|
Adenomyomatosis
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition characterized by hyperplastic changes of unknown cause involving the wall of the gallbladder. Adenomyomatosis is caused by an overgrowth of the mucosa, thickening of the muscular wall, and formation of intramural diverticula or sinus tracts termed Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses, also called entrapped epithelial crypts. Signs and symptoms Pathophysiology Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses are pseudodiverticula or pockets in the wall of the gallbladder. They may be microscopic or macroscopic. Histologically, they are outpouchings of gallbladder mucosa into the gallbladder muscle layer and subserosal tissue as a result of hyperplasia and herniation of epithelial cells through the fibromuscular layer of the gallbladder wall. Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses are not of themselves considered abnormal but they can be associated with cholecystitis. They form as a result of increased pressure in the gallbladder and recurrent damag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder Disorders
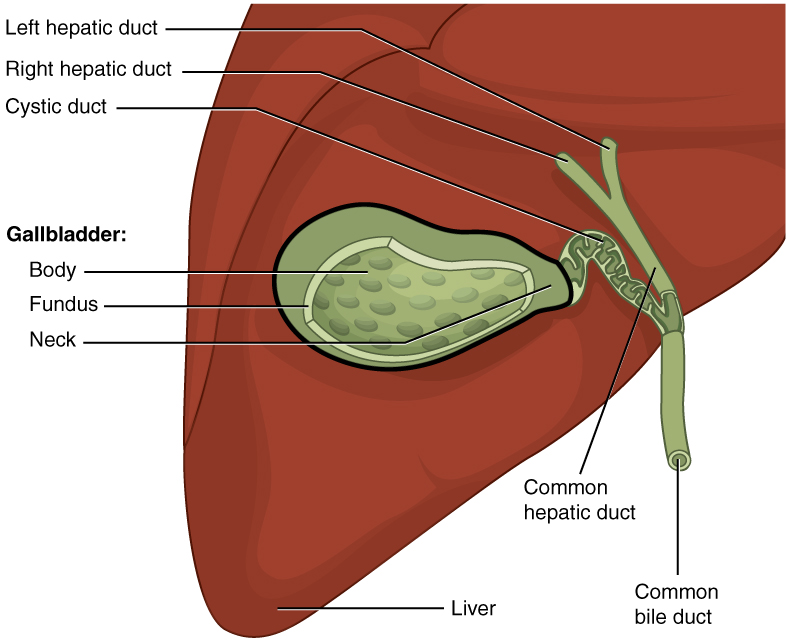
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticulum
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false. In medicine, the term usually implies the structure is not normally present, but in embryology, the term is used for some normal structures arising from others, as for instance the thyroid diverticulum, which arises from the tongue. The word comes from Latin ''dīverticulum'', "bypath" or "byway". Classification Diverticula are described as being true or false depending upon the layers involved: *False diverticula (also known as "pseudodiverticula") do not involve muscular layers or adventitia. False diverticula, in the gastrointestinal tract for instance, involve only the submucosa and mucosa. *True diverticula involve all layers of the structure, including muscularis propria and adventitia, such as Meckel's diverticulum. Embryology *The kidneys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholelithiasis
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts ( cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include pain that lasts longer than five hours, fever, yellowish skin, vomiting, dark urin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound Of Gallbladder Adenomyosis
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
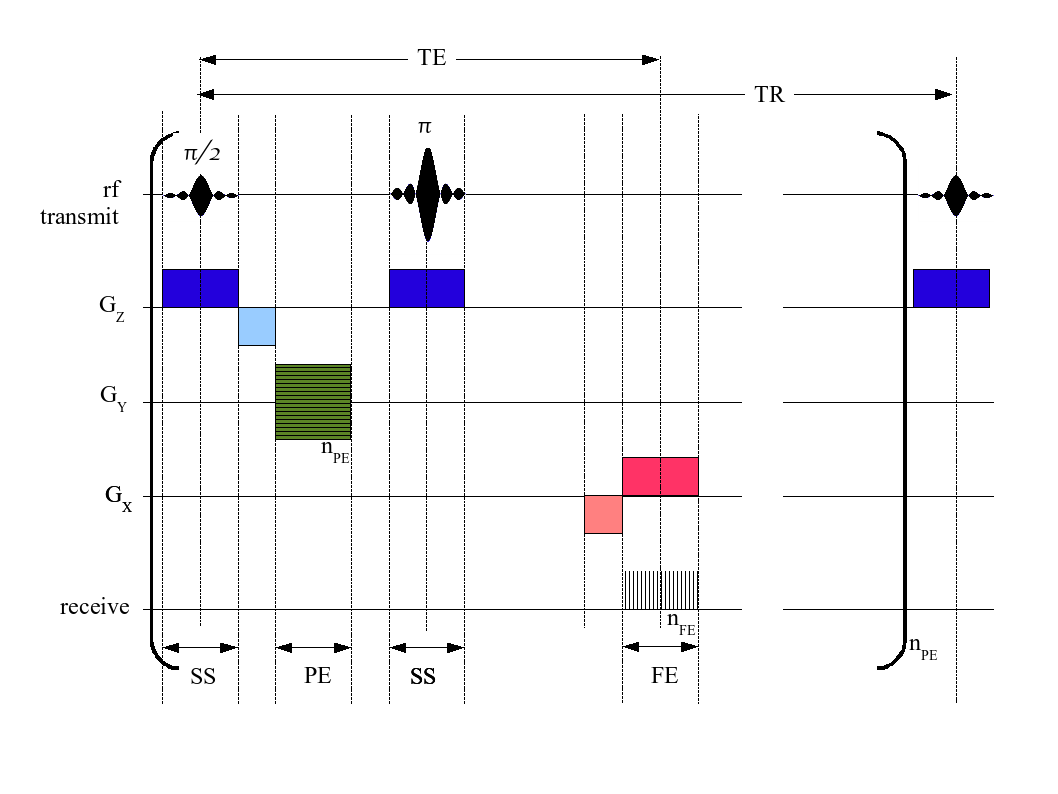
MRI Sequence
An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including other specialized MRI configurations such as spectroscopy. Spin echo T1 and T2 Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent relaxation processes of T1 ( spin-lattice; that is, magnetization in the same direction as the static magnetic field) and T2 ( spin-spin; transverse to the static magnetic field). To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characterizing focal liver lesions, and in general, obtaining morphological information, as well as for post-contrast imaging. To create a T2-weighted image, magnetizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
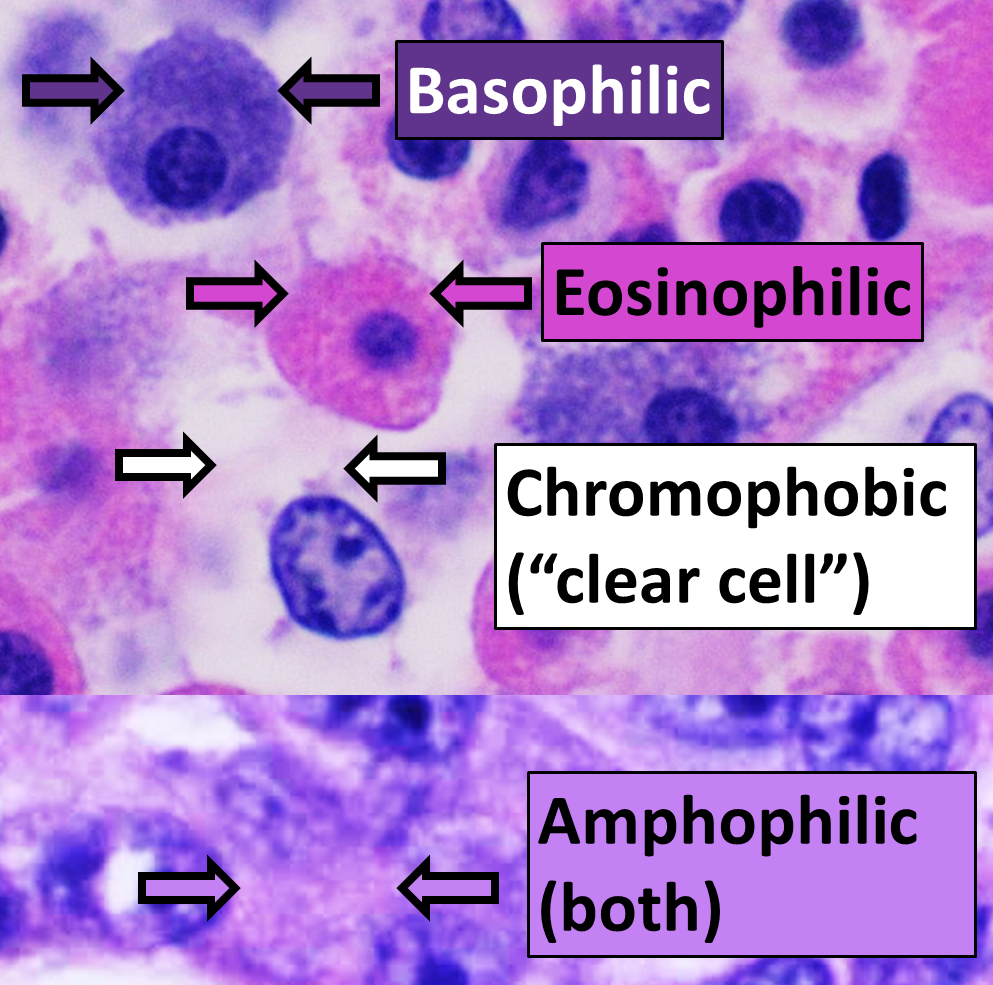
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry Gallbladder
In surgical pathology, strawberry gallbladder, more formally cholesterolosis of the gallbladder and gallbladder cholesterolosis, is a change in the gallbladder wall due to excess cholesterol. - cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk. The name ''strawberry gallbladder'' comes from the typically stippled appearance of the l surface on , which resembles a . Cholesterolosis results from abnormal deposits of cholesterol esters in macrophages with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Aschoff
Karl Albert Ludwig Aschoff (10 January 1866 – 24 June 1942) was a German physician and pathologist. He is considered to be one of the most influential pathologists of the early 20th century and is regarded as the most important German pathologist after Rudolf Virchow. Early life and education Aschoff was born in Berlin, Prussia on 10 January 1866. He studied medicine at the University of Bonn, University of Strasbourg, and the University of Würzburg. Career After his habilitation in 1894, Ludwig Aschoff was appointed professor for pathology at the University of Göttingen in 1901. Aschoff transferred to the University of Marburg in 1903 to head the department for pathological anatomy. In 1906, he accepted a position as ordinarius at the University of Freiburg, where he remained until his death. Aschoff was interested in the pathology and pathophysiology of the heart. He discovered nodules in the myocardium present during rheumatic fever, the so-called Aschoff bodies. Aschoff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |