|
Amentum
An ''amentum'' (Greek ''ἀγκύλη'') was a leather strap attached to a javelin used in ancient Greek athletics, hunting, and warfare, which helped to increase the range and the stability of the javelin in flight. Stability in flight was important because it allowed the javelin to land on its point, which was the only way the throw could be accurately recorded in competition or be useful against a live target. An amentum also increased the effective length of the throwing arm, as does a spear-thrower, and so enhanced speed. It is very similar to the Swiss arrow. Throwing technique The javelin was held at ear level and released after a short run. The amentum was looped over the first two fingers of the throwing hand so as to slip off when the throw was made. In competition throwing for distance, including the Ancient Olympic pentathlon at Olympia, Greece, a blunt javelin would be launched at about 45 degrees, but in war or the chase, a sharp weapon was thrown much closer to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store energy during the throw. It may consist of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the spear. It's usually about as long as the user's arm or forearm. The user holds the spear-thrower in one hand, gripping near the end farthest from the cup. The user puts the butt end of the spear, or dart, in the cup, or grabs the spur with the end of the spear. The spear is much longer than the thrower. The user holds the spear parallel to the spear-thrower and going in the other direction. The user can hold the spear, with the index and thumb, with the same hand as the thrower, with the other fingers. The user reaches back with the spear pointed at the target. Then they make an overhand throwing motion with the thrower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
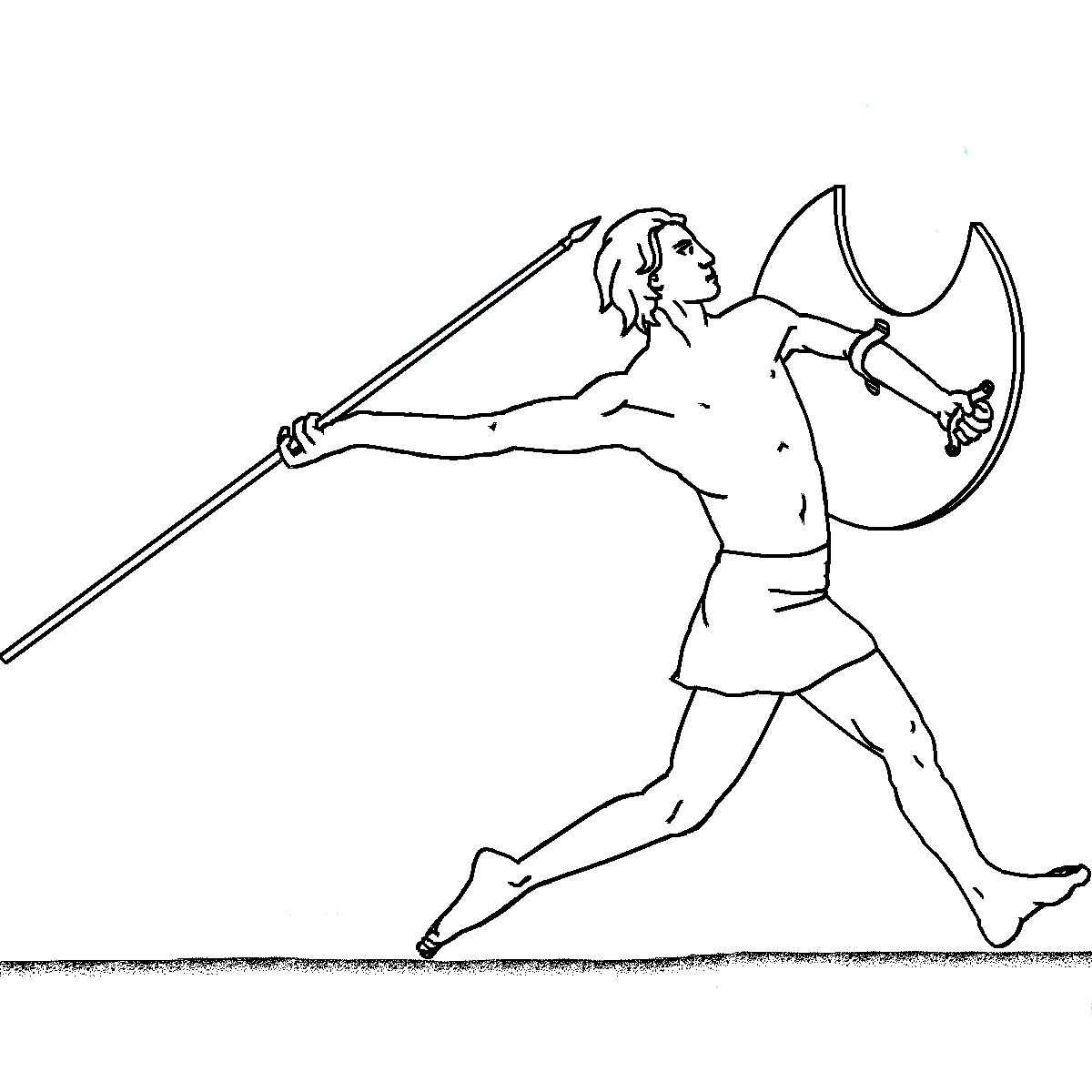
Javelin Thrower Louvre G384
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Arrow
A Swiss arrow (also known as a Yorkshire arrow, Dutch arrow, Scotch arrow, or Gypsy arrow) is a weapon similar to an arrow, but thrown with a lanyard, retained via a small notch close to the fletching. It is very similar to an amentum and uses the same principle as a spear-thrower. Design The arrow shaft is made from wood. A slit is cut at one end to take a pair of card flights, and the other end is given a point. An all-important notch or shallow groove is cut into or around the shaft, just below the flights. After the flights are inserted, the open end of the slit is closed with string or a rubber band to prevent the flights from falling out. Use To launch the arrow, the thrower uses a length of string that is longer than the length of the arrow itself. A knot is tied in one end of the string, and this is placed into the notch or groove in the arrow shaft. The rest of the string is then passed around the shaft once, and is made to align over and above the knot before being str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentathlon
A pentathlon is a contest featuring five events. The name is derived from Greek: combining the words ''pente'' (five) and -''athlon'' (competition) ( gr, πένταθλον). The first pentathlon was documented in Ancient Greece and was part of the Ancient Olympic Games. Five events were contested over one day for the Ancient Olympic pentathlon, starting with the long jump, javelin throwing, and discus throwing, followed by the '' stadion'' (a short foot race) and wrestling. Pentathletes were considered to be among the most skilled athletes, and their training was often part of military service—each of the five events in the pentathlon was thought to be useful in war or battle. With the revival of the Olympic Games in the modern era, the pentathlon returned in two formats. The athletics pentathlon was a modern variation on the original events, with a competition over five track and field events. The modern pentathlon, invented by Pierre de Coubertin (father of the Modern Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympia, Greece
Olympia ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ολυμπία ; grc, Ὀλυμπία ), officially Archaia Olympia ( el, label=Modern Greek, Αρχαία Ολυμπία; grc, Ἀρχαία Ὀλυμπία, links=no; "Ancient Olympia"), is a small town in Elis on the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, famous for the nearby archaeological site of the same name. This site was a major Panhellenic religious sanctuary of ancient Greece, where the ancient Olympic Games were held every four years throughout Classical antiquity, from the 8th century BC to the 4th century AD. They were restored on a global basis in 1894 in honor of the ideal of peaceful international contention for excellence. The sacred precinct, named the Altis, was primarily dedicated to Zeus, although other gods were worshipped there. The games conducted in his name drew visitors from all over the Greek world as one of a group of such "Panhellenic" centres, which helped to build the identity of the ancient Greeks as a nation. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
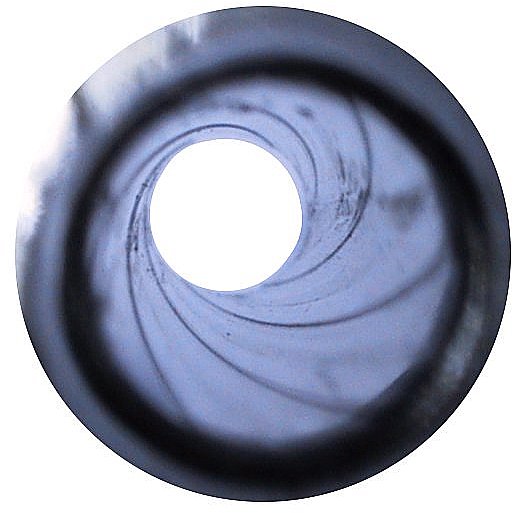
Rifling
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the projectile longitudinally by conservation of angular momentum, improving its aerodynamic stability and accuracy over smoothbore designs. Rifling is characterized by its twist rate, which indicates the distance the rifling takes to complete one full revolution, such as "1 turn in 10 inches" (1:10 inches), "1 turn in 254 mm" ("1:254 mm" or "1:25.4 cm)", or the like. Normally, an experienced shooter can infer the units of measurement from the numbers alone. A shorter distance indicates a faster twist, meaning that for a given velocity the projectile will rotate at a higher spin rate. The combination of length, weight, and shape of a projectile determines the twist rate needed to gyroscopically stabilize it – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Verchère De Reffye
Jean-Baptiste Verchère de Reffye (30 July 1821 – 6 December 1880) was a French artillery general of the 19th century, and superintendent of the works at Meudon. He was a former Ammunition#Ordnance ammunition, ordnance officer for Napoleon III. He also established the gun manufacture in Tarbes. Reffye mitrailleuse De Reffye developed in 1866 the mitrailleuse, Reffye mitrailleuse (named "Canon à balles"), one of the best early machine guns, which was used during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870. It was based on the earlier Belgian Montigny mitrailleuse of 1863. Breech-loading cannons Jean-Baptiste Verchère de Reffye took a key role in introducing rifled breech loading cannons, a marked improvement over the previous La Hitte system which had been in place since 1858. The La Hitte system used rifled weapons, but they were muzzle-loading, which had the advantage of structural strength, but the disadvantage of slowness in loading. In 1870, de Reffye developed the Reffye 85mm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew of Napoleon I, he was the last monarch to rule over France. Elected to the presidency of the Second Republic in 1848, he seized power by force in 1851, when he could not constitutionally be reelected; he later proclaimed himself Emperor of the French. He founded the Second Empire, reigning until the defeat of the French Army and his capture by Prussia and its allies at the Battle of Sedan in 1870. Napoleon III was a popular monarch who oversaw the modernization of the French economy and filled Paris with new boulevards and parks. He expanded the French overseas empire, made the French merchant navy the second largest in the world, and engaged in the Second Italian War of Independence as well as the disastrous Franco-Prussian W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nydam Mose
The Nydam Mose, also known as Nydam Bog, is an archaeological site located at Øster Sottrup, a town located in Sundeved, eight kilometres from Sønderborg, Denmark. History In the Iron Age, the site of the bog was a sacred place, where the weapons and ships of vanquished armies were offered to the indigenous gods in thanks for victory over the fallen enemy. Many items were deliberately destroyed (bent, broken or hacked into pieces) in ritual sacrificial acts, from the period 200–400 CE. The first known finds from the bog date from the 1830s, when a local farmer gave old swords and shields as toys to his children. Amongst numerous other items, three boats were found in Nydam Bog. In particular, the long oak boat, commonly known as "the Nydam Boat", maintains a distinguished position amongst Danish Iron Age finds, as it is one of the oldest known rowing vessel in Northern Europe (the Hjortspring boat, also found in Denmark, is even older). The oak boat (''egetræsbåden'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Caledonia
) , anthem = "" , image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of New Caledonia , map_caption = Location of New Caledonia , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Annexed by France , established_date = 24 September 1853 , established_title2 = Overseas territory , established_date2 = 1946 , established_title3 = Nouméa Accord , established_date3 = 5 May 1998 , official_languages = French , regional_languages = , capital = Nouméa , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , demonym = New Caledonian , government_type = Devolved parliamentary dependency , leader_title1 = President of France , leader_name1 = Emmanuel Macron , leader_title2 = President of the Government , leader_name2 = Louis Mapou , leader_title3 = President of the Congress , leader_name3 = Roch Wamytan , leader_title4 = High Commissioner , leader_name4 = Patr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)