|
Antifouling
Biofouling or biological fouling is the accumulation of microorganisms, plants, algae, or small animals where it is not wanted on surfaces such as ship and submarine hulls, devices such as water inlets, pipework, grates, ponds, and rivers that cause degradation to the primary purpose of that item. Such accumulation is referred to as ''epibiosis'' when the host surface is another organism and the relationship is not parasitic. Since biofouling can occur almost anywhere water is present, biofouling poses risks to a wide variety of objects such as boat hulls and equipment, medical devices and membranes, as well as to entire industries, such as paper manufacturing, food processing, underwater construction, and desalination plants. Anti-fouling is the ability of specifically designed materials (such as toxic biocide paints, or non-toxic paints) to remove or prevent biofouling. The buildup of biofouling on marine vessels poses a significant problem. In some instances, the hull s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-fouling Paint
Anti-fouling paint is a specialized category of coatings applied as the outer (outboard) layer to the hull of a ship or boat, to slow the growth of and facilitate detachment of subaquatic organisms that attach to the hull and can affect a vessel's performance and durability. It falls into a category of commercially available underwater hull paints, also known as ''bottom paints''. Anti-fouling paints are often applied as one component of multi-layer coating systems which may have other functions in addition to their antifouling properties, such as acting as a barrier against corrosion on metal hulls that will degrade and weaken the metal, or improving the flow of water past the hull of a fishing vessel or high-performance racing yachts. Although commonly discussed as being applied to ships, antifouling paints are also of benefit in many other sectors such as off-shore structures and fish farms. History In the Age of Sail, sailing vessels suffered severely from the growth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
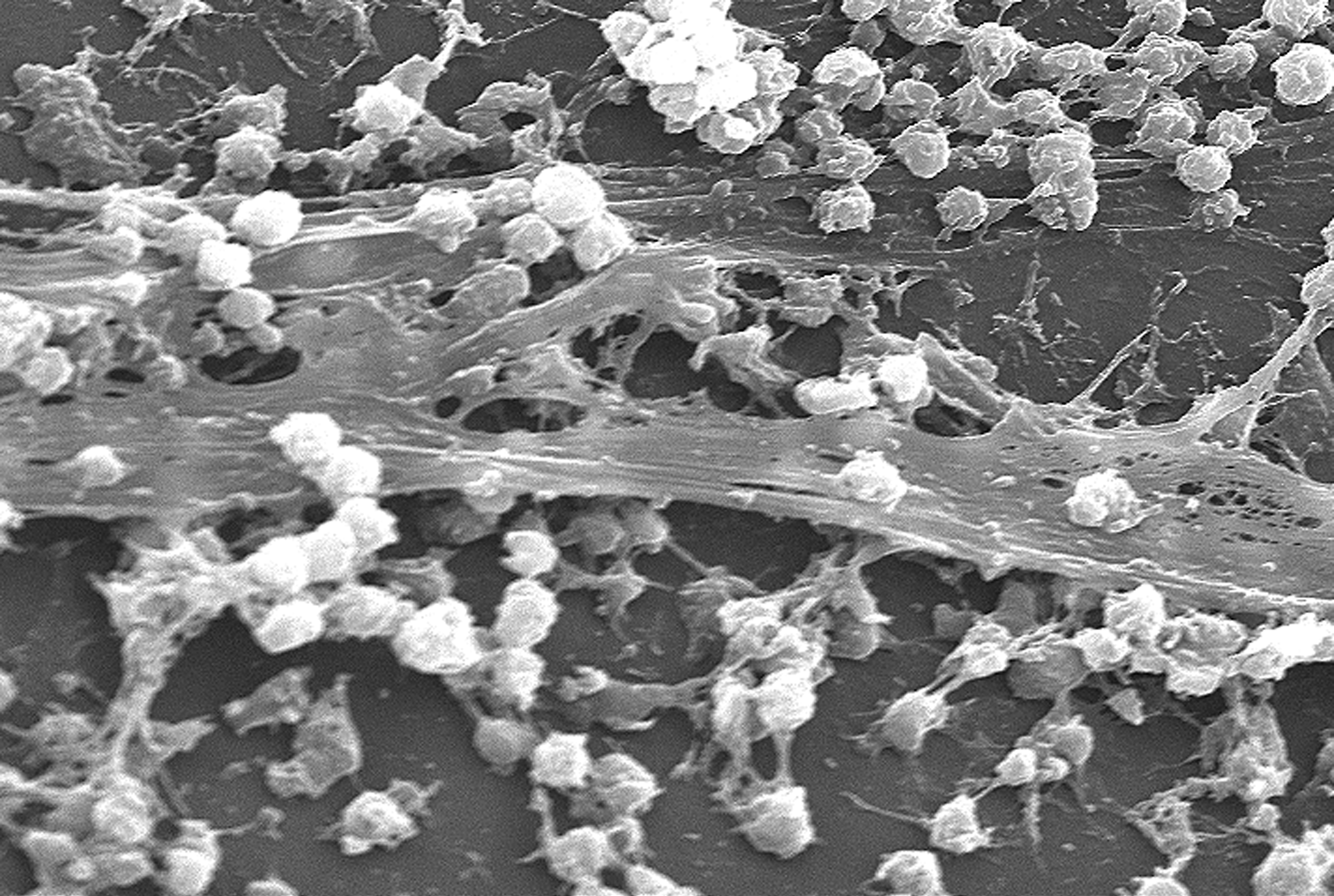
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofilm Formation
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebra Mussel GLERL 4
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebra''). Zebras share the genus ''Equus'' with horses and asses, the three groups being the only living members of the family Equidae. Zebra stripes come in different patterns, unique to each individual. Several theories have been proposed for the function of these stripes, with most evidence supporting them as a deterrent for biting flies. Zebras inhabit eastern and southern Africa and can be found in a variety of habitats such as savannahs, grasslands, woodlands, shrublands, and mountainous areas. Zebras are primarily grazers and can subsist on lower-quality vegetation. They are preyed on mainly by lions, and typically flee when threatened but also bite and kick. Zebra species differ in social behaviour, with plains and mountain zebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon, producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to a urchin population surge which destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global agricultural practice, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (zoology)
Sessility is the biological property of an organism describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile organisms for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile organisms can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other sessile organisms grow from a solid such as a rock, dead tree trunk, or a man-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunicates
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata (). It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. They are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the 'seriation of the gill slits'. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and become colonies, each unit being known as a zooid. They are marine filter feeders with a water-filled, sac-like body structure and two tubular openings, known as siphons, through which they draw in and expel water. During their respiration and feeding, they take in water through the incurrent (or inhalant) siphon and expel the filtered water through the excurrent (or exhalant) siphon. Most adult tunicates are sessile, immobile and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorticella
''Vorticella'' is a genus of bell-shaped ciliates that have stalks to attach themselves to substrates. The stalks have contractile myonemes, allowing them to pull the cell body against substrates. The formation of the stalk happens after the free-swimming stage. Etymology The organism is named ''Vorticella'' due to the beating cilia creating whirlpools, or vortices. It is also known as the “Bell Animalcule” due to its bell-shaped body. History ''Vorticella'' was first described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in a letter dated October 9, 1676. Leeuwenhoek thought that ''Vorticella'' had two horns moving like horse ears near the oral part, which turned out to be oral cilia beating to create water flow. In 1755, German miniature painter August Johann Rösel described ''Vorticella'', which was named ''Hydra convallaria'' by Linnaeus in 1758. However, in 1767, it was renamed ''Vorticella convallaria''. Otto Friedrich Müller listed 127 species of ''Vorticella'' in 1786, but many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulothrix
''Ulothrix'' is a genus of green algae in the family Ulotrichaceae. ''Ulothrix'' is a genus of non-branching filamentous green algae, generally found in fresh and marine water. Its cells are normally as broad as they are long, and they thrive in the low temperatures of spring and winter. They become attached to surfaces by a modified holdfast cell. Reproduction is normally vegetative. They are Eukaryotic and multicellular because the cells have specific functions as the lowermost cell serves as holdfast and it doesn't have chloroplast, and the apical cell is dome-shaped. The genus includes: * ''Ulothrix aequalis'' KützingGuiry, M.D., John, D.M., Rindi, F and McCarthy, T.K. (ed.) 2007. ''New Survey of Clare Island Volume: The Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae''. Royal Irish Academy. . * ''Ulothrix moniliformis'' Kützing * ''Ulothrix flacca'' (Dillwyn) Thuret in Le JolisBurrows, E.M. 1991. ''Seaweeds of the British Isles Volume 2: Chlorophyta''. Natural History Museum, London . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteromorpha Intestinalis
''Ulva intestinalis'' is a green alga in the family Ulvaceae, known by the common names sea lettuce, green bait weed, gutweed and grass kelp. Until they were reclassified by genetic work completed in the early 2000s, the tubular members of the sea lettuce genus ''Ulva'' were placed in the genus ''Enteromorpha''.Guiry, M.D., John, D.M., Rindi, F. and McCarthy, T.K. (Eds) 2007. ''New Survey of Clare Island. Volume 6: The Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae.'' p. 23. Royal Irish Academy. Distribution Generally world-wide.Burrows, E.M. 1991. ''Seaweeds of the British Isles. Volume 2 Chlorophyta''. British Museum (Natural History). It can be found in Bering Sea near Alaska, Aleutian islands, Puget Sound, Japan, Korea, Mexico, Philippines, and Russia. Besides this, places it can be found in Israel, and in such European countries as Azores, Belgium, Denmark, Ireland, Norway, Poland, and in such seas as the Baltic, and Mediterranean Sea. It is also found in the shores of the Pacific O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Putrefaciens
''Shewanella putrefaciens'' is a Gram-negative pleomorphic bacterium. It has been isolated from marine environments, as well as from anaerobic sandstone in the Morrison Formation in New Mexico. ''S. putrefaciens'' is also a facultative anaerobe with the ability to reduce iron and manganese metabolically; that is, it can use iron and manganese as the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain (in contrast to obligate aerobes which must use oxygen for this purpose). It is also one of the organisms associated with the odor of rotting fish, as it is a marine organism which produces trimethylamine (hence the species name putrefaciens, from putrid). In both solid and liquid media, ''S. putrefaciens'' is often recognizable by its bright pink color. On solid media, the colonies are round, fast-growing, and pink. The organism is also fast-growing in liquid media, and there will give the liquid an overall pink hue. On blood agar plates, the colonies are typically con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Alginolyticus
''Vibrio alginolyticus'' is a Gram-negative marine bacterium. It is medically important since it causes otitis and wound infection. It is also present in the bodies of animals such as pufferfish, where it is responsible for the production of the potent neurotoxin, tetrodotoxin. ''Vibrio alginolyticus'' are commonly found in aquatic environments. Some strains of ''V. alginolyticus'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified many strains of ''Vibrio alginolyticus'' from nine marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe .... ''V. alginolyticus'' was first identified as a pathogen of humans in 1973.Longo, Dan, et al. Harrison's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |