|
Anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Greek origin: ''an-'' (ἀν-, prefix denoting negation) and ''orexis'' (ὄρεξις, "appetite"), translating literally to "a loss of appetite"; the adjective ''nervosa'' indicating the functional and non-organic nature of the disorder. ''Anorexia nervosa'' was coined by Gull in 1873 but, despite literal translation, the feeling of hunger is frequently present and the pathological control of this instinct is a source of satisfaction for the patients. Individuals with anorexia nervosa have a fear of being overweight or being seen as such, although they are in fact underweight. The DSM-5 describes this perceptual symptom as "disturbance in the way in which one's body weight or shape is experienced". In research and clinical settings, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eating Disorder
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that negatively affect a person's physical or mental health. Only one eating disorder can be diagnosed at a given time. Types of eating disorders include binge eating disorder, where the patient eats a large amount in a short period of time; anorexia nervosa, where the person has an intense fear of gaining weight and restricts food or overexercises to manage this fear; bulimia nervosa, where individuals eat a large quantity (binging) then try to rid themselves of the food (purging); pica, where the patient eats non-food items; rumination syndrome, where the patient regurgitates undigested or minimally digested food; avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), where people have a reduced or selective food intake due to some psychological reasons (see below); and a group of other specified feeding or eating disorders. Anxiety disorders, depression and substance abuse are common among people with e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Image Disturbance
Body image disturbance (BID) is a common symptom in patients with eating disorders and is characterized by an altered perception of one's own body. The onset is mainly attributed to patients with anorexia nervosa who persistently tend to subjectively discern themselves as average or overweight despite adequate, clinical grounds for a classification of being considerably or severely underweight. The symptom is an altered perception of one's body and a severe state of bodily dissatisfaction characterizing the body image disturbance. It is included among the diagnostic criteria for anorexia nervosa in DSM-5 ( criterion C). The disturbance is associated with significant bodily dissatisfaction and is a source of severe distress, often persisting even after seeking treatment for an eating disorder, and is regarded as difficult to treat. Thus, effective body image interventions could improve the prognosis of patients with ED, as experts have suggested. However, there is no hard evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Gull
Sir William Withey Gull, 1st Baronet (31 December 181629 January 1890) was an English physician. Of modest family origins, he established a lucrative private practice and served as Governor of Guy's Hospital, Fullerian Professor of Physiology and President of the Clinical Society. In 1871, having successfully treated the Prince of Wales during a life-threatening attack of typhoid fever, he was created a Baronet and appointed to be one of the Physicians-in-Ordinary to Queen Victoria. Gull made some significant contributions to medical science, including advancing the understanding of myxoedema, Bright's disease, paraplegia and anorexia nervosa (for which he first established the name). A widely discredited masonic/royal conspiracy theory created in the 1970s alleged that Gull knew the identity of Jack the Ripper, or even that he himself was the murderer. Although scholars have dismissed it, and Gull was 71 years old and in ill health when the murders were committed, it has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
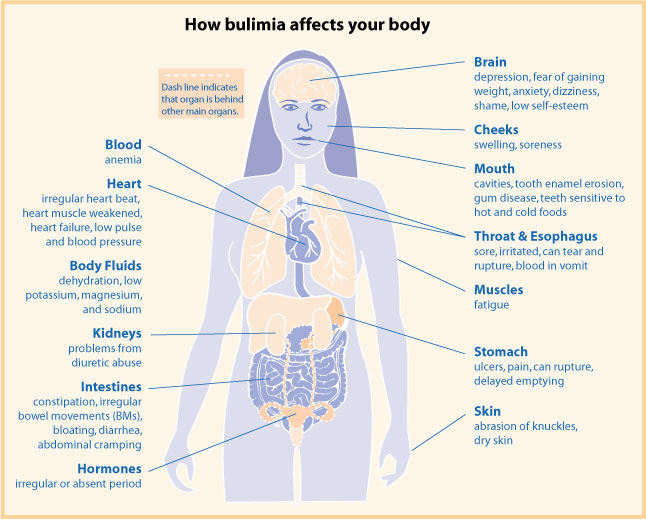
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten from the binging phase of the process. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in thickened skin on the knuckles, breakdown of the teeth and effects on metabolic rate and caloric intake which cause thyroid dysfunction. Bulimia is frequently associated with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder and problems with drugs or alcohol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underweight
An underweight person is a person whose body weight is considered too low to be healthy. A person who is underweight is malnourished. Assessment The body mass index, a ratio of a person's weight to their height, has traditionally been used to assess the health of a person as it pertains to weight: under the cut-off point at a BMI of 18.5, a person is considered underweight. The calculation is either weight in kilograms divided by height in meters, squared, or weight in pounds times 703, divided by height in inches, squared. Another measure of underweight is through comparison to the average weight of a cohort of people of a similar age and height: people who are at least 15% to 20% below the average weight for the group are considered underweight. Body fat percentage has been suggested as another way to assess whether a person is underweight. Unlike the body mass index, which is a proxy measurement, the body fat percentage takes into account the difference in composition be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (such as thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes) and their associated behaviors to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. Though it was originally designed to treat depression, its uses have been expanded to include the treatment of many mental health conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies. CBT is a common form of talk therapy based on the combination of the basic principles from behavioral and cognitive psychology. It is different from historical approaches to psychotherapy, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen, most commonly, during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). Outside the reproductive years, there is absence of menses during childhood and after menopause. Amenorrhoea is a symptom with many potential causes. Primary amenorrhea is defined as an absence of secondary sexual characteristics by age 13 with no menarche or normal secondary sexual characteristics but no menarche by 15 years of age. It may be caused by developmental problems, such as the congenital absence of the uterus, failure of the ovary to receive or maintain egg cells, or delay in pubertal development. Secondary amenorrhoea, ceasing of menstrual cycles after menarche, is defined as the absence of menses for three months in a woman with previously normal menstruation, or six months for women with a history of oligomenorrhoea. It is often caused by hormonal disturbances from the hypothalamu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identical Twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two embryos, or ''dizygotic'' ('non-identical' or 'fraternal'), meaning that each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell. Since identical twins develop from one zygote, they will share the same sex, while fraternal twins may or may not. In rare cases twins can have the same mother and different fathers (heteropaternal superfecundation). In contrast, a fetus that develops alone in the womb (the much more common case, in humans) is called a ''singleton'', and the general term for one offspring of a multiple birth is a ''multiple''. Unrelated look-alikes whose resemblance parallels that of twins are referred to as doppelgängers. Statistics The human twin birth rate in the United States rose 76% from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasogastric Feeding
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (nasogastric tube or NG tube) through the nose, down the oesophagus, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (orogastric tube) through the mouth. Abraham Louis Levin invented the NG tube. Nasogastric tube is also known as Ryle's tube in Commonwealth countries, after John Alfred Ryle. Uses A nasogastric tube is used for feeding and administering drugs and other oral agents such as activated charcoal. For drugs and for minimal quantities of liquid, a syringe is used for injection into the tube. For continuous feeding, a gravity based system is employed, with the solution placed higher than the patient's stomach. If accrued supervision is required for the feeding, the tube is often connected to an electronic pump which can control and measure the patient's intake and signal any interruption in the feeding. Nasogastric tubes may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Restraint
Physical restraint refers to means of purposely limiting or obstructing the freedom of a person's bodily movement. Basic methods Usually, binding objects such as handcuffs, legcuffs, ropes, chains, straps or straitjackets are used for this purpose. Alternatively different kinds of arm locks deriving from unarmed combat methods or martial arts are frequently used to restrain a person, which are predominantly used by trained police or correctional officers. This less commonly also extends to joint locks and pinning techniques. The freedom of movement in terms of locomotion is usually limited, by locking a person into an enclosed space, such as a prison cell and by chaining or binding someone to a heavy or immobile object. This effect can also be achieved by seizing and withholding specific items of clothing, that are normally used for protection against common adversities of the environment. Examples can be protective clothing against temperature, forcing the individual to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia, hyperthyroidism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)