|
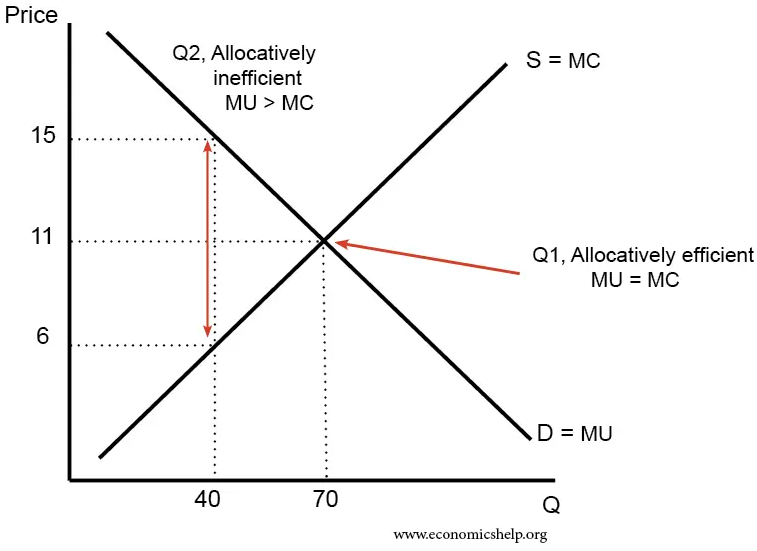
Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with consumer preferences; in particular, every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a marginal benefit to consumers equal to the marginal cost of producing. Description In contract theory, allocative efficiency is achieved in a contract in which the skill demanded by the offering party and the skill of the agreeing party are the same. Resource allocation efficiency includes two aspects: # At the macro aspect, it is the allocation efficiency of social resources, which is achieved through the economic system arrangements of the entire society. # The micro aspect is the use efficiency of resources, which can be understood as the production efficiency of the organization, which can be improved through innovation and progress within the organizations. Although there are different standards of evaluation for the concept of allocative efficiency, the basic principle ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contract Theory
From a legal point of view, a contract is an institutional arrangement for the way in which resources flow, which defines the various relationships between the parties to a transaction or limits the rights and obligations of the parties. From an economic perspective, contract theory studies how economic actors can and do construct contractual arrangements, generally in the presence of information asymmetry. Because of its connections with both agency and incentives, contract theory is often categorized within a field known as law and economics. One prominent application of it is the design of optimal schemes of managerial compensation. In the field of economics, the first formal treatment of this topic was given by Kenneth Arrow in the 1960s. In 2016, Oliver Hart and Bengt R. Holmström both received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for their work on contract theory, covering many topics from CEO pay to privatizations. Holmström (MIT) focused more on the connectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale University Press publishes approximately 300 new hardcover and 150 new paperback books annually and has a backlist of about 5,000 books in print. Its books have won five National Book Awards, two National Book Critics Circle Awards and eight Pulitzer Prizes. The press maintains offices in New Haven, Connecticut and London, England. Yale is the only American university press with a full-scale publishing operation in Europe. It was a co-founder of the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Harvard University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Series and publishing programs Yale Series of Younger Poets Since its inception in 1919, the Yale Series of Younger Poets Competition has published the first collection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-inefficiency
X-inefficiency is the divergence of a firm’s observed behavior in practice, influenced by a lack of competitive pressure, from efficient behavior assumed or implied by economic theory. The concept of X-inefficiency was introduced by Harvey Leibenstein. X-Inefficiency is introduced in 1966 by the professor of Harvard University, Harvey Leibenstein's publication in the ''American Economic Review,'' named "Allocative efficiency vs. X efficiency". X-Inefficiency refer to the firm's production that fails to make full use of its resources, resulting reaches to the maximum possible level of output given the existing resources and environment, namely the efficiency frontier. X-inefficiency pin out irrational actions performed by firms in the market. Overview The difference between the actual and minimum cost of production for a given output produces X-inefficiency. Companies will incur X-Inefficiency as a result of lack of motivation to control its costs, which brings the average cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productive Efficiency
In microeconomic theory, productive efficiency (or production efficiency) is a situation in which the economy or an economic system (e.g., bank, hospital, industry, country) operating within the constraints of current industrial technology cannot increase production of one good without sacrificing production of another good. In simple terms, the concept is illustrated on a production possibility frontier (PPF), where all points on the curve are points of productive efficiency. An equilibrium may be productively efficient without being allocatively efficient — i.e. it may result in a distribution of goods where social welfare is not maximized (bearing in mind that social welfare is a nebulous objective function subject to political controversy). Productive efficiency is an aspect of economic efficiency that focuses on how to maximize output of a chosen product portfolio, without concern for whether your product portfolio is making goods in the right proportion; in misguided a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Market Efficiency
There are several concepts of efficiency for a financial market. The most widely discussed is informational or price efficiency, which is a measure of how quickly and completely the price of a single asset reflects available information about the asset's value. Other concepts include functional/operational efficiency, which is inversely related to the costs that investors bear for making transactions, and allocative efficiency, which is a measure of how far a market channels funds from ultimate lenders to ultimate borrowers in such a way that the funds are used in the most productive manner. Market efficiency types Three common types of market efficiency are allocative, operational and informational. However, other kinds of market efficiency are also recognised. James Tobin identified four efficiency types that could be present in a financial market: 1. Information arbitrage efficiency Asset prices fully reflect all of the privately available information (the least demanding r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin Sickles
Robin C. Sickles is an American economist. Life and work He has worked extensively in modeling productivity and efficiency and health outcomes and risk factors that impact health. His research provides new methodological approaches to model and measure complicated economic behaviors and outcomes. His work also focuses on the role that econometrics plays in policy issues, such as market regulation, market transition, and deterrence versus preventive measures in the criminal justice system. After graduating from Georgia Institute of Technology in 1972 (B.S., Economics), he earned a Ph.D. in Economics in 1976 from the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. He is the Reginald Henry Hargrove Chair in Economics Emeritus and Professor Statistics Emeritus at Rice University. He is a Fellow of the Journal of Econometrics and the International Association of Applied Econometrics, has served as the Editor-in-Chief for the Journal of Productivity Analysis, and has held positions as Asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FT Press
Financial Times Press in the United States and Financial Times Publishing in the United Kingdom are the book publishing imprints related to the ''Financial Times'' newspaper. The book imprints are owned by Pearson plc, a global publishing company which formerly also owned the newspaper. FT Press/Publishing creates books in the areas of General Business, Finance and Investing, Sales and Marketing, Leadership, Management and Strategy, Human Resources, and Global Business. FT Press is also the publishing partner for Wharton School Publishing. When ''Financial Times'' was sold to Nikkei, Inc. in 2015, Pearson retained the book publishing imprints of ''FT'' and licensed the ''FT'' trademark from Nikkei. FTPress.com is one of three websites of the InformIT Network. This site features free articles, blogs, and podcasts on business topics, as well as a bookstore carrying all FT Press and Wharton School Publishing titles in print and electronic formats. FT Press and Wharton School P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Saddle River, NJ
Upper Saddle River is a borough in Bergen County, New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 8,208,DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Upper Saddle River borough, Bergen County, New Jersey , . Accessed February 16, 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |