|
Antistaphylococcal Penicillins
Antistaphylococcal penicillins are a chemical compound. They are a class of Beta lactam antibiotics used to treat infections caused by bacteria. History Penicillin resistance in ''Staphylococcus aureus'' appeared very soon after penicillin entered general clinical use in 1943, and the mechanism of resistance was the production of β-lactamase. Modification of the penicillin molecule so that it was resistant to being broken down by β-lactamase was able to temporarily overcome this problem. These compounds became known as antistaphylococcal penicillins. The first of these compounds was methicillin, which is no longer in general use. The range of these penicillins available in each country is very different, and the reasons for this are historical. Penicillin family *Cloxacillin (Canada) *Flucloxacillin (UK and Australia) *Dicloxacillin (US) *Methicillin (Withdrawn; was once sold in UK) *Nafcillin (US) *Oxacillin (US) See also *History of penicillin *List of antibiotics *Sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloxacillin
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes impetigo, cellulitis, pneumonia, septic arthritis, and otitis externa. It is not effective for methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). It is used by mouth and by injection. Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. ''Clostridium difficile'' diarrhea may also occur. It is not recommended in people who have previously had a penicillin allergy. Use during pregnancy appears to be relatively safe. Cloxacillin is in the penicillin family of medications. Cloxacillin was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States. Mechanism of action It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
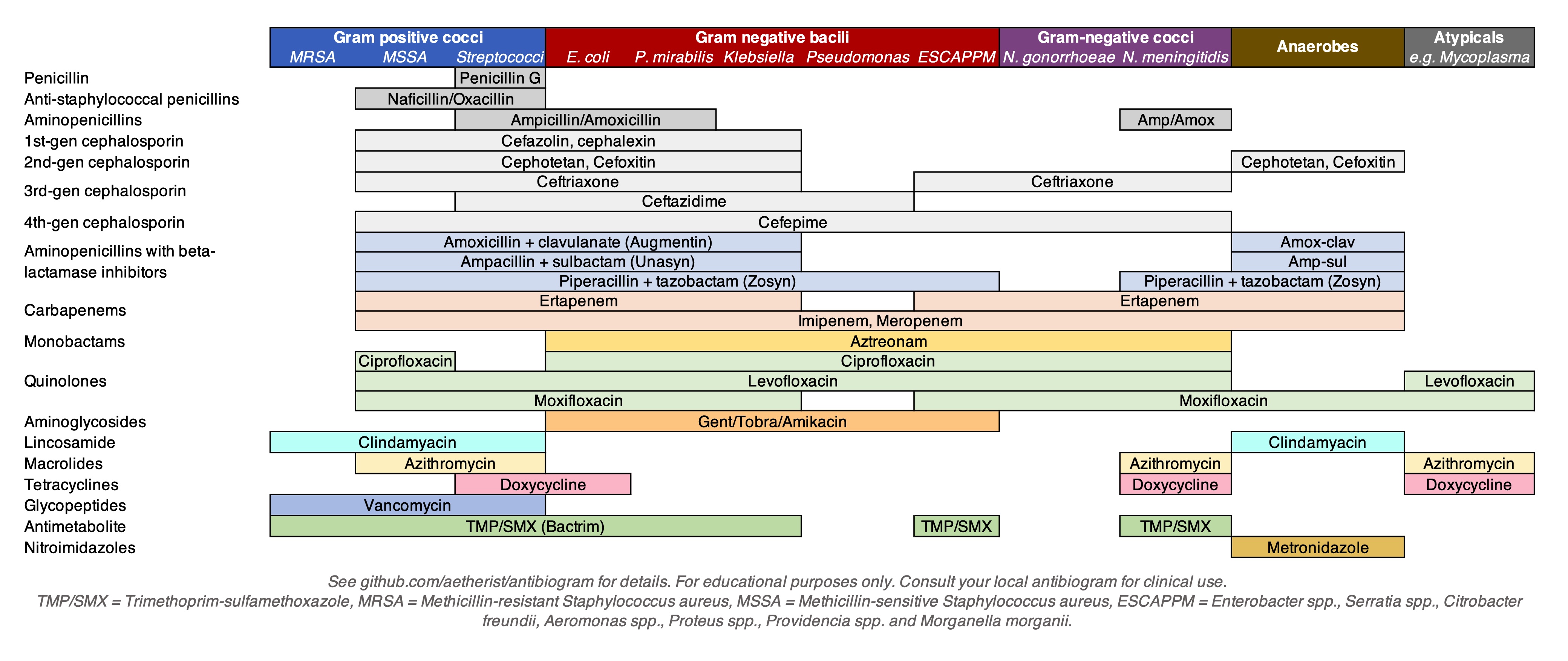
List Of Antibiotics
The following is a list of antibiotics. The highest division between antibiotics is bactericidal and bacteriostatic. Bactericidals kill bacteria directly, whereas bacteriostatics prevent them from dividing. However, these classifications are based on laboratory behavior.The development of antibiotics has had a profound effect on health in people for many years. Also, for both people and animals have used antibiotics to treat infections and diseases. In practice, both treat a bacterial infection. By coverage The following are lists of antibiotics for specific microbial coverage. MRSA Antibiotics that cover methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA): * Vancomycin * Teicoplanin * Linezolid * Daptomycin * Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole * Doxycycline * Ceftobiprole (5th generation) * Ceftaroline (5th generation) * Clindamycin * Dalbavancin * Fusidic acid * Mupirocin (topical) * Omadacycline * Oritavancin * Tedizolid * Telavancin * Tigecycline (also covers gram negatives) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Penicillin
The history of penicillin follows a number of observations and discoveries of apparent evidence of antibiotic activity of the mould ''Penicillium'' that led to the development of penicillins that became the most widely used antibiotics. Following the identification of ''Penicillium rubens'' as the source of the compound in 1928 and with the production of pure compound in 1942, penicillin became the first naturally derived antibiotic. There are anecdotes about ancient societies using moulds to treat infections, and in the following centuries many people observed the inhibition of bacterial growth by various moulds. However, it is unknown if the species involved were ''Penicillium'' species or if the antimicrobial substances produced were penicillin. While working at St Mary's Hospital in London, Scottish physician Alexander Fleming was the first to experimentally discover that a ''Penicillium'' mould secretes an antibacterial substance, and the first to concentrate the active sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxacillin
Oxacillin (trade name Bactocill) is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class developed by Beecham. It was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1962. Medical uses Oxacillin is a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam. It is similar to methicillin, and has replaced methicillin in clinical use. Other related compounds are nafcillin, cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, and flucloxacillin. Since it is resistant to penicillinase enzymes, such as that produced by ''Staphylococcus aureus'', it is widely used clinically in the US to treat penicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. However, with the introduction and widespread use of both oxacillin and methicillin, antibiotic-resistant strains called methicillin-resistant and oxacillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA/ORSA) have become increasingly prevalent worldwide. MRSA/ORSA can be treated with vancomycin or other new antibiotics. Contraindications The use of oxacillin is contraindicated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nafcillin
Nafcillin sodium is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. As a beta-lactamase-resistant penicillin, it is used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, in particular, species of staphylococci that are resistant to other penicillins. Nafcillin is considered therapeutically equivalent to oxacillin, although one retrospective study found greater rates of hypokalemia and acute kidney injury in patients taking nafcillin compared to patients taking oxacillin. Indications Nafcillin is indicated in the treatment of staphylococcal infections, except those caused by MRSA. Retrieved on July 10, 2009. Freely available with registration. U.S. clinical practice guidelines recommend either nafcillin or oxacillin as the first-line treatment of choice for staphylococcal endocarditis in patients without artificial heart valves. Side-effects As with all penicillins, serious life-threatening allergic reactions can occur. Milder side-effects include: * Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin
Methicillin (USAN), also known as meticillin (INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. Methicillin was discovered in 1960. Medical uses Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance due to β-lactamase, it is less active, can be administered only parenterally, and has a higher frequency of interstitial nephritis, an otherwise-rare adverse effect of penicillins. However, selection of methicillin depended on the outcome of susceptibility testing of the sampled infection, and since it is no longer produced, it is also not routinely tested for any more. It also served a purpose in the laboratory to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' to other penicillins facing β-lactam resistance; this role has now been passed on to other penicillins, namely ''cloxacillin'', as well as genetic testing for the presence of ''mecA'' gene by '' PCR''. Spectrum of activity At one time, methicillin was used to tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria.Product Information: DICLOXACILLIN SODIUM-dicloxacillin sodium capsule. Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc, Revised 8/2015 It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as ''Staphylococcus aureus'', which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil (BMS). It was patented in 1961 and approved for medical use in 1968. Medical uses Dicloxacillin is used to treat mild-to-moderate staphylococcal infections. To decrease the development of resistance, dicloxacillin is recommended to treat infections that are suspected or proven to be caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. Dicloxacillin is similar in pharmacokinetics, antibacterial activity, and indications to flucloxacillin, and the two agents are considered interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent '' Staphylococcus'' infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle. Common side effects include an upset stomach. Other side effects may include muscle or joint pains, shortness of breath, and liver problems. It appears to be safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It should not be used in those who are allergic to penicillin. It is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is similar in effect to cloxacillin and dicloxacillin, being active against penicillinase forming bacteria. Flucloxacillin was patented in 1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin
Methicillin (USAN), also known as meticillin (INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. Methicillin was discovered in 1960. Medical uses Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance due to β-lactamase, it is less active, can be administered only parenterally, and has a higher frequency of interstitial nephritis, an otherwise-rare adverse effect of penicillins. However, selection of methicillin depended on the outcome of susceptibility testing of the sampled infection, and since it is no longer produced, it is also not routinely tested for any more. It also served a purpose in the laboratory to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' to other penicillins facing β-lactam resistance; this role has now been passed on to other penicillins, namely ''cloxacillin'', as well as genetic testing for the presence of ''mecA'' gene by '' PCR''. Spectrum of activity At one time, methicillin was used to tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-lactamase
Beta-lactamases, (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to target a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a ''Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |