|
Aminosteroid
Aminosteroids are a group of steroids with a similar structure based on an amino- substituted steroid nucleus. They are neuromuscular blocking agents, acting as competitive antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and block the signaling of acetylcholine in the nervous system. These drugs include candocuronium iodide (chandonium iodide), dacuronium bromide, dihydrochandonium, dipyrandium, malouetine, pancuronium bromide, pipecuronium bromide, rapacuronium bromide, rocuronium bromide, stercuronium iodide, and vecuronium bromide. See also * Benzylisoquinolines, such as atracurium and tubocurarine Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or ..., the other major group of neuromuscular blocking agents References Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
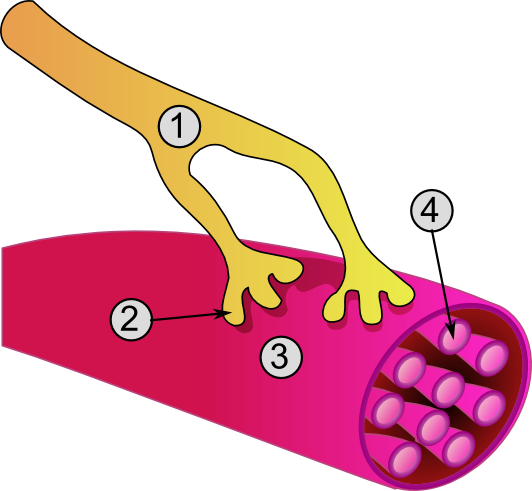
Neuromuscular Blocking Agent
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit intubation of the trachea, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate respiration. Patients are still aware of pain even after full conduction block has occurred; hence, general anesthetics and/or analgesics must also be given to prevent anesthesia awareness. Nomenclature Neuromuscular blocking drugs are often classified into two broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancuronium
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States. Mechanism of action Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It competitively inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the binding of acetylcholine. It has slight vagolytic activity, causing an increase in heart rate, but no ganglioplegic (i.e., blocking ganglions) activity. It is a very potent muscle relaxant drug, with an ED95 (i.e., the dose that causes 95% depression of muscle twitch response) of only 60 µg/kg body weight. Onset of action is relatively slow compared to other similar drugs, in part due to its low dose: an intubating dose takes 3–6 minutes for full effect. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancuronium Bromide
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States. Mechanism of action Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It competitively inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the binding of acetylcholine. It has slight vagolytic activity, causing an increase in heart rate, but no ganglioplegic (i.e., blocking ganglions) activity. It is a very potent muscle relaxant drug, with an ED95 (i.e., the dose that causes 95% depression of muscle twitch response) of only 60 µg/kg body weight. Onset of action is relatively slow compared to other similar drugs, in part due to its low dose: an intubating dose takes 3–6 minutes for full effect. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malouetine
Malouetine is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent and antinicotinic alkaloid isolated from '' Malouetia'' spp. The structure of malouetine inspired the development of modern aminosteroid muscle relaxants such as pancuronium bromide and vecuronium bromide by workers at Organon The ''Organon'' ( grc, Ὄργανον, meaning "instrument, tool, organ") is the standard collection of Aristotle's six works on logical analysis and dialectic. The name ''Organon'' was given by Aristotle's followers, the Peripatetics. The six .... References Nicotinic antagonists Steroidal alkaloids Alkaloids found in Apocynaceae Neuromuscular blockers Quaternary ammonium compounds {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Antagonists
A nicotinic antagonist is a type of anticholinergic drug that inhibits the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. These compounds are mainly used for peripheral muscle paralysis in surgery, the classical agent of this type being tubocurarine,P. Taylor (1990). In ''Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th Ed.'', (A. G. Gilman et al., Eds.), pp. 166-186, New York: Pergamon Press. but some centrally acting compounds such as bupropion, mecamylamine, and 18-methoxycoronaridine block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain and have been proposed for treating nicotine addiction. *Note: Succinylcholine is a nicotinic agonist. See neuromuscular blocking agents page for details on the mechanism of action. See also * Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor * Nicotinic agonist * Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor * Muscarinic agonist * Muscarinic antagonist A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Relaxants
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
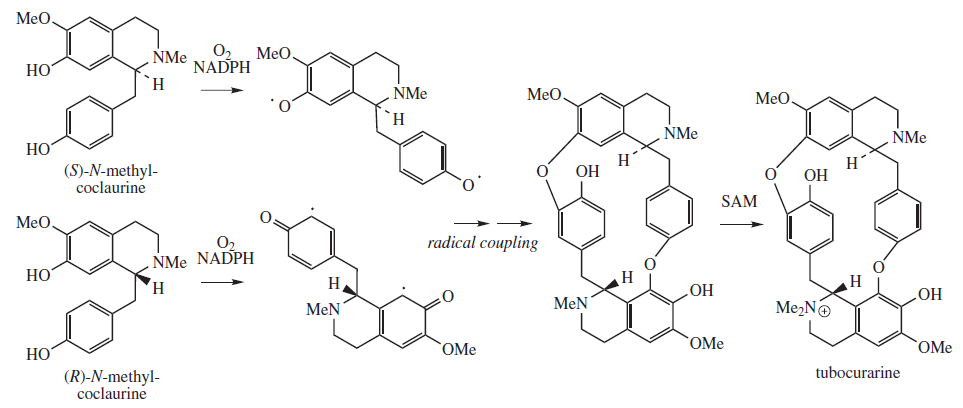
Tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is now rarely used as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia because safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, are available. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceae, Menispermaceous South American plant ''Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocurarine cannot easily cross mucous membranes. Thus, tubocurarine is effective only if given parenterally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atracurium
Atracurium besilate, also known as atracurium besylate, is a medication used in addition to other medications to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It can also be used to help with endotracheal intubation but suxamethonium (succinylcholine) is generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Common side effects include flushing of the skin and low blood pressure. Serious side effects may include allergic reactions; however, it has not been associated with malignant hyperthermia. Prolonged paralysis may occur in people with conditions like myasthenia gravis. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Atracurium is in the neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. Atracurium was approved for medical use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylisoquinoline
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine. Biosynthesis (''S'')-Norcoclaurine (higenamine) has been identified as the central 1-benzyl-tetrahydro-isoquinoline precursor from which numerous complex biosynthetic pathways eventually emerge. These pathways collectively lead to the structurally disparate compounds comprising the broad classification of plant natural products referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vecuronium Bromide
Vecuronium bromide, sold under the brand name Norcuron among others, is a medication used as part of general anesthesia to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is also used to help with endotracheal intubation; however, agents such as suxamethonium (succinylcholine) or rocuronium are generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Side effects may include low blood pressure and prolonged paralysis. Allergic reactions are rare. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Vecuronium is in the aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by competitively blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. The effects may be reversed with sugammadex or a combination of neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. To minimize residual blockade, reversal should onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stercuronium Iodide
Stercuronium iodide (INN, USAN) (developmental code names MYC-1080, MYSC-1080) is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent which was never marketed. It acts as a competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and is also reported to be an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and .... References Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists Quaternary ammonium compounds Neuromuscular blockers {{musculoskeletal-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |