|
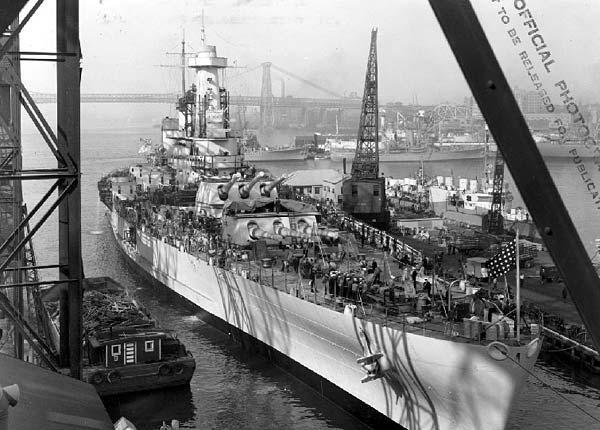
Armoured Flight Deck
An armoured flight deck is an aircraft carrier flight deck that incorporates substantial armour in its design. Comparison is often made between the carrier designs of the Royal Navy (RN) and the United States Navy (USN). The two navies followed differing philosophies in the use of armour on carrier flight decks, starting with the design of the RN's and ending with the design of the , when the USN also adopted armoured flight decks. The two classes most easily compared are the RN's ''Illustrious'' class and and their nearest USN contemporaries, the and es. The ''Illustrious'' class followed the ''Yorktown'' but preceded the ''Essex'', while the ''Implacable''-class design predated the ''Essex'' but these ships were completed after the lead ships of the ''Essex'' class. The development of armoured flight deck carriers proceeded during World War II, and before the end of World War II both the USN, with , and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), with and would also commission armour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second London Naval Treaty
The Second London Naval Treaty was an international treaty signed as a result of the Second London Naval Disarmament Conference held in London, the United Kingdom. The conference started on 9 December 1935 and the treaty was signed by the participating nations on 25 March 1936. Treaty The signatories were France, the United States, and most members of the British Commonwealth: Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom (on behalf of itself and "all parts of the British Empire which are not separate Members of the League of Nations"). Two Commonwealth Dominions declined to sign: South Africa and the Irish Free State, the latter because it had no navy. Japan, a signatory of the First London Naval Treaty and already at war on the Asian mainland, withdrew from the conference on 15 January. Italy also declined to sign the treaty, largely as a result of the controversy over its invasion of Abyssinia (Ethiopia); Italy was under sanctions from the League of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or from a potentially dangerous environment or activity (e.g. cycling, construction sites, etc.). Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships, armoured fighting vehicles, and some mostly ground attack combat aircraft. A second use of the term ''armour'' describes armoured forces, armoured weapons, and their role in combat. After the development of armoured warfare, tanks and mechanised infantry and their combat formations came to be referred to collectively as "armour". Etymology The word "armour" began to appear in the Middle Ages as a derivative of Old French. It is dated from 1297 as a "mail, defensive covering worn in combat". The word originates from the Old French , itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground attack and some types, such as fighter-bombers, are designed from the outset for dual roles. Other fighter designs are highly specialized while still filling the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Blue Blanket
The big blue blanket was an air defense system devised by John Thach during World War II for protecting American warships from attack by Japanese kamikazes. History and tactics As the American island hopping campaign got closer to Japan, the Japanese military began to employ suicide operations more extensively. As Allied losses mounted, a system for countering incoming suicide aircraft was developed. Thach, serving on Admiral Halsey's and Admiral McCain's staff as air operations officer, developed a plan that called for the constant presence of the blue-painted Hellcats and Corsairs over the fleet at all hours. He recommended larger combat air patrols (CAP) stationed farther away from the carriers, a line of picket destroyers and destroyer escorts placed 50 or more miles from the main body of the fleet to provide earlier radar intercepts, and improved coordination between the fighter director officers on board the carriers. Thach also called for dawn-to-dusk fighter sweeps o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F4U Corsair
The Vought F4U Corsair is an American fighter aircraft which saw service primarily in World War II and the Korean War. Designed and initially manufactured by Chance Vought, the Corsair was soon in great demand; additional production contracts were given to Goodyear, whose Corsairs were designated FG, and Brewster, designated F3A. The Corsair was designed and operated as a carrier-based aircraft, and entered service in large numbers with the U.S. Navy in late 1944 and early 1945. It quickly became one of the most capable carrier-based fighter-bombers of World War II. Some Japanese pilots regarded it as the most formidable American fighter of World War II and its naval aviators achieved an 11:1 kill ratio. Early problems with carrier landings and logistics led to it being eclipsed as the dominant carrier-based fighter by the Grumman F6F Hellcat, powered by the same Double Wasp engine first flown on the Corsair's initial prototype in 1940. Instead, the Corsair's early deploy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
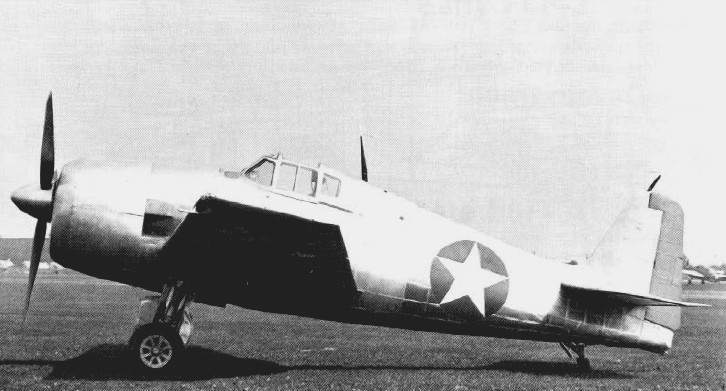
Grumman F6F Hellcat
The Grumman F6F Hellcat is an American Carrier-based aircraft, carrier-based fighter aircraft of World War II. Designed to replace the earlier Grumman F4F Wildcat, F4F Wildcat and to counter the Japanese Mitsubishi A6M Zero, it was the United States Navy's dominant fighter in the second half of the Pacific War. In gaining that role, it prevailed over its faster competitor, the Vought F4U Corsair, which initially had problems with visibility and carrier landings. Powered by a Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp, the same powerplant used for both the Corsair and the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) Republic P-47 Thunderbolt fighters, the F6F was an entirely new design, but it still resembled the Wildcat in many ways. Some military observers tagged the Hellcat as the "Wildcat's big brother".Sullivan 1979, p. 4. The F6F made its combat debut in September 1943. It subsequently established itself as a rugged, well-designed carrier fighter, which was able to outperform the A6M Zer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Air Patrol
Combat air patrol (CAP) is a type of flying mission for fighter aircraft. A combat air patrol is an aircraft patrol provided over an objective area, over the force protected, over the critical area of a combat zone, or over an air defense area, for the purpose of intercepting and destroying hostile aircraft before they reach their target. Combat air patrols apply to both overland and overwater operations, protecting other aircraft, fixed and mobile sites on land, or ships at sea. Known by the acronym CAP, it typically entails fighters flying a tactical pattern around or screening a defended target, while looking for incoming attackers. Effective CAP patterns may include aircraft positioned at both high and low altitudes, in order to shorten response times when an attack is detected. Modern CAPs are either GCI or AWACS-controlled to provide maximum early warning for defensive reaction. The first CAPs were characteristic of aircraft carrier operations, where CAPs were flown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implacable-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Implacable''-class aircraft carrier consisted of two aircraft carriers built for the Royal Navy during World War II. Derived from the design of the , they were faster and carried more aircraft than the older ships. They were initially assigned to the Home Fleet when completed in 1944 and attacked targets in Norway as well as the . Subsequently, they were assigned to the British Pacific Fleet (BPF). was the first ship to go to the Pacific and attacked Japanese-controlled oil refineries in Sumatra en route. She participated in Operation Iceberg, the invasion of Okinawa in March–April 1945. s arrival in the Pacific was delayed by a refit and she did not begin operations against the Japanese until June. The sister ships participated in the attacks on the Japanese Home Islands in July and August. ''Indefatigable'' was the only carrier chosen to continue operations after most of the BPF withdrew to prepare for further operations in early August. After the Japanese formal sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 1867, acquired more businesses, and began branching out into military hardware and shipbuilding. In 1911, the company expanded into aircraft manufacture and opened a flying school. They expanded even further into electrical and railway manufacturing, and in 1928 acquired an interest in the Supermarine. Beginning in the 1960s, various parts of the company were nationalised, and in 1999 the rest of the company was acquired by Rolls-Royce plc, who sold the defence arm to Alvis plc. The Vickers name lived on in Alvis Vickers, until the latter was acquired by BAE Systems in 2004 to form BAE Systems Land Systems. History Early history Vickers was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law George Naylor in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 2 Pounder Naval Gun
The 2-pounder gun, officially the QF 2-pounder ( QF denoting "quick firing") and universally known as the pom-pom, was a British autocannon, used as an anti-aircraft gun by the Royal Navy.British military of the period traditionally denoted smaller guns in terms of the approximate weight of the standard projectile, rather than by its bore diameter, which in this case was 40 mm. References to 40-mm anti-aircraft guns invariably mean the Bofors gun, while references to 2-pounder anti-aircraft guns mean this gun. The name came from the sound that the original models make when firing. This QF 2-pounder was not the same gun as the Ordnance QF 2-pounder, used by the British Army as an anti-tank gun and a tank gun, although they both fired , projectiles. Predecessors - Boer War and the Great War QF 1 pounder The first gun to be called a pom-pom was the 37 mm Nordenfelt-Maxim or "QF 1-pounder" introduced during the Second Boer War, the smallest artillery piece of that war. It fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 4
QF may stand for: * Qantas, an airline of Australia (IATA code QF) * Qatar Foundation, a private, chartered, non-profit organization in the state of Qatar * Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system * Quick-firing gun, a sort of artillery piece * Quiverfull, a movement of Christians who eschew all forms of birth control * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges (see British ordnance terms#QF) * Quds Force The Quds Force ( fa, نیروی قدس, niru-ye qods, Jerusalem Force) is one of five branches of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) specializing in unconventional warfare and military intelligence operations. U.S. Army's Iraq War ... an expeditionary warfare unit of IRGC {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_on_fire_1945.jpg)


.jpg)