|
Adjustable Pressure Limiting Valve
An adjustable pressure-limiting valve (commonly abbreviated to APL valve, and also referred to as an expiratory valve, relief valve or spill valve) is a type of flow control valve used in anaesthesiology as part of a breathing system. It allows excess fresh gas flow Fresh gas flow refers to the mixture of medical gases and volatile anaesthetic agents which is produced by an anaesthetic machine. The flow rate and composition of the fresh gas flow is determined by the anaesthetist. Typically the fresh gas flow ... and exhaled gases to leave the system while preventing ambient air from entering. Mechanism Such valves were first described by the American dentist Jay Heidbrink, who used a thin disc that was held in place by a spring. The valve is adjustable and spring-loaded, allowing the opening pressure of the valve to be controlled by screwing the valve top which modifies the pressure on the spring. A very light spring is used, so that at its minimum setting the valve can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Control Valve
A flow control valve regulates the flow or pressure of a fluid. Control valves normally respond to signals generated by independent devices such as flow meters or temperature gauges. Operation Control valves are normally fitted with actuators and positioners. Pneumatically-actuated globe valves and diaphragm valves are widely used for control purposes in many industries, although quarter-turn types such as (modified) ball and butterfly valves are also used. Control valves can also work with hydraulic actuators (also known as hydraulic pilots). These types of valves are also known as automatic control valves. The hydraulic actuators respond to changes of pressure or flow and will open/close the valve. Automatic control valves do not require an external power source, meaning that the fluid pressure is enough to open and close them. Automatic control valves include pressure reducing valves, flow control valves, back-pressure sustaining valves, altitude valves, and relief val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesiology
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries, the terms are synonymous, while in other countries they refer to different positions, and ''anesthetist'' is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists. The core element of the specialty is the study and use of anesthesia to safely support a patient's vital functions through the perioperative period. Since the 19th century, anesthesiology has developed from an experimental area with non-specialist practitioners using novel, untested drugs and techniques into what is now a highly refined, safe and effective field of medicine. In some countries anesthesiol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathing Circuit
A breathing system or breathing circuit is a medical device used to deliver oxygen, remove carbon dioxide, and deliver inhalational anaesthetic agents to a patient. Originally developed for use in anaesthesiology, many variants of breathing system are in clinical use, but most comprise a source of fresh gas flow, a length of breathing tubing to direct the gas, an adjustable pressure limiting valve to control pressure within the system and direct waste away, and a reservoir bag to allow assisted ventilation. Types There are many forms of breathing system, each having somewhat different mechanisms of action. They have traditionally been classified by the way in which the system interacts with fresh air from the surrounding atmosphere, and by whether the patient rebreathes gases that they have previously exhaled. However, there is no international standard for classifying breathing systems, and the terms "semi-open" and "semi-closed" may cause confusion in particular between US and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresh Gas Flow
Fresh gas flow refers to the mixture of medical gases and volatile anaesthetic agents which is produced by an anaesthetic machine. The flow rate and composition of the fresh gas flow is determined by the anaesthetist. Typically the fresh gas flow emerges from the common gas outlet, a specific outlet on the anaesthetic machine to which the breathing attachment is then connected. Some older forms of breathing attachment, such as the Magill attachment, require high fresh gas flows (e.g. 7 litres/min) to prevent the patient from rebreathing their own expired carbon dioxide. More modern systems, e.g. the circle breathing attachment, use soda lime to absorb carbon dioxide, so that expired gas becomes suitable to re-use. With a very efficient circle system, the fresh gas flow may be reduced to the patient's minimum oxygen requirements (e.g. 250ml/min), plus a little volatile. See also * Anaesthetic vaporiser * Anaesthetic machine * Soda lime Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthetic Equipment
Following is a list of instruments used in the practice of anesthesia __TOC__ Instrument list Anesthetic machine General anesthesia does not always require the anesthetic machine, tested daily, as basic equipment. Anesthesia machines may differ in appearance, size and degree of sophistication but generally speaking, they consist of sections for: * ventilation * Peripheral Nerve Stimulator * space for monitoring equipment * accessories * storage space * worktop It is imperative that essential medical pipeline gas supply, ''e.g.'' oxygen], nitrous oxide and air, are secured firmly to the machine, and readily available without any obstructions, defects or pressure leaks. They should also be checked in between cases, ensuring that the breathing apparatus and breathing circuit are fully patent, for the safe anesthesia of patients. Major manufacturers of anesthetic machines are General Electric (GE), Larsen & Toubro Limited, Draeger and MAQUET. Image gallery Image:Bag valve mask.jpg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Medical And Surgical Specialties
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
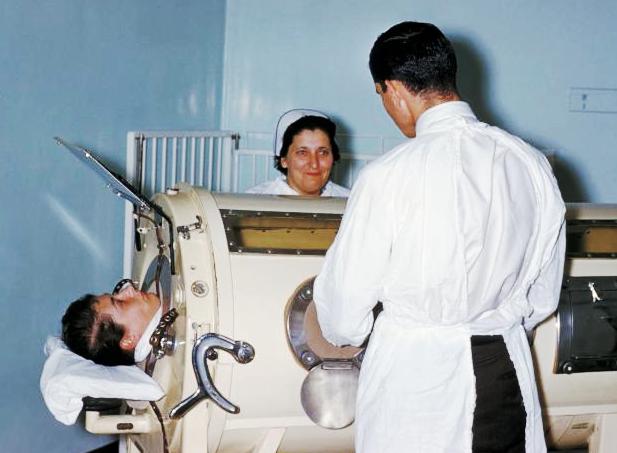
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Valves
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk. Meanings There are two slightly different meanings of ''safety''. For example, ''home safety'' may indicate a building's ability to protect against external harm events (such as weather, home invasion, etc.), or may indicate that its internal installations (such as appliances, stairs, etc.) are safe (not dangerous or harmful) for its inhabitants. Discussions of safety often include mention of related terms. Security is such a term. With time the definitions between these two have often become interchanged, equated, and frequently appear juxtaposed in the same sentence. Readers unfortunately are left to conclude whether they comprise a redundancy. This confuses the uniqueness that should be reserved for each by itself. When seen as unique, as we intend here, each term will a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)