|
Anterior Tibial Recurrent Artery
The anterior tibial recurrent artery is a small artery in the leg. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, as soon as that vessel has passed through the interosseous space. It ascends in the tibialis anterior muscle, ramifies on the front and sides of the knee-joint, and assists in the formation of the patellar plexus by anastomosing An anastomosis (, plural anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal ... with the genicular branches of the popliteal, and with the highest genicular artery. References External links Arteries of the lower limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Network
The patellar network (circulatory anastomosis around the knee-joint, patellar anastomosis, genicular anastomosis, articular vascular network of knee or rete articulare genushttp://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/rete+articulare+genus) is an intricate network of blood vessels around and above the patella, and on the contiguous ends of the femur and tibia, forming a Superficial vein, superficial and a Deep vein, deep plexus. * The ''superficial plexus'' is situated between the fascia and skin around about the patella, and forms three well-defined arches: one, above the upper border of the patella, in the loose connective tissue over the Quadriceps femoris; the other two, below the level of the patella, are situated in the fat behind the ligamentum patellæ. * The ''deep plexus'', which forms a close net-work of vessels, lies on the lower end of the femur and upper end of the tibia around their articular surfaces, and sends numerous offsets into the interior of the joint. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
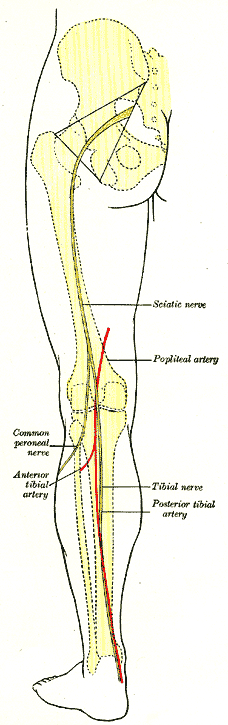
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsum (biology), dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery *anterior tibial recurrent artery *muscular branches *anterior medial malleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsalis Pedis Artery
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery (dorsal artery of foot) is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space (as the first dorsal metatarsal artery and the deep plantar artery). It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve. Structure The dorsalis pedis artery is located 1/3 from medial malleolus of the ankle. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery. It ends at the proximal part of the first intermetatarsal space. Here, it divides into two branches, the first dorsal metatarsal artery, and the deep plantar artery. It is covered by skin and fascia, but is fairly superficial. The dorsalis pedis communicates with the plantar blood supply of the foot through the deep plantar artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsum (biology), dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery *anterior tibial recurrent artery *muscular branches *anterior medial malleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin. It is situated on the lateral side of the tibia; it is thick and fleshy above, tendinous below. The tibialis anterior overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve in the upper part of the leg. Structure The tibialis anterior muscle arises from: * the lateral condyle of the tibia. * the upper 2/3 of the lateral surface of the tibia. * the adjoining part of the interosseous membrane. * the deep surface of the fascia. * the intermuscular septum between it and the extensor digitorum longus. The fibers of this circumpennate muscle are relatively parallel to the plane of insertion, ending in a tendon, apparent on the anteriomedial dorsal aspect of the foot close to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knee-joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis. It is often termed a ''compound joint'' having tibiofemoral and patellofemoral components. (The fibular collateral ligament is often considered with tibiofemoral components.) Structure The knee is a modified hinge joint, a type of synovial joint, which is composed of three functional compartments: the patellofemoral articulation, consisting of the patella, or "kneecap", and the patellar groove on the front of the femur through which it slides; and the medial and lateral tibiofemoral articulations linking the femur, or thigh bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Plexus
The patellar plexus is a plexus of fine nerves situated in front of the patella, the ligamentum patellae and the upper end of the tibia. It is formed by contribution from the following: 1)The anterior division of lateral cutaneous nerve 2)The intermediate cutaneous nerve 3)The anterior division of the medial cutaneous nerve 4)The infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve The saphenous nerve (long or internal saphenous nerve) is the largest cutaneous branch Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve. Dermatome (Anatomy), Dermatomes are similar; however, a .... References Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso Nerve plexus {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory Anastomosis
A circulatory anastomosis is a connection (an anastomosis) between two blood vessels, such as between arteries (arterio-arterial anastomosis), between veins (veno-venous anastomosis) or between an artery and a vein (arterio-venous anastomosis). Anastomoses between arteries and between veins result in a multitude of arteries and veins, respectively, serving the same volume of tissue. Such anastomoses occur normally in the body in the circulatory system, serving as backup routes for blood to flow if one link is blocked or otherwise compromised, but may also occur pathologically. Physiologic Arterio-arterial anastomoses include actual (e.g., palmar and plantar arches) and potential varieties (e.g., coronary arteries and cortical branch of cerebral arteries). There are many examples of normal arterio-arterial anastomoses in the body. Clinically important examples include: *Circle of Willis (in the brain) *Coronary: anterior interventricular artery and posterior interventricular art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior tibial artery, anterior and Posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the Intercondylar fossa of femur, intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior tibial artery, anterior and Posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the Intercondylar fossa of femur, intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |