|
Alhagi
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Baikonur 07
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including ''Coleophora, Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic language, Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian language, Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Canescens
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Baikonur 06
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Sparsifolia
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Nepalensis
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Kirghisorum
''Alhagi'' is a genus of Old World plants in the family Fabaceae. They are commonly called camelthorns or manna trees. There are three to five species. ''Alhagi'' species have proportionally the deepest root system of any plants - a 1 m high shrub may have a main root more than 15 m long; due to their deep root system ''Alhagi'' species are drought-avoiding plants that utilize ground water, adapting in that way perfectly to the hyper-arid environment. ''Alhagi'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Coleophora argyrella'' which feeds exclusively on ''A. maurorum''. The genus name comes from the Arabic word for ''pilgrim''. Uses in Traditional Medicine ''Alhagi'' in Persian is "KhareShotor" which means ''thistle of camels'', as camels can eat it with its thorns. As such, it was figured out that the plant can sustain the abdominal organs in severe thirst. In the Middle East, its boiled or distilled juice is used against kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Maurorum
''Alhagi maurorum'' is a species of legume commonly known, variously, as camelthorn, camelthorn-bush, Caspian manna, and Persian mannaplant. This shrub is native to the region extending from the Mediterranean to Russia, but has been introduced to many other areas of the world, including Australia, southern Africa, and the western United States. The perennial plant grows from a massive rhizome system which may extend over six feet into the ground. New shoots can appear over 20 feet from the parent plant. Above the ground, the plant rarely reaches four feet in height. It is a heavily branched, gray-green thicket with long spines along the branches. It bears small, bright pink to maroon pea flowers and small legume pods, which are brown or reddish and constricted between the seeds. The seeds are mottled brown beans. Distribution ''Alhagi maurorum'' is indigenous to temperate and tropical Eurasia and the Middle East, in: Afghanistan; Armenia; Azerbaijan; northwest China; Cyprus; no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhagi Graecorum
''Alhagi graecorum'' is a species of legume commonly known as mannatree or manna tree. Previously it was considered a subspecies of ''Alhagi maurorum ''Alhagi maurorum'' is a species of legume commonly known, variously, as camelthorn, camelthorn-bush, Caspian manna, and Persian mannaplant. This shrub is native to the region extending from the Mediterranean to Russia, but has been introduced ...''. Drought-tolerant, it is found in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q12222306 Hedysareae Flora of Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedysareae
Hedysareae is a tribe of plants in the subfamily Faboideae. Hedysareae species have loments, a type of modified legume that breaks apart at constrictions occurring between the segments of the seeds. Genera The tribe consists of the following genera: Caraganean Clade * ''Calophaca'' Fisch. ex DC. * ''Caragana'' Fabr. * ''Halimodendron'' Fisch. ex DC. Chesneyean Clade * ''Chesneya'' Lindl. ex Endl. * '' Gueldenstaedtia'' Fisch. * '' Spongiocarpella'' Yakovlev & N. Ulziykh. * '' Tibetia'' (Ali) H. P. Tsui Hedysaroid Clade * ''Alhagi'' Gagnebin * ''Corethrodendron'' Fisch. ex Bashiner * ''Ebenus'' L. * ''Eversmannia'' Bunge * ''Greuteria'' Amirahmadi & Kaz. Osaloo. * ''Hedysarum'' L. * ''Onobrychis'' Mill. * ''Sartoria'' Boiss. & Heldr. * ''Sulla'' Medik. * ''Taverniera'' DC. Systematics Molecular phylogenetics Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faboideae
The Faboideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. An acceptable alternative name for the subfamily is Papilionoideae, or Papilionaceae when this group of plants is treated as a family. This subfamily is widely distributed, and members are adapted to a wide variety of environments. Faboideae may be trees, shrubs, or herbaceous plants. Members include the pea, the sweet pea, the laburnum, and other legumes. The pea-shaped flowers are characteristic of the Faboideae subfamily and root nodulation is very common. Genera The type genus, ''Faba'', is a synonym of ''Vicia'', and is listed here as ''Vicia''. *''Abrus'' *''Acmispon'' *''Acosmium'' *'' Adenocarpus'' *'' Adenodolichos'' *'' Adesmia'' *'' Aenictophyton'' *''Aeschynomene'' *'' Afgekia'' *''Aganope'' *'' Airyantha'' *''Aldina'' *''Alexa'' *''Alhagi'' *'' Alistilus'' *'' Almaleea'' *'' Alysicarpus'' *'' Amburana'' *''Amicia'' *'' Ammodendron'' *'' Ammopiptanthus'' *'' Ammothamnus'' *'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
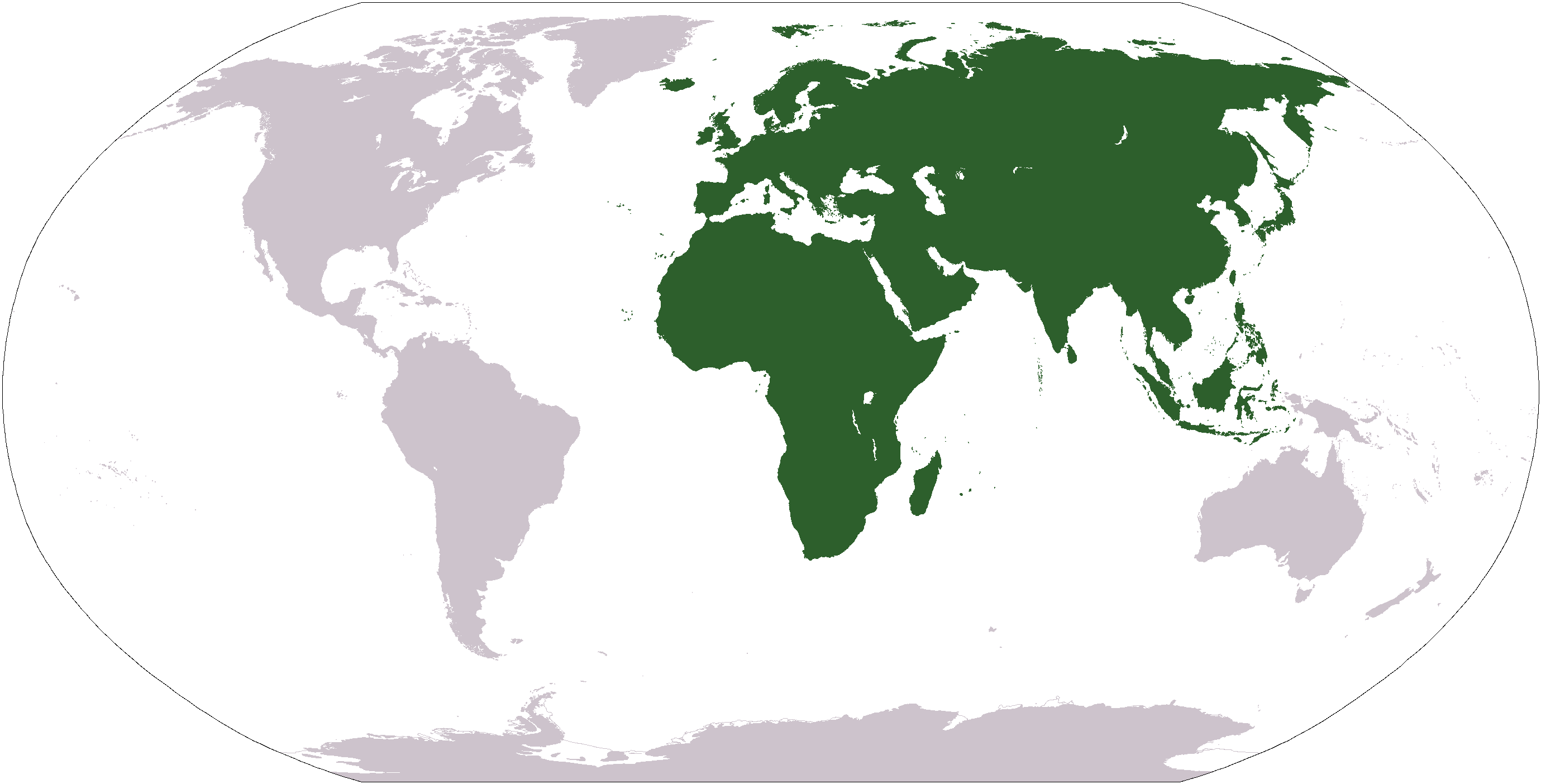
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they have a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |