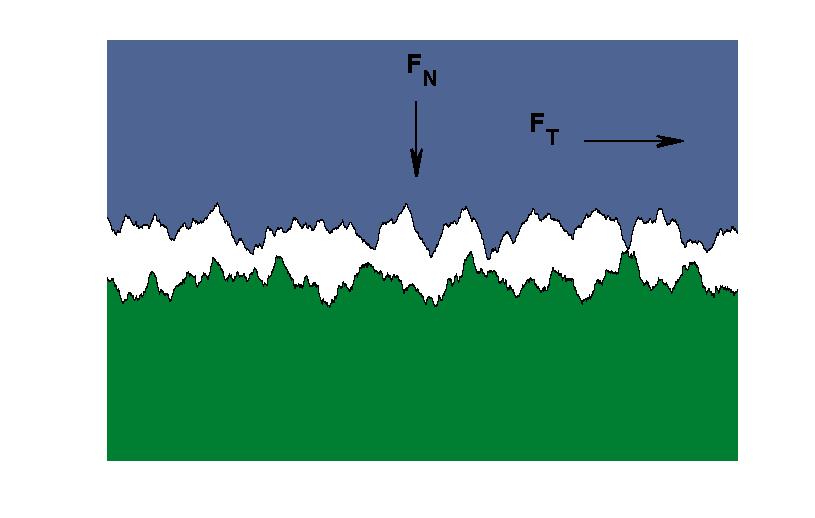
In materials science, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness" (from the Latin ''asper''—"rough"), has implications (for example) in physics and seismology. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, are not truly smooth on a microscopic scale. They are rough, with sharp, rough or rugged projections, termed "asperities". Surface asperities exist across multiple scales, often in a self affine or fractal geometry. The fractal dimension of these structures has been correlated with the contact mechanics exhibited at an interface (chemistry), interface in terms of friction and Normal contact stiffness , contact stiffness. When two macroscopically smooth surfaces come into contact, initially they only touch at a few of these asperity points. These cover only a very small portion of the surface area. Friction and wear originate at these points, and thus understanding their behavior becomes important when studying materials in contact. When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Mechanics
Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points.Johnson, K. L, 1985, Contact mechanics, Cambridge University Press.Popov, Valentin L., 2010, ''Contact Mechanics and Friction. Physical Principles and Applications'', Springer-Verlag, 362 p., . A central distinction in contact mechanics is between stresses acting perpendicular to the contacting bodies' surfaces (known as normal stress) and frictional stresses acting tangentially between the surfaces (shear stress). Normal contact mechanics or frictionless contact mechanics focuses on normal stresses caused by applied normal forces and by the adhesion present on surfaces in close contact, even if they are clean and dry. ''Frictional contact mechanics'' emphasizes the effect of friction forces. Contact mechanics is part of mechanical engineering. The physical and mathematical formulation of the subject is built upon the mechanics of materials and continuum mechanics and fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
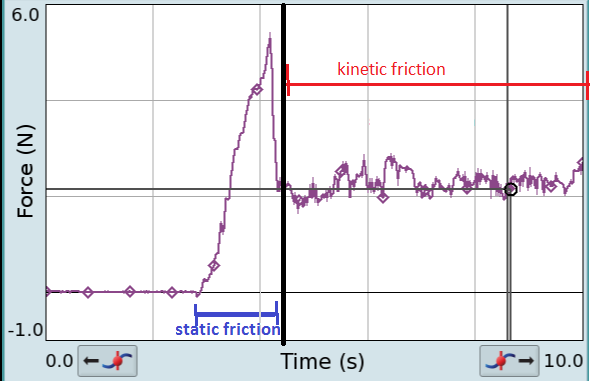
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperities
In materials science, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness" (from the Latin ''asper''—"rough"), has implications (for example) in physics and seismology. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, are not truly smooth on a microscopic scale. They are rough, with sharp, rough or rugged projections, termed "asperities". Surface asperities exist across multiple scales, often in a self affine or fractal geometry. The fractal dimension of these structures has been correlated with the contact mechanics exhibited at an interface (chemistry), interface in terms of friction and Normal contact stiffness , contact stiffness. When two macroscopically smooth surfaces come into contact, initially they only touch at a few of these asperity points. These cover only a very small portion of the surface area. Friction and wear originate at these points, and thus understanding their behavior becomes important when studying materials in contact. When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnishing (metal)
Burnishing is the plastic deformation of a surface due to sliding contact with another object. It smooths the surface and makes it shinier. Burnishing may occur on any sliding surface if the contact stress locally exceeds the yield strength of the material. The phenomenon can occur both unintentionally as a failure mode, and intentionally as part of a manufacturing process. It is a squeezing operation under cold working. Mechanics The action of a hardened ball against a softer, flat plate illustrates the process of burnishing. If the ball is pushed directly into the plate, stresses develop in both objects around the area where they contact. As this normal force increases, both the ball and the plate's surfaces deform. The deformation caused by the hardened ball increases with the magnitude of the force pressing against it. If the force on it is small, when the force is released both the ball and plate's surface will return to their original, undeformed shape. In that case, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Contact Stiffness
Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a rigid body or a second similar rough surface. Rough surfaces can be seen as consisting of large numbers of asperities. As two solid bodies of the same material approach one another, the asperities interact, and they transition from conditions of non-contact to homogeneous bulk behaviour. The varying values of stiffness and true contact area that is exhibited at an interface during this transition are dependent on the conditions of applied pressure and are of importance for the study of systems involving the physical interactions of multiple bodies including granular matter, electrode contacts, and thermal contacts, where the interface-localized structures govern overall system performance. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wear
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology. Wear in machine elements, together with other processes such as fatigue and creep, causes functional surfaces to degrade, eventually leading to material failure or loss of functionality. Thus, wear has large economic relevance as first outlined in the Jost Report. Abrasive wear alone has been estimated to cost 1-4% of the gross national product of industrialized nations. Wear of metals occurs by plastic displacement of surface and near-surface material and by detachment of particles that form wear debris. The particle size may vary from millimeters to nanometers. This process may occur by contact with other metals, nonmetallic solids, flowing liquids, solid particles or liquid droplets entrained in flowing gasses. The wear rate is affected by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archard Equation
The Archard wear equation is a simple model used to describe sliding wear and is based on the theory of asperity contact. The Archard equation was developed much later than (sometimes also known as energy dissipative hypothesis), though both came to the same physical conclusions, that the volume of the removed debris due to wear is proportional to the work done by friction forces. Theodor Reye's model became popular in Europe and it is still taught in university courses of applied mechanics. Until recently, Reye's theory of 1860 has, however, been totally ignored in English and American literature where subsequent works by Ragnar Holm and John Frederick Archard are usually cited. In 1960, and Mikhail Alekseevich Babichev published a similar model as well. In modern literature, the relation is therefore also known as Reye–Archard–Khrushchov wear law. In 2022, the steady-state Archard wear equation was extended into the running-in regime using the bearing ratio curve repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled sphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Dimension
In mathematics, more specifically in fractal geometry, a fractal dimension is a ratio providing a statistical index of complexity comparing how detail in a pattern (strictly speaking, a fractal pattern) changes with the scale at which it is measured. It has also been characterized as a measure of the space-filling capacity of a pattern that tells how a fractal scales differently from the space it is embedded in; a fractal dimension does not have to be an integer. The essential idea of "fractured" dimensions has a long history in mathematics, but the term itself was brought to the fore by Benoit Mandelbrot based on his 1967 paper on self-similarity in which he discussed ''fractional dimensions''. In that paper, Mandelbrot cited previous work by Lewis Fry Richardson describing the counter-intuitive notion that a coastline's measured length changes with the length of the measuring stick used ( see Fig. 1). In terms of that notion, the fractal dimension of a coastline quantifies ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface (chemistry)
In the physical sciences, an interface is the boundary between two spatial regions occupied by different matter, or by matter in different physical states. The interface between matter and air, or matter and vacuum, is called a surface, and studied in surface science. In thermal equilibrium, the regions in contact are called phases, and the interface is called a phase boundary. An example for an interface out of equilibrium is the grain boundary in polycrystalline matter. The importance of the interface depends on the type of system: the bigger the quotient area/volume, the greater the effect the interface will have. Consequently, interfaces are very important in systems with large interface area-to-volume ratios, such as colloids. Interfaces can be flat or curved. For example, oil droplets in a salad dressing are spherical but the interface between water and air in a glass of water is mostly flat. Surface tension is the physical property which rules interface processes involvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |