|
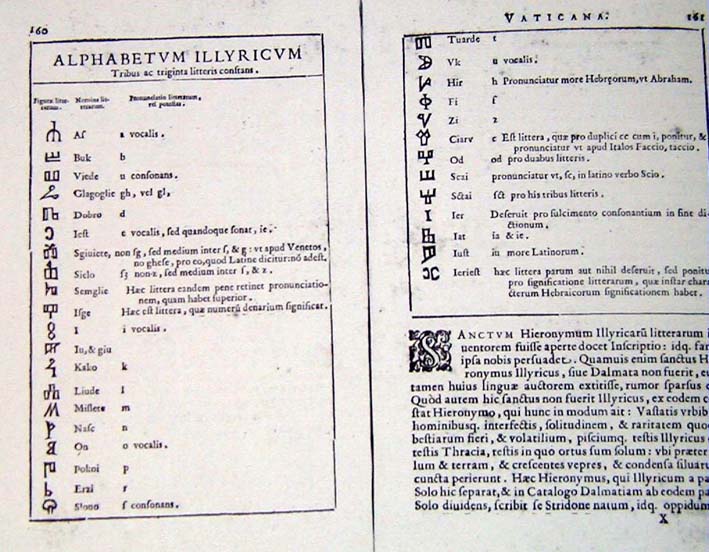
Angular Glagolitic
Croatian Glagolitic or Croatian Glagolitic Script is a style of Glagolitic bookhand used in Croatia. This form of the Glagolitic script is also known as Angular Glagolitic ( hr, uglata glagoljica). Some of the letters of the original Glagolitic script are abandoned in the Croatian recension of Church Slavonic: Yer, Yus, and Yery; a new letter Short I was introduced. After Glagolitic became the main script in Croatia in the 11th and 12th centuries, it experienced a boom in the 13th century due to favorable church and political factors. Intensified literary activity in Croatia in the 13th century led to the formation of a special type of Glagolitic writing – an Uncial (statutory) Glagolitic script. The 14th century and especially the 15th century are considered a golden age in the Croatian Glagolitic tradition. The sources for the approximate proportions and shape (construction) of the letters in the drawing of the antiqua are the Reims Gospel and several Breviaries from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breviaries
A breviary (Latin: ''breviarium'') is a liturgical book used in Christianity for praying the canonical hours, usually recited at seven fixed prayer times. Historically, different breviaries were used in the various parts of Christendom, such as Aberdeen Breviary, Belleville Breviary, Stowe Breviary and Isabella Breviary, although eventually the Roman Breviary became the standard within the Roman Catholic Church (though it was later supplanted with the Liturgy of the Hours); in other Christian denominations such as the Lutheran Churches, different breviaries continue to be used, such as The Brotherhood Prayer Book. Different breviaries In the Catholic Church, Pope Nicholas III approved a Franciscan breviary, for use in that religious order, and this was the first text that bore the title of breviary. However, the "contents of the breviary, in their essential parts, are derived from the early ages of Christianity", consisting of psalms, Scripture lessons, writings of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Croatian Language And Linguistics
The Institute of Croatian Language and Linguistics ( hr, Institut za hrvatski jezik i jezikoslovlje) is an official institute in Croatia whose purpose is to preserve and foster the Croatian language. It traces its history back to 1948, when it was part of the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts (today's Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts). The modern institute dates back to Croatia's independence in 1991. The Institute publishes ''Rasprave'', a biannual journal. Directors * Antun Barac * Stjepan Musulin (1948–1958) * Mate Hraste (1958–1965) * Ljudevit Jonke (1965–1973) * Božidar Finka (1973–1977) * Antun Šojat (1977–1982) * Božidar Finka (1982–1987) * Mijo Lončarić (1987–1996) * Miro Kačić (1996–2001) * Marko Samardžija (2001–2002) * Dunja Brozović-Rončević (2003–2011) * Željko Jozić Željko (), sometimes written Zeljko, is a South Slavic masculine given name. In Croatia, the name Željko was among the most common masculine given names in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Glagolitic
Bulgarian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria * Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group * Bulgarian language, a Slavic language * Bulgarian alphabet * A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria * Bulgarian culture * Bulgarian cuisine, a representative of the cuisine of Southeastern Europe See also * * List of Bulgarians, include * Bulgarian name, names of Bulgarians * Bulgarian umbrella, an umbrella with a hidden pneumatic mechanism * Bulgar (other) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (other) The term Bulgarian-Serbian War or Serbian-Bulgarian War may refer to: * Bulgarian-Serbian War (839-842) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (853) * Bulgarian-Serbian wars (917-924) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1330) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1885) * Bulgarian-Serbi ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravna Monastery
Ravna may refer: ;Bosnia and Herzegovina: * Ravna, Jablanica - a city in Jablanica municipality, Herzegovina-Neretva Canton, Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina * Ravna (Maglaj) - a city in Maglaj municipality, Zenica-Doboj Canton, Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina ;Bulgaria (written in Cyrillic as Равна): * Ravna, Montana Province - a village in Chiprovtsi municipality, Montana Province * Ravna, Sofia Province - a village in Godech municipality, Sofia Province * Ravna, Varna Province - a village in Provadiya Municipality, Varna Province ; Serbia (written in Cyrillic as Равна): * Ravna, Knjaževac - a village in Knjaževac municipality, Zaječar District ; Slovenia * Ravna, Kanal, a village in the Municipality of Kanal, western Slovenia See also * Ravina (other) * Ravna Gora (other) * Ravna planina * Ravna Monastery {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preslav Literary School
The Preslav Literary School ( bg, Преславска книжовна школа), also known as the Pliska Literary School or Pliska-Preslav Literary school was the first literary school in the medieval Bulgarian Empire. It was established by Boris I in 886 in Bulgaria's capital, Pliska. In 893, Simeon I moved the seat of the school from the First Bulgarian capital Pliska to the new capital, Preslav (meaning of the name in Bulgarian language - "very glorious"). Preslav was captured and burnt by the Byzantine Emperor John I Tzimisces in the year 972 in the aftermath of Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria. History The Preslav Literary School was the most important literary and cultural centre of the Bulgarian Empire and of all Slavs. A number of prominent Bulgarian writers and scholars worked at the school, including Naum of Preslav until 893; Constantine of Preslav; Joan Ekzarh (also transcr. John the Exarch); and Chernorizets Hrabar, among others. The school was also a centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychron
Polychron Monastery was a medieval Byzantine monastery in Bithynia founded in the 5th century. It is located on the slope of the Asia Minor Olympus (today's Uludağ, near Bursa, Turkey). In 851, Saint Methodius of Thessaloniki came to the monastery, later becoming its head. After his mission to the Saracens, the same year Saint Constantine-Cyril the Philosopher also settled in the monastery. In this monastery in 855, on the basis of the developed Byzantine minuscule writing system, Cyril and Methodius created the first Slavic alphabet – the Glagolitic script The Glagolitic script (, , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed to have been created in the 9th century by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byza .... References {{Ancient settlements in Turkey Byzantine church buildings in Turkey Eastern Orthodox monasteries in Turkey 5th-century churches Glagolitic script Cyrill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the other modern European languages. With modifications, it is also used for other alphabets, such as the Vietnamese alphabet. Its modern repertoire is standardised as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new letters, like the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. Letter shapes have evolved over the centuries, including the development in Medieval Latin of lower-case, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reims Gospel
Reims Gospel ( French: ''Texte du Sacre'' which means "coronation text"; also referred to in some Czech sources as the ''Emmaus Evangelie'' or ''Remešský kodex'') is an illuminated manuscript of Slavonic (Slavic) origin which became part of the Reims Cathedral treasury. According to a refuted legend, Henry III of France and several of his successors including Louis XIV took their oath on it.František Bílý: ''Od kolébky našeho obrození'', Prague 1904, pp. 7–12 In the time of Charles IV, who gave it to the just-founded Emmaus monastery in Prague, the text was believed to have been written by the hand of St. Procopius. Description Out of a total of 47 double-sided sheets, 16 sheets are written in Cyrillic (as a fragment) and 31 sheets in the Glagolitic alphabet.Jacques-Paul Migne''Dictionnaire d'épigraphie Chrétienne'' Paris 1852 The book used to have a treasure binding, richly decorated and embellished with gold, precious stones, and relics, among t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glagolitic
The Glagolitic script (, , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed to have been created in the 9th century by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzantine Emperor Michael III in 863 to Great Moravia to spread Christianity among the West Slavs in the area. The brothers decided to translate liturgical books into the contemporary Slavic language understandable to the general population (now known as Old Church Slavonic). As the words of that language could not be easily written by using either the Greek or Latin alphabets, Cyril decided to invent a new script, Glagolitic, which he based on the local dialect of the Slavic tribes from the Byzantine theme of Thessalonica. After the deaths of Cyril and Methodius, the Glagolitic alphabet ceased to be used in Moravia for political or religious needs. In 885, Pope Stephen V issued a papal bull to restrict spreading and reading Christian services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiqua (typeface Class)
Antiqua () is a style of typeface used to mimic styles of handwriting or calligraphy common during the 15th and 16th centuries. Letters are designed to flow and strokes connect together in a continuous fashion; in this way it is often contrasted with Fraktur-style typefaces where the individual strokes are broken apart. The two typefaces were used alongside each other in the germanophone world, with the Antiqua–Fraktur dispute often dividing along ideological or political lines. After the mid-20th century, Fraktur fell out of favor and Antiqua-based typefaces became the official standard. History Antiqua typefaces are typefaces designed between 1470 and 1600 AD, specifically those by Nicolas Jenson and the Aldine roman commissioned by Aldus Manutius and cut by Francesco Griffo. The letterforms were based on a synthesis of Roman inscriptional capitals and Carolingian writing. Florentine poet Petrarch was one of the few medieval authors to have touched on the handwriti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncial Script
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters were used to write Greek and Latin, as well as Gothic and Coptic. Development Early uncial script most likely developed from late rustic capitals. Early forms are characterized by broad single-stroke letters using simple round forms taking advantage of the new parchment and vellum surfaces, as opposed to the angular, multiple-stroke letters, which are more suited for rougher surfaces, such as papyrus. In the oldest examples of uncial, such as the fragment of '' De bellis macedonicis'' in the British Library, of the late 1st-early 2nd century, all of the letters are disconnected from one another, and word separation is typically not used. Word separation, however, is characteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |