|
Antinaturalism (politics)
Antinaturalism, or anti-naturalism, is a movement arguing against naturalist and essentialist ideology; it is associated with antispeciesism, anti-racism, and feminism. Its philosophy is closely linked to the French animal rights movement and is also supported by xenofeminists, who advocate for a form of feminism holding that if nature is unjust, it should be changed, as well as transhumanists. Notable advocates include David Olivier and Yves Bonnardel. Philosophy Antinaturalists defend the inherent and absolute moral permissibility of abortion, body modification, divorce, contraception, sex reassignment surgery, and other means by which they believe human beings can assume control of their own bodies and their own environments. Antinaturalism stands in contrast to some radical environmentalist movements, which state that nature itself is sacred and should be preserved for its own sake; instead it advances the idea that all human acts are natural and that ecological preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antispeciesism
Speciesism () is a term used in philosophy regarding the treatment of individuals of different species. The term has several different definitions within the relevant literature. A common element of most definitions is that speciesism involves treating members of one species as morally more important than members of other species in the context of their similar interests. Some sources specifically define speciesism as discrimination or unjustified treatment based on an individual's species membership,Horta, O., 2010. ''What is speciesism?''. Journal of agricultural and environmental ethics, 23(3), pp.243-266, p.247 " eciesism is the unjustified disadvantageous consideration or treatment of those who are not classified as belonging to one or more particular species" while other sources define it as differential treatment without regard to whether the treatment is justified or not. Richard Ryder, who coined the term, defined it as "a prejudice or attitude of bias in favour of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Environmentalist
Radical environmentalism is a grass-roots branch of the larger environmental movement that emerged from an ecocentrism-based frustration with the co-option of mainstream environmentalism. As a movement Philosophy The radical environmental movement aspires to what scholar Christopher Manes calls "a new kind of environmental activism: iconoclastic, uncompromising, discontented with traditional conservation policy, at times illegal". Radical environmentalism presupposes a need to reconsider Western ideas of religion and philosophy, including capitalism, patriarchy, and globalization, sometimes through "resacralising" and reconnecting with nature.Manes, Christopher (1990). ''Green Rage: Radical Environmentalism and the Unmaking of Civilization'', Boston: Little, Brown and Co. The movement is typified by leaderless resistance organizations such as Earth First!, which subscribe to the idea of taking direct action in defense of Mother Nature including civil disobedience, ecotage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Rights Movement
The animal rights (AR) movement, sometimes called the animal liberation, animal personhood, or animal advocacy movement, is a social movement that seeks an end to the rigid moral and legal distinction drawn between human and non-human animals, an end to the status of animals as property, and an end to their use in the research, food, clothing, and entertainment industries. Terms and factions All animal liberationists believe that the individual interests of non-human animals deserve recognition and protection, but the movement can be split into two broad camps. Animal rights advocates believe that these basic interests confer moral rights of some kind on the animals, and/or ought to confer legal rights on them;"Animal rights," ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2007. see, for example, the work of Tom Regan. Utilitarian liberationists, on the other hand, do not believe that animals possess moral rights, but argue, on utilitarian grounds — utilitarianism in its simplest form advoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
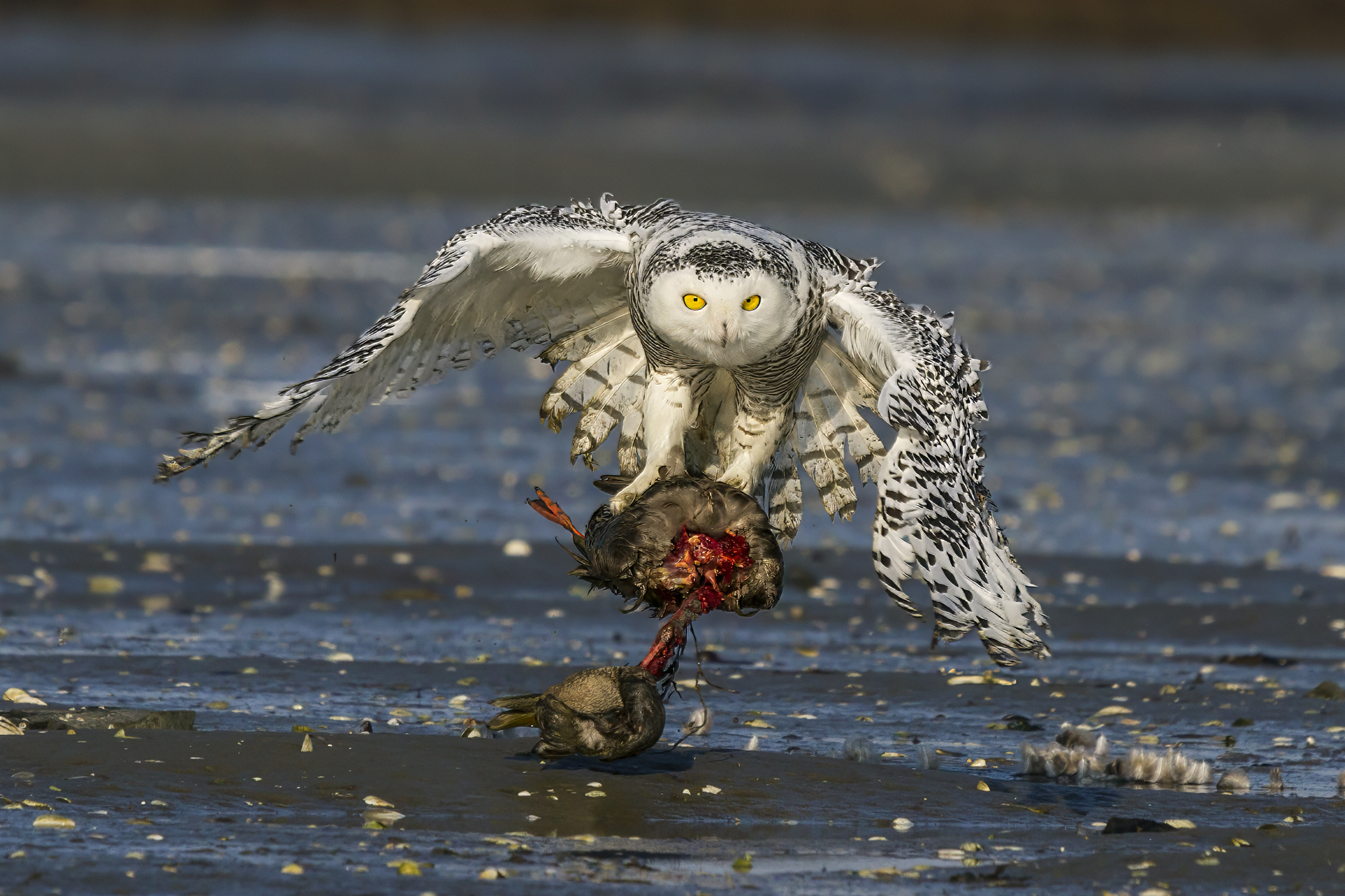
Wild Animal Suffering
Wild animal suffering is the suffering experienced by nonhuman animals living outside of direct human control, due to harms such as disease, injury, parasitism, starvation and malnutrition, dehydration, weather conditions, natural disasters, and killings by other animals, as well as psychological stress. Some estimates indicate that these individual animals make up the vast majority of animals in existence. An extensive amount of natural suffering has been described as an unavoidable consequence of Darwinian evolution and the pervasiveness of reproductive strategies which favor producing large numbers of offspring, with a low amount of parental care and of which only a small number survive to adulthood, the rest dying in painful ways, has led some to argue that suffering dominates happiness in nature. The topic has historically been discussed in the context of the philosophy of religion as an instance of the problem of evil. More recently, starting in the 19th century, a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
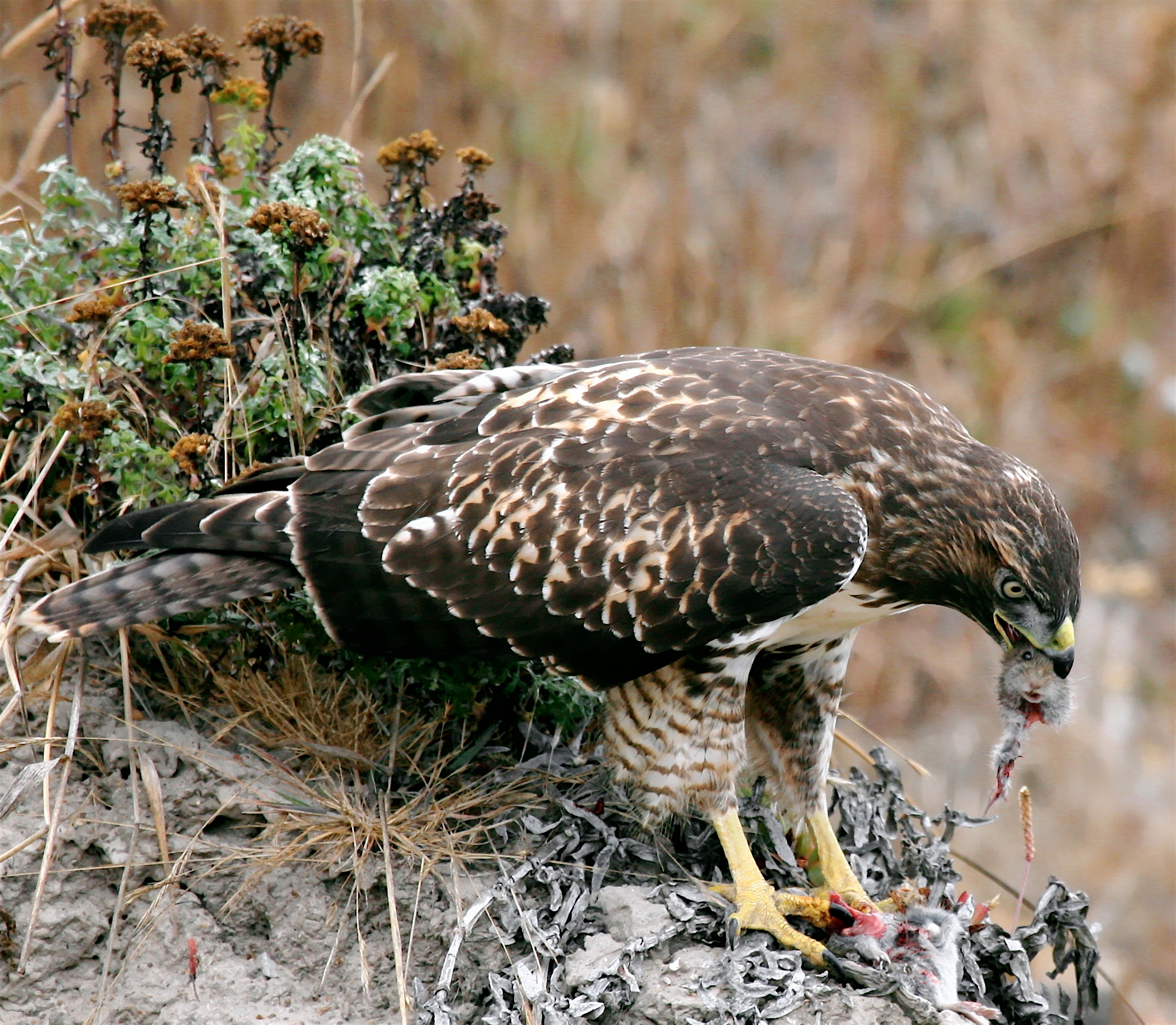
Predation Problem
The predation problem or predation argument refers to the consideration of the harms experienced by animals due to predation as a moral problem, that humans may or may not have an obligation to work towards preventing. Discourse on this topic has, by and large, been held within the disciplines of animal and environmental ethics. The issue has particularly been discussed in relation to animal rights and wild animal suffering. Some critics have considered an obligation to prevent predation as untenable or absurd and have used the position as a ''reductio ad absurdum'' to reject the concept of animal rights altogether. Others have criticized any obligation implied by the animal rights position as environmentally harmful. Responses from animal ethicists and rights advocates have been varied. Some have rejected the claim that animal rights as a position implies that we are obligated to prevent predation, while others have argued that the animal rights position does imply that predation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphological Freedom
Morphological freedom refers to a proposed civil right of a person to either maintain or modify their own body, on their own terms, through informed, consensual recourse to, or refusal of, available therapeutic or enabling medical technology. The term may have been coined by transhumanist Max More in his 1993 article, “Technological Self-Transformation: Expanding Personal Extropy”, where he defined it as "the ability to alter bodily form at will through technologies such as surgery, genetic engineering, nanotechnology, uploading". The term was later used by science debater and futurist Anders Sandberg as "an extension of one’s right to one’s body, not just self-ownership but also the right to modify oneself according to one’s desires." The Massachusetts, USA headquartered charity, the Freedom of Form Foundation, was founded in 2018 to advocate and fund scientific research furthering progress on morphological freedom, the tools required to achieve it and its general acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender Essentialism
Gender essentialism is a theory that is used to examine the attribution of distinct, fixed, intrinsic qualities to women and men. In this theory, based in essentialism, there are certain universal, innate, biologically or psychologically based features of gender that are at the root of observed differences in the behavior of men and women. In Western civilization, it is suggested in writings going back to ancient Greece. With the advent of Christianity, the earlier Greek model was expressed in theological discussions as the doctrine that there are two distinct sexes, male and female created by God, and that individuals are immutably one or the other. This view remained essentially unchanged until the middle of the 19th century. This changed the locus of the origin of the essential differences from religion to biology, in Sandra Bem's words, "from God's grand creation oits scientific equivalent: evolution's grand creation," but the belief in an immutable origin had not changed. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appeal To Nature
An appeal to nature is an argument or rhetorical tactic in which it is proposed that "a thing is good ''because'' it is 'natural', or bad ''because'' it is 'unnatural. It is generally considered to be a bad argument because the implicit (unstated) primary premise "What is ''natural'' is ''good''" is typically irrelevant, having no cogent meaning in practice, or is an opinion instead of a fact. For example, it might be argued that polio is good because it is natural. In practice, polio has little to recommend it, and if there were any good effects to be found, they would not be specifically because it's a natural disease, as an artificial disease could well have the same properties. Forms General form of this type of argument: In some contexts, the use of the terms of "nature" and "natural" can be vague, leading to unintended associations with other concepts. The word "natural" can also be a loaded term – much like the word "normal", in some contexts, it can carry an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speciesism
Speciesism () is a term used in philosophy regarding the treatment of individuals of different species. The term has several different definitions within the relevant literature. A common element of most definitions is that speciesism involves treating members of one species as morally more important than members of other species in the context of their similar interests. Some sources specifically define speciesism as discrimination or unjustified treatment based on an individual's species membership,Horta, O., 2010. ''What is speciesism?''. Journal of agricultural and environmental ethics, 23(3), pp.243-266, p.247 " eciesism is the unjustified disadvantageous consideration or treatment of those who are not classified as belonging to one or more particular species" while other sources define it as differential treatment without regard to whether the treatment is justified or not. Richard Ryder, who coined the term, defined it as "a prejudice or attitude of bias in favour of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacted laws of a state or society). According to natural law theory (called jusnaturalism), all people have inherent rights, conferred not by act of legislation but by "God, nature, or reason." Natural law theory can also refer to "theories of ethics, theories of politics, theories of civil law, and theories of religious morality." In the Western tradition, it was anticipated by the pre-Socratics, for example in their search for principles that governed the cosmos and human beings. The concept of natural law was documented in ancient Greek philosophy, including Aristotle, and was referred to in ancient Roman philosophy by Cicero. References to it are also to be found in the Old and New Testaments of the Bible, and were later expou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentient Beings
Sentience is the capacity to experience feelings and sensations. The word was first coined by philosophers in the 1630s for the concept of an ability to feel, derived from Latin '' sentientem'' (a feeling), to distinguish it from the ability to think (''reason''). In modern Western philosophy, sentience is the ability to experience sensations. In different Asian religions, the word 'sentience' has been used to translate a variety of concepts. In science fiction, the word "sentience" is sometimes used interchangeably with "sapience", "self-awareness", or "consciousness". Some writers differentiate between the mere ability to perceive sensations, such as light or pain, and the ability to perceive emotions, such as fear or grief. The subjective awareness of experiences by a conscious individual are known as qualia in Western philosophy. Philosophy and sentience In philosophy, different authors draw different distinctions between ''consciousness'' and sentience. According to Antoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)