|
Aerial Cable
An aerial cable or air cable is an insulated cable usually containing all conductors required for an electrical distribution system (typically using aerial bundled cables) or a telecommunication line, which is suspended between utility poles or electricity pylons. As aerial cables are completely insulated there is no danger of electric shock when touching them and there is no requirement for mounting them with insulators on pylons and poles. A further advantage is they require less right of way than overhead lines for the same reason. They can be designed as shielded cables for telecommunication purposes. If the cable falls, it may still operate if its insulation is not damaged. As aerial cables are installed on pylons or poles, they may be cheaper to install than underground cables, as no work for digging is required, which can be very expensive in rocky areas. Use Aerial cables are mostly used for telecommunication systems or for power transmissions with voltages bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is generated by the flow of negatively charged electrons, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases. In order for current to flow within a closed electrical circuit, it is not necessary for one charged particle to travel from the component producing the current (the current source) to those consuming it (the loads). Instead, the charged particle simply needs to nudge its neighbor a finite amount, who will nudge ''its'' neighbor, and on and on until a particle is nudged into the consumer, thus powering it. Essentially what is occurring is a long chain of momentum transfer between mobile charge carriers; the Drude model of conduction describes this process more rigorously. This momentum transfer model makes metal an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Bundled Cable
Aerial bundled cables (also aerial bundled conductors or simply ABC) are overhead power lines using several insulated phase conductors bundled tightly together, usually with a bare neutral conductor. This contrasts with the traditional practice of using uninsulated conductors separated by air gaps. This variation of bundled conductors utilizes the same principles as overhead power lines, except that they are closer together to the point of touching but each conductor is surrounded by an insulating layer (except for the neutral line). The main objections to the traditional design are that the multiple conductors are considered unappealing, and external forces (such as high winds) can cause them to touch and short circuit. The resultant sparks have been a cause of bushfires in drier climates. In the UK where some supplies to rural property are converted to PME/MEN from TT Earthing system concerns have been expressed that the lower conductor alone may be broken, (by high vehicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Pole
A utility pole is a column or post typically made out of wood used to support overhead power lines and various other public utilities, such as electrical cable, optical fiber, fiber optic cable, and related equipment such as Distribution transformer, transformers and street lights. It can be referred to as a transmission pole, telephone pole, telecommunication pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post, depending on its application. A Stobie pole is a multi-purpose pole made of two steel joists held apart by a slab of concrete in the middle, generally found in South Australia. Electrical wires and cables are routed overhead on utility poles as an inexpensive way to keep them insulated from the ground and out of the way of people and vehicles. Utility poles can be made of wood, metal, concrete, or composites like fiberglass. They are used for two different types of power lines: ''sub transmission lines'', which carry higher voltage power between substations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
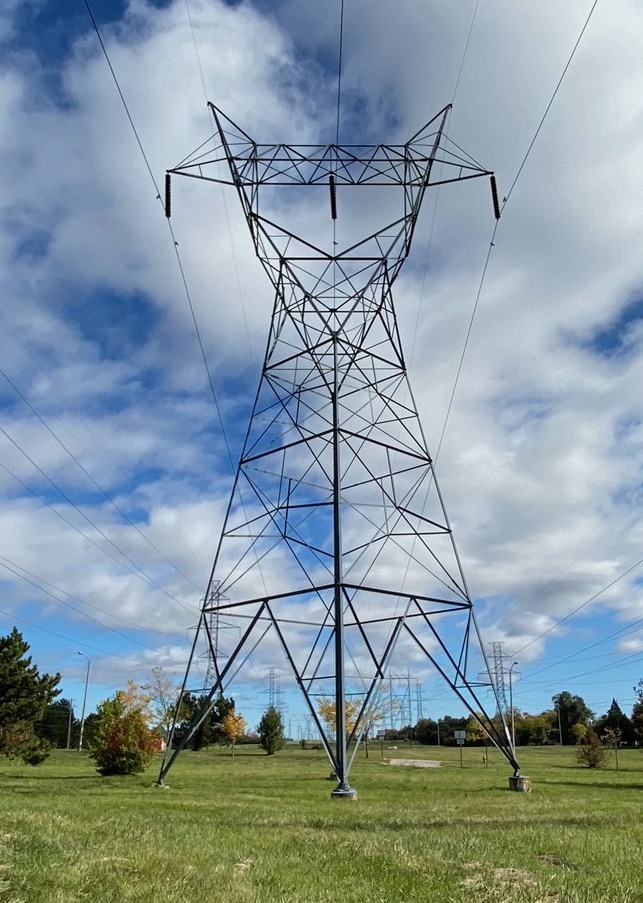
Transmission Tower
A transmission tower, also known as an electricity pylon or simply a pylon in British English and as a hydro tower in Canadian English, is a tall structure, usually a steel lattice tower, used to support an overhead power line. In electrical grids, they are generally used to carry high-voltage transmission lines that transport bulk electric power from generating stations to electrical substations; utility poles are used to support lower-voltage subtransmission and distribution lines that transport power from substations to electric customers. They come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Typical height ranges from , though the tallest are the towers of a span between the islands Jintang and Cezi in China's Zhejiang province. The longest span of any hydroelectric crossing ever built belongs to Ameralik Span, the powerline crossing of Ameralik fjord with a length of . In addition to steel, other materials may be used, including concrete and wood. There are four major categ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Shock
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a light tingling sensation. A shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. Stronger currents may cause some degree of discomfort or pain, while more intense currents may induce involuntary muscle contractions, preventing the person from breaking free of the source of electricity. Still larger currents result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. Consequences of injury from electricity may include amputations, bone fractures and orthopedic and musculoskeletal injuries. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to as electrocution. Electric injury occurs upon contact of a body part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electricity)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges ( charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shielded Cable
A shielded cable or screened cable is an electrical cable that has a common conductive layer around its conductors for electromagnetic shielding. This shield is usually covered by an outermost layer of the cable. Common types of cable shielding can most broadly be categorized as foil type (hereunder: metallised film), contraspiralling wire strands ( braided or unbraided) or both. A longitudinal wire may be necessary with dielectric spiral foils to short out each turn. The shield acts as a Faraday cage – a surface that reflects electromagnetic radiation. This reduces both the interference from outside noise onto the signals and the signals from radiating out and potentially disturbing other devices (see electromagnetic compatibility). To be effective against electric fields (see also capacitive coupling), the shield must be grounded. The shield should be electrically continuous to maximize effectiveness, including any cable splices. For high frequency signals (above a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undergrounding
In civil engineering, undergrounding is the replacement of overhead cables providing electrical power or telecommunications, with underground cables. It helps in wildfire prevention and in making the power lines less susceptible to outages during high winds, thunderstorms or heavy snow or ice storms. An added benefit of undergrounding is the aesthetic quality of the landscape without the powerlines. Undergrounding can increase the capital cost of electric power transmission and distribution but may decrease operating costs over the lifetime of the cables. History Early undergrounding had a basis in the detonation of mining explosives and in undersea telegraph cables. Electric cables were used in Russia to detonate mining explosives in 1812, and to carry telegraph signals across the English Channel in 1850. With the spread of early electrical power systems, undergrounding began to increase as well. Thomas Edison used underground DC “street pipes” in his early distributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Insert
In telecommunications an aerial insert is a segment of cabling that rises from ground to a point above ground, followed by an overhead run, e.g. on poles, followed by a drop back into the ground. An aerial insert is used in places where it is not possible or practical to place a cable underground. Aerial inserts might be encountered in crossing deep ditches, canals, rivers, or subway lines. Aerial inserts can be found for the same reason also in underground power transmission lines. However for this purpose, the aerial insert is in most cases realized as classical overhead line. It is also possible that a powerline consists of multiple underground and overhead sections of different length. See also * Aerial cable An aerial cable or air cable is an insulated cable usually containing all conductors required for an electrical distribution system (typically using aerial bundled cables) or a telecommunication line, which is suspended between utility poles o ... References T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Power Line
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy across large distances. It consists of one or more uninsulated electrical cables (commonly multiples of three for three-phase power) suspended by towers or poles. Since most of the insulation is provided by the surrounding air, overhead power lines are generally the least costly method of power transmission for large quantities of electric energy. Construction Towers for support of the lines are made of wood either grown or laminated, steel or aluminum (either lattice structures or tubular poles), concrete, and occasionally reinforced plastics. The bare wire conductors on the line are generally made of aluminum (either plain or reinforced with steel or composite materials such as carbon and glass fiber), though some copper wires are used in medium-voltage distribution and low-voltage connections to customer premises. A major goal of overhead power line d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Cables
A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Power cables that are bundled inside thermoplastic sheathing and that are intended to be run inside a building are known as NM-B (nonmetallic sheathed building cable). Flexible power cables are used for portable devices, mobile tools, and machinery. History The first power distribution system developed by Thomas Edison in 1882 in New York City used copper rods, wrapped in jute and placed in rigid pipes filled with a bituminous compound. Although vulcanized rubber had been patented by Charles Goodyear in 1844, it was not applied to cable insulation until the 1880s, when it was used for lighting circuits. Rubber-insulated cable was used for 11,000-volt circuits in 1897 install ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |