|
Acid Strength
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. :HA -> H+ + A- Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), perchloric acid (HClO4), nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in equilibrium with each other. :HA H+ + A- Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_\ce value. The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be attached. Acid strength is solvent-dependent. For example, hydrogen chloride is a strong acid in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for acetic acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leveling Effect
Leveling effect or solvent leveling refers to the effect of solvent on the properties of acids and bases. The strength of a strong acid is limited ("leveled") by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly the strength of a strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. When a strong acid is dissolved in water, it reacts with it to form hydronium ion (H3O+).Zumdahl, S. S. “Chemistry” Heath, 1986: Lexington, MA. ISBN 0-669--04529-2. An example of this would be the following reaction, where "HA" is the strong acid: :HA + H2O → A− + H3O+ Any acid that is stronger than H3O+ reacts with H2O to form H3O+. Therefore, no acid stronger than H3O+ exists in H2O. For example, aqueous perchloric acid (HClO4), aqueous hydrochloric acid (HCl) and aqueous nitric acid (HNO3) are all completely ionized, and are all equally strong acids. Similarly, when ammonia is the solvent, the strongest acid is ammonium (NH4+), thus HCl and a super acid exert the same acidifying effect. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Capacity
A buffer solution (more precisely, pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. In nature, there are many living systems that use buffering for pH regulation. For example, the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood, and bicarbonate also acts as a buffer in the ocean. Principles of buffering Buffer solutions resist pH change because of a chemical equilibrium between the weak acid HA and its conjugate base A−: When some strong acid is added to an equilibrium mixture of the weak acid and its conjugate base, hydrogen ions (H+) are added, and the equilibrium is shifted to the left, in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle. Because of this, the hydrogen ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO has the unusual property that many individuals perceive a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO makes contact with their skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Dimethyl sulfoxide is produced industrially from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the Kraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strong Acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. :HA -> H+ + A- Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), perchloric acid (HClO4), nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in equilibrium with each other. :HA H+ + A- Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_\ce value. The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be attached. Acid strength is solvent-dependent. For example, hydrogen chloride is a strong acid in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms. Chemists carefully measure substance proportions, chemical reaction rates, and other chemical properties. In Commonwealth English, pharmacists are often called chemists. Chemists use their knowledge to learn the composition and properties of unfamiliar substances, as well as to reproduce and synthesize large quantities of useful naturally occurring substances and create new artificial substances and useful processes. Chemists may specialize in any number of subdisciplines of chemistry. Materials scientists and metallurgists share much of the same education and skills with chemists. The work of chemists is often related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superacid
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid is a medium in which the chemical potential of the proton is higher than in pure sulfuric acid. Commercially available superacids include trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (), also known as triflic acid, and fluorosulfuric acid (), both of which are about a thousand times stronger (i.e. have more negative ''H''0 values) than sulfuric acid. Most strong superacids are prepared by the combination of a strong Lewis acid and a strong Brønsted acid. A strong superacid of this kind is fluoroantimonic acid. Another group of superacids, the carborane acid group, contains some of the strongest known acids. Finally, when treated with anhydrous acid, zeolites (microporous aluminosilicate minerals) will contain superacidic sites within their pores. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammett Acidity Function
The Hammett acidity function (''H''0) is a measure of acidity that is used for very concentrated solutions of strong acids, including superacids. It was proposed by the physical organic chemist Louis Plack Hammett and is the best-known acidity function used to extend the measure of Brønsted–Lowry acidity beyond the dilute aqueous solutions for which the pH scale is useful. In highly concentrated solutions, simple approximations such as the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation are no longer valid due to the variations of the activity coefficients. The Hammett acidity function is used in fields such as physical organic chemistry for the study of acid-catalyzed reactions, because some of these reactions use acids in very high concentrations, or even neat (pure).Gerrylynn K. Roberts, Colin Archibald Russell. ''Chemical History: Reviews of the Recent Literature''. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2005. . Definition The Hammett acidity function, ''H''0, can replace the pH in concentrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consi .... It is an industrially significant Commodity chemicals, commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It Combustion, ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO has the unusual property that many individuals perceive a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO makes contact with their skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Dimethyl sulfoxide is produced industrially from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the Kraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
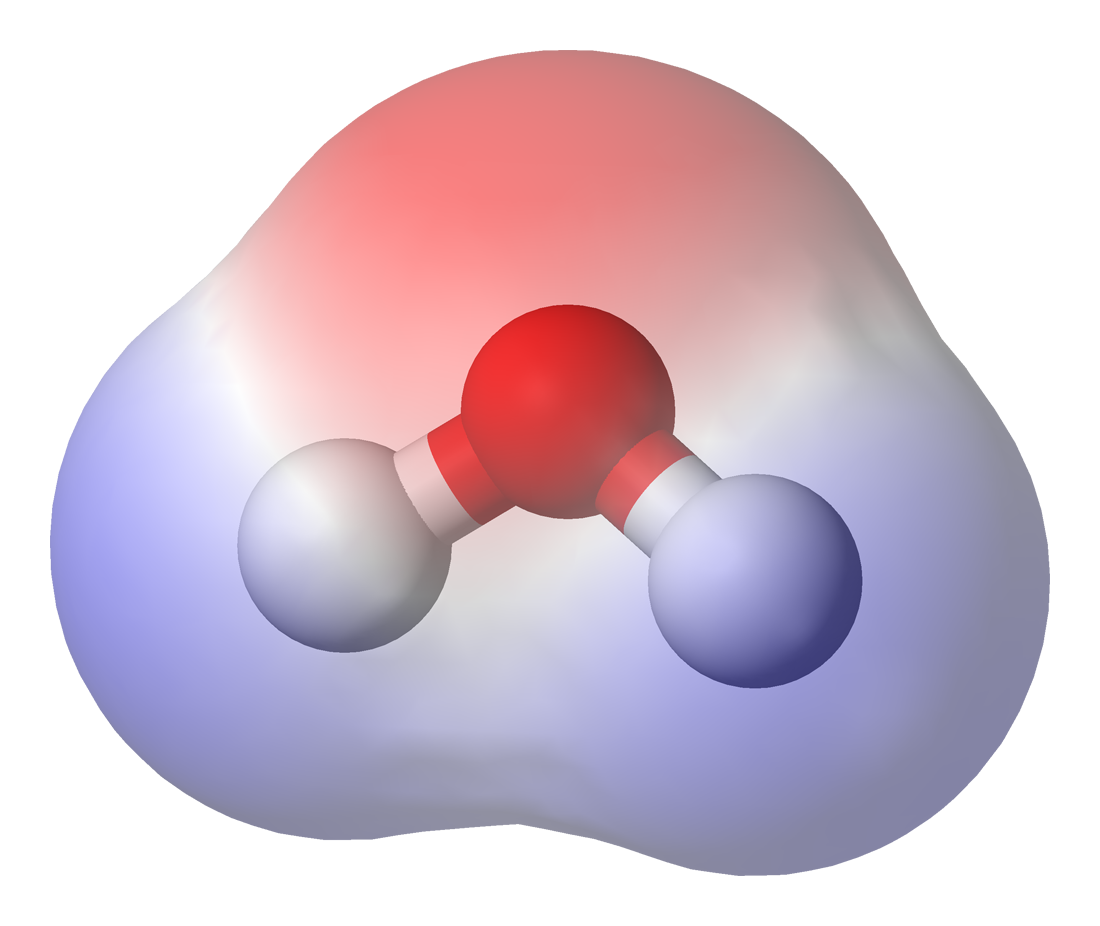
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |