|
Antepartum Hemorrhage
Antepartum bleeding, also known as antepartum haemorrhage (APH) or prepartum hemorrhage, is genital bleeding during pregnancy after the 28th week of pregnancy up to delivery. It can be associated with reduced fetal birth weight. Use of aspirin before 16 weeks of pregnancy to prevent pre-eclampsia also appears effective at preventing antepartum bleeding. In regard to treatment, it should be considered a medical emergency (regardless of whether there is pain), as if it is left untreated it can lead to death of the mother or baby. Classification The total amount of blood loss and signs of circulatory shock due to blood determine the severity of the antepartum haemorrhaging. There are 4 degrees of antepartum haemorrhaging: Causes Placenta praevia Placenta praevia refers to when the placenta of a growing foetus is attached abnormally low within the uterus. Intermittent antepartum haemorrhaging occurs in 72% of women living with placenta praevia. The severity of a patient's pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic villi are villi that sprout from the chorion to provide maximal contact area with maternal blood. They are an essential element in pregnancy from a histomorphologic perspective, and are, by definition, a product of conception. Branches of the umbilical arteries carry embryonic blood to the villi. After circulating through the capillaries of the villi, blood returns to the embryo through the umbilical vein. Thus, villi are part of the border between maternal and fetal blood during pregnancy. Structure Villi can also be classified by their relations: * Floating villi float freely in the intervillous space. They exhibit a bi-layered epithelium consisting of cytotrophoblasts with overlaying syncytium ( syncytiotrophoblast). * Anchoring (stem) villi stabilize mechanical integrity of the placental-maternal interface. Development The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic villi, which invade and destroy the uterine decidua and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta Praevia
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated with pain. Complications may include placenta accreta, dangerously low blood pressure, or bleeding after delivery. Complications for the baby may include fetal growth restriction. Risk factors include pregnancy at an older age and smoking as well as prior cesarean section, labor induction, or termination of pregnancy. Diagnosis is by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For those who are less than 36 weeks pregnant with only a small amount of bleeding recommendations may include bed rest and avoiding sexual intercourse. For those after 36 weeks of pregnancy or with a significant amount of bleeding, cesarean section is generally recommended. In those less than 36 weeks pregnant, corticosteroids may be given to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Dilation
Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically or medically. In childbirth In the later stages of pregnancy, the cervix may already have opened up to 1–3 cm (or more in rarer circumstances), but during labor, repeated uterine contractions lead to further widening of the cervix to about 6 centimeters. From that point, pressure from the presenting part (head in vertex births or bottom in breech births), along with uterine contractions, will dilate the cervix to 10 centimeters, which is "complete." Cervical dilation is accompanied by effacement, the thinning of the cervix. General guidelines for cervical dilation: * Latent phase: 0–3 centimeters * Active Labor: 4–7 centimeters * Transition: 8–10 centimeters * Complete: 10 centimeters. Delivery of the infant takes place sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Os
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix, the neck of the uterus. Anatomy The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus (or internal os) and with the vagina via the external orifice of the uterus (ostium of uterus or external os). The internal orifice of the uterus is an interior narrowing of the uterine cavity. It corresponds to a slight constriction known as the ''isthmus'' that can be seen on the surface of the uterus about midway between the apex and base. The external orifice of the uterus is a small, depressed, somewhat circular opening on the rounded extremity of the cervix, opening to the vagina. Through this aperture, the cervical cavity communicates with that of the vagina. The external orifice is bounded by two lips, an anterior and a posterior. The anterior is shorter and thicker, though it projects lower than the posterior because of the slope of the cervix. Normally, both lips are in con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessels
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasa Praevia
Vasa praevia is a condition in which fetal blood vessels cross or run near the internal opening of the uterus. These vessels are at risk of rupture when the supporting membranes rupture, as they are unsupported by the umbilical cord or placental tissue. Risk factors include low-lying placenta, in vitro fertilization. Vasa praevia occurs in about 0.6 per 1000 pregnancies. The term "vasa previa" is derived from the Latin; "vasa" means vessels and "previa" comes from "pre" meaning "before" and "via" meaning "way". In other words, vessels lie before the fetus in the birth canal and in the way. Cause Vasa previa is present when unprotected fetal vessels traverse the fetal membranes over the internal cervical os. These vessels may be from either a velamentous insertion of the umbilical cord or may be joining an accessory (succenturiate) placental lobe to the main disk of the placenta. If these fetal vessels rupture the bleeding is from the fetoplacental circulation, and fetal exs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus. For humans, the amniotic fluid is commonly called water or waters (Latin liquor amnii). Development Amniotic fluid is present from the formation of the gestational sac. Amniotic fluid is in the amniotic sac. It is generated from maternal plasma, and passes through the fetal membranes by osmotic and hydrostatic forces. When fetal kidneys begin to function around week 16, fetal urine also contributes to the fluid. In earlier times, it was believed that the amniotic fluid was composed entirely of fetal urine. The fluid is absorbed through the fetal tissue and skin. After 22 to 25 week of pregnancy, keratinization of an embryo's skin occurs. When this process completes around the 25th week, the fluid is primarily absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preterm Labour
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 36 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their Visual impairment, vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through healthy blood vessels in the circulatory system. In the microcirculation consisting of the very small and smallest blood vessels the capillaries, tiny thrombi known as microclots can obstruct the flow of blood in the capillaries. This can cause a number of problems particularly affecting the alveoli in the lungs of the respiratory system resulting from reduced oxygen supply. Microclots have been found to be a characteristic feature in severe cases of COVID-19, and in long COVID. Mural thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
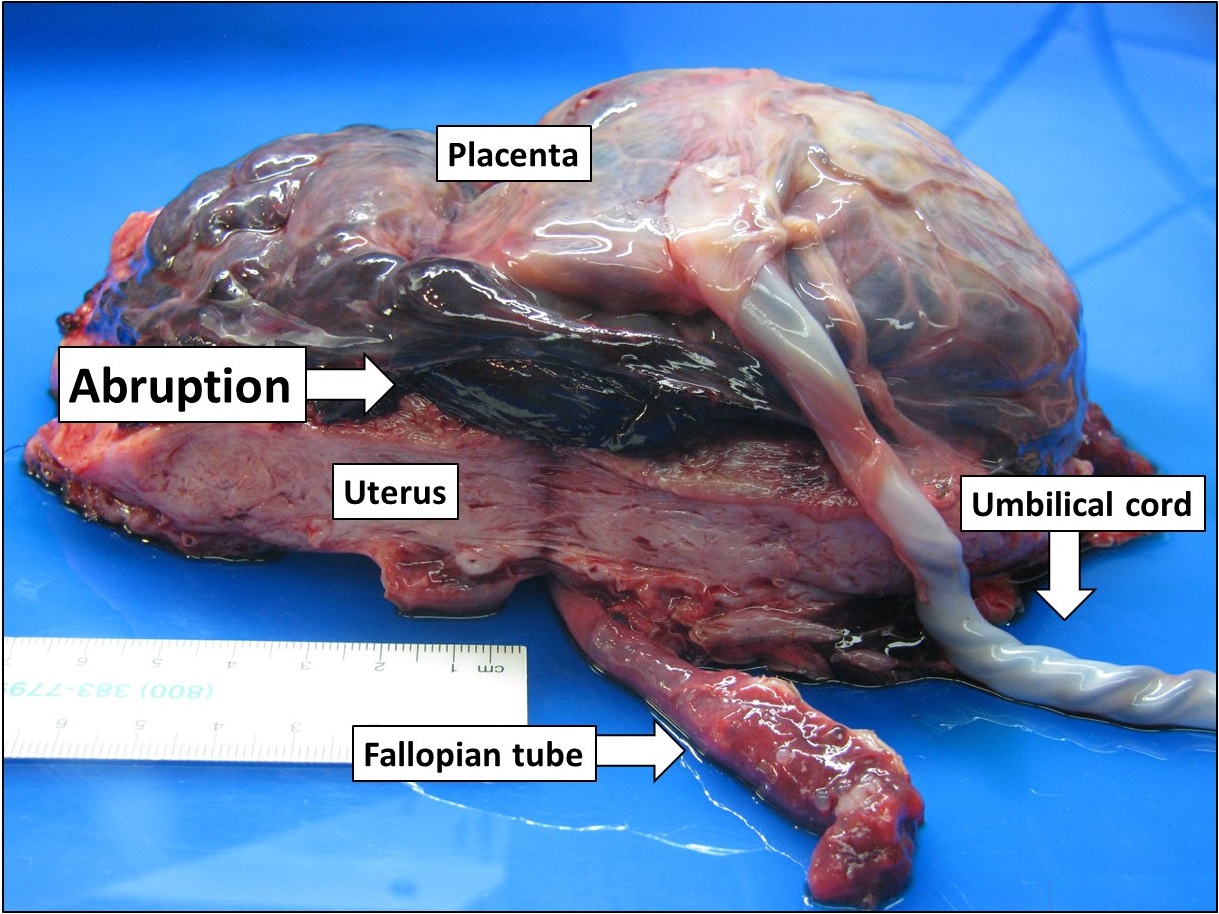
Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth. The cause of placental abruption is not entirely clear. Risk factors include smoking, pre-eclampsia, prior abruption (most important and predictive risk factor), trauma during pregnancy, cocaine use, and previous cesarean section. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and supported by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For small abruption, bed rest may be recommended, while for more significant abruptions or those that occur near term, delivery may be recommended. If everything is stable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |