|
Amalgamation (land)
Amalgamation in English and Welsh land law is a simple process carried out in registered land. It combines neighbouring parcels (holdings) of land which are freehold. In leasehold land interests (which can be at any storey) respective surrenders and a new combined lease followed by its registration instead is the process used: combination of leases — this can also be called the surrender and regrant involving more than one surrender. Statute and regulations A small fee is payable to HM Land Registry rule 3 of the Land Registration Rules 2003 for amalgamation or subdivision. Effects A single title with a larger plot shown in its associated title plan results. It avoids: *Duplication of data. *The risk of a part of the land being forgotten in a mortgage or sale. *Inappropriate boundary features (fences/railings) being inadvertently kept/installed on the ground between two parcels in common ownership. It enables: *New geometric subdivision of the land (sometimes called seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Land Law
English land law is the law of real property in England and Wales. Because of its heavy historical and social significance, land is usually seen as the most important part of English property law. Ownership of land has its roots in the feudal system established by William the Conqueror after 1066, and with a gradually diminishing aristocratic presence, now sees a large number of owners playing in an active market for real estate. The modern law's sources derive from the old courts of common law and equity, along with legislation such as the Law of Property Act 1925, the Settled Land Act 1925, the Land Charges Act 1972, the Trusts of Land and Appointment of Trustees Act 1996 and the Land Registration Act 2002. At its core, English land law involves the acquisition, content and priority of rights and obligations among people with interests in land. Having a property right in land, as opposed to a contractual or some other personal right, matters because it creates privileges over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Land
Alienated Real property, land is that which has been acquired from customary landowners by the government, either for its own use or for private development requiring a mortgage or other forms of guarantees. The term refers historically to the appropriation of customary land by European colonialism, colonial powers. Land was alienated in all colonies.it is set aside to be used for certain projects See also *Alienation (property law) *Land rights *Aboriginal land claim Property law {{law-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
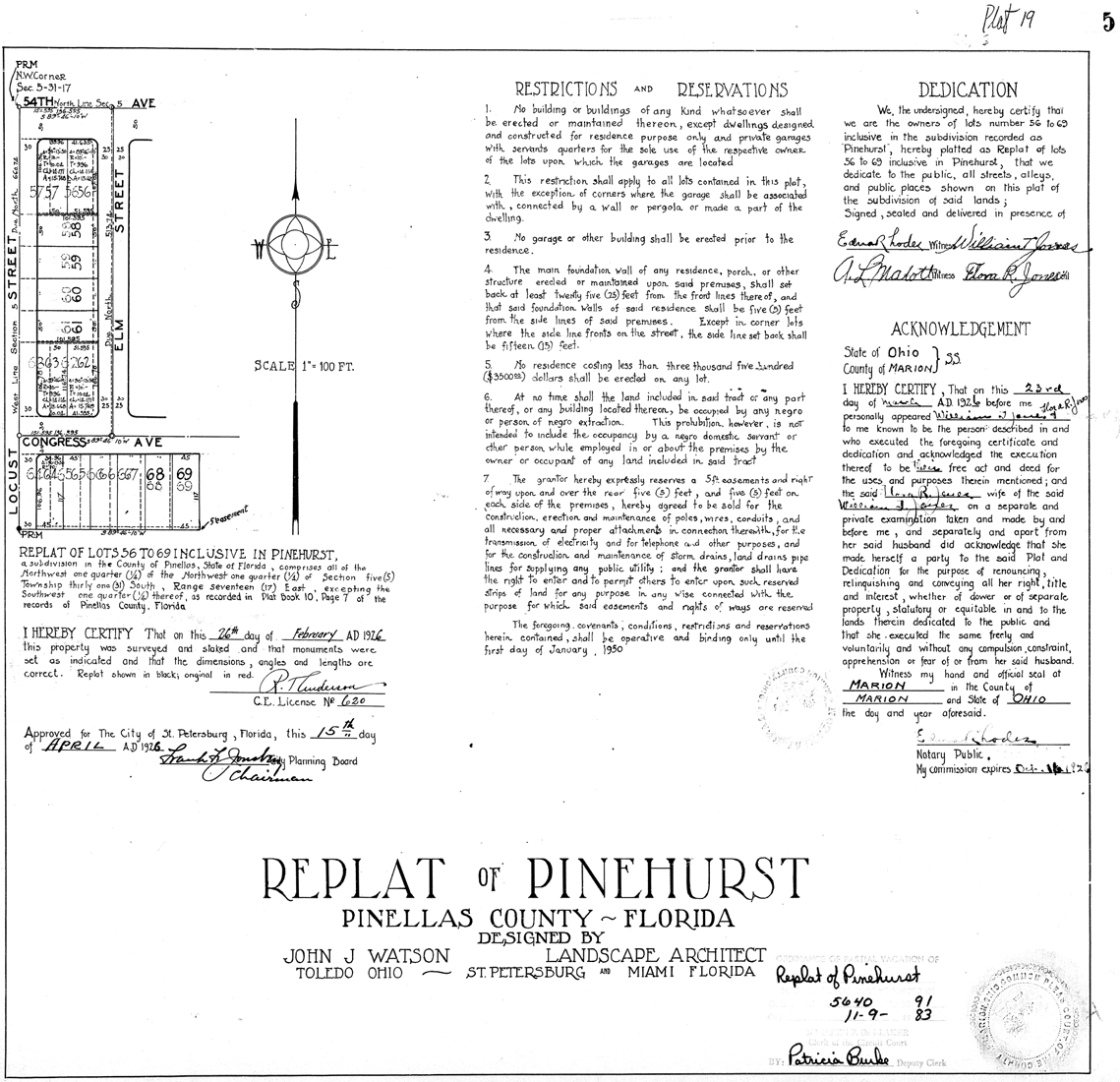
Freehold (law)
In common law jurisdictions such as England and Wales, Australia, Canada, and Ireland, a freehold is the common mode of ownership of real property, or land, and all immovable structures attached to such land. It is in contrast to a leasehold, in which the property reverts to the owner of the land after the lease period expires or otherwise lawfully terminates. For an estate to be a freehold, it must possess two qualities: immobility (property must be land or some interest issuing out of or annexed to land) and ownership of it must be forever ("of an indeterminate duration"). If the time of ownership can be fixed and determined, it cannot be a freehold. It is "An estate in land held in fee simple, fee tail or for term of life." The default position subset is the perpetual freehold, which is "an estate given to a grantee for life, and then successively to the grantee's heirs for life." England and Wales Diversity of freeholds before 1925 In England and Wales, before the Law of Prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leasehold Estate
A leasehold estate is an ownership of a temporary right to hold land or property in which a lessee or a tenant holds rights of real property by some form of title from a lessor or landlord. Although a tenant does hold rights to real property, a leasehold estate is typically considered personal property. Leasehold is a form of land tenure or property tenure where one party buys the right to occupy land or a building for a given length of time. As a lease is a legal estate, leasehold estate can be bought and sold on the open market. A leasehold thus differs from a freehold or fee simple where the ownership of a property is purchased outright and thereafter held for an indeterminate length of time, and also differs from a tenancy where a property is let (rented) on a periodic basis such as weekly or monthly. Terminology and types of leasehold vary from country to country. Sometimes, but not always, a residential tenancy under a lease agreement is colloquially known as renting. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storey
A storey (British English) or story (American English) is any level part of a building with a floor that could be used by people (for living, work, storage, recreation, etc.). Plurals for the word are ''storeys'' (UK) and ''stories'' (US). The terms ''floor'', ''level'', or ''deck'' are used in similar ways, except that it is usual to speak of a "16-''storey'' building", but "the 16th ''floor''". The floor at ground or street level is called the "ground floor" (i.e. it needs no number; the floor below it is called "basement", and the floor above it is called "first") in many regions. However, in some regions, like the U.S., ''ground floor'' is synonymous with ''first floor'', leading to differing numberings of floors, depending on region – even between different national varieties of English. The words ''storey'' and ''floor'' normally exclude levels of the building that are not covered by a roof, such as the terrace on the rooftops of many buildings. Nevertheless, a flat r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender And Regrant
During the Tudor conquest of Ireland (c.1540–1603), "surrender and regrant" was the legal mechanism by which Irish clans were to be converted from a power structure rooted in clan and kin loyalties, to a late-feudal system under the English legal system. The policy was an attempt to incorporate the clan chiefs into the English-controlled Kingdom of Ireland, and to guarantee their property under English common law, as distinct from the traditional Irish Brehon law system. This strategy was the primary non-violent method for Crown officials in the Dublin Castle administration to subjugate Irish clan leaders during the conquest. It was an unanticipated consequence to be required to pay fealty in currency instead of trade labor or commodities. The process of "surrender and regrant" thus created new, unfamiliar debt structures among the Irish, and these debts had social and political consequences. Policy The policy of surrender and regrant was led by King Henry VIII of England (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Registration Act 2002
The Land Registration Act 2002c 9 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which repealed and replaced previous legislation governing land registration, in particular the Land Registration Act 1925, which governed an earlier, though similar, system. The Act, together with the Land Registration Rules, regulates the role and practice of HM Land Registry. Background The Land Registration Act 2002 was introduced in response to the Law Commission and HM Land Registry report, ''Land Registration for the Twenty-first Century'' (2001). The Act: *Simplified and modernised the law of land registration; *Made the register reflect a more accurate picture of a title to land, showing more fully the rights and subsidiary interests that affect it; and *Was intended to facilitate the introduction of e-conveyancing. The Act made some major changes to the law regulating registered land. Specifically, it: *Enabled shorter leases to be registered; *Further encouraged voluntary land registr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severance (land)
A severance can in law mean the act of severing a piece of land from a larger tract of land. The severed parcel of land becomes a separate lot (parcel). Second, it can refer to, in jurisdictions that have the form of co-ownership, the ending of a joint tenancy by act or event other than death. Third, it can be defined in a definitions clause or table in ways including the removal of a party from an agreement, or a permitted ending of the agreement (e.g. break clause) — in an employment contract/negotiations especially common as to severance pay and other terms of severance — or part of the agreement in which case it may be either capable of forming the heart of a new agreement, that is being superseded or instead varied to be non-binding (avoided) as to future conduct (see voidable contract) and the parties should ensure which meaning is meant in this third range of senses. Transfer of part In many jurisdictions, land use laws require that severances of land occur in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Registry
Land registration is any of various systems by which matters concerning ownership, possession, or other rights in land are formally recorded (usually with a government agency or department) to provide evidence of title, facilitate transactions, and prevent unlawful disposal. The information recorded and the protection provided by land registration varies widely by jurisdiction. In common law countries, particularly in jurisdictions in the Commonwealth of Nations, when replacing the deeds registration system, title registrations are broadly classified into two basic types: the Torrens title system and the English system, a modified version of the Torrens system.Lyall, Andrew. ''Land Law in Ireland''. ; Ch. 24 Cadastral systems and land registration are both types of land recording and complement each other.Jo Henssen, BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE MAIN CADASTRAL SYSTEMS IN THE WORLD, Implementations Americas Canada Falkland Islands The Falkland Islands registry holds copies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easement
An easement is a nonpossessory right to use and/or enter onto the real property of another without possessing it. It is "best typified in the right of way which one landowner, A, may enjoy over the land of another, B". An easement is a property right and type of incorporeal property in itself at common law in most jurisdictions. An easement is similar to real covenants and equitable servitudes. In the United States, the Restatement (Third) of Property takes steps to merge these concepts as servitudes. Easements are helpful for providing access across two or more pieces of property, allowing individuals to access other properties or a resource, for example to fish in a privately owned pond or to have access to a public beach. The rights of an easement holder vary substantially among jurisdictions. Types Historically, common law courts would enforce only four types of easement: * Right-of-way (easements of way) * Easements of support (pertaining to excavations) * Easemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenant (law)
A covenant, in its most general sense and historical sense, is a solemn promise to engage in or refrain from a specified action. Under historical English common law, a covenant was distinguished from an ordinary contract by the presence of a seal. Because the presence of a seal indicated an unusual solemnity in the promises made in a covenant, the common law would enforce a covenant even in the absence of consideration. In United States contract law, an implied ''covenant'' of good faith is presumed. A covenant is an agreement like a contract. The covenantor makes a promise to a covenantee to perform an action ''(affirmative covenant'' in the United States or ''positive covenant'' in England and Wales) or to refrain from an action (negative covenant). In real property law, the term ''real covenants'' means that conditions are tied to the ownership or use of land. A "covenant running with the land", meeting tests of wording and circumstances laid down in precedent, imposes duti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Land
Alienated Real property, land is that which has been acquired from customary landowners by the government, either for its own use or for private development requiring a mortgage or other forms of guarantees. The term refers historically to the appropriation of customary land by European colonialism, colonial powers. Land was alienated in all colonies.it is set aside to be used for certain projects See also *Alienation (property law) *Land rights *Aboriginal land claim Property law {{law-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |