|
Abreugraphy
Chest photofluorography, or abreugraphy (also called mass miniature radiography), is a photofluorography technique for mass screening for tuberculosis using a miniature (50 to 100 mm) photograph of the screen of an X-ray fluoroscopy of the thorax, first developed in 1936. History Abreugraphy receives its name from its inventor, Dr. Manuel Dias de Abreu, a Brazilian physician and pulmonologist. It has received several different names, according to the country where it was adopted: mass radiography, miniature chest radiograph (United Kingdom and United States), roentgenfluorography (Germany), radiophotography (France), schermografia (Italy), photoradioscopy (Spain) and photofluorography (Sweden). In many countries, miniature mass radiographs (MMR) was quickly adopted and extensively utilized in the 1950s. For example, in Brazil and in Japan, tuberculosis prevention laws went into effect, obligating ca. 60% of the population to undergo MMR screening. A model of a mass radiograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Dias De Abreu
Manuel Dias de Abreu (January 4, 1894 – January 30, 1962) was a Brazilian physician and scientist, the inventor of ''abreugraphy'', a rapid radiography of the lungs for screening tuberculosis. He is considered one of the most important Brazilian physicians, side by side with Carlos Chagas, Vital Brazil and Oswaldo Cruz. Early career Abreu was born in São Paulo, Brazil, and obtained his M.D. in medicine at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro in 1914. Shortly afterwards, he travelled to France, where he first worked in the service of Dr. Louis Gaston, at the Nouvel Hôpital de la Pitié, in 1915. Charged with photographing surgical pathology specimens, Abreu quickly developed new and better devices and methods for this. In 1916, Abreu started to work at the Hôtel-Dieu and had his first contact with medical radiography, which had been discovered by the German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen just 20 years before. He became the director of the laboratory of radiology of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abreugraphy
Chest photofluorography, or abreugraphy (also called mass miniature radiography), is a photofluorography technique for mass screening for tuberculosis using a miniature (50 to 100 mm) photograph of the screen of an X-ray fluoroscopy of the thorax, first developed in 1936. History Abreugraphy receives its name from its inventor, Dr. Manuel Dias de Abreu, a Brazilian physician and pulmonologist. It has received several different names, according to the country where it was adopted: mass radiography, miniature chest radiograph (United Kingdom and United States), roentgenfluorography (Germany), radiophotography (France), schermografia (Italy), photoradioscopy (Spain) and photofluorography (Sweden). In many countries, miniature mass radiographs (MMR) was quickly adopted and extensively utilized in the 1950s. For example, in Brazil and in Japan, tuberculosis prevention laws went into effect, obligating ca. 60% of the population to undergo MMR screening. A model of a mass radiograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photofluorography
Photofluorography (sometimes called just fluorography) is photography of X-ray images from a fluorescence, fluorescent screen. It is commonly used in some countries for chest X-ray screening, e.g. to diagnose tuberculosis (see Abreugraphy for more information on such usage of this technique). Method of image formation in photofluorography X-ray beams from the tube get attenuation, attenuated by the patient producing a transmitted intensity (physics), radiation intensity corresponding to the part of the body traversed by the X-ray beam. Transmitted intensities now fall on the photocathode stimulating it to produce electrons in quantities external to the light intensities emitted by the input. This is caused by the formation of a light image of the transmitted radiation pattern. Electrons from the photocathode are accelerated and focused electronically out on the output phosphor which emits light as a result of electron bombardment. This shows a magnified image of what appears on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms bears the motto "Liberté et patrie" on a white-green bicolour. Vaud is the third largest canton of the country by population and fourth by size. It is located in Romandy, the French-speaking western part of the country; and borders the canton of Neuchâtel to the north, the cantons of Fribourg and Bern to the east, the canton of Valais to the south, the canton of Geneva to the south-west and France to the west. The geography of the canton includes all three natural regions of Switzerland: the Jura Mountains, the Swiss Plateau and the (Swiss) Alps. It also includes some of the largest lakes of the country: Lake Geneva and Lake Neuchâtel. It is a major tourist destination, renowned for its landscapes and gastronomy. The largest city is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm. Fluoroscopy is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
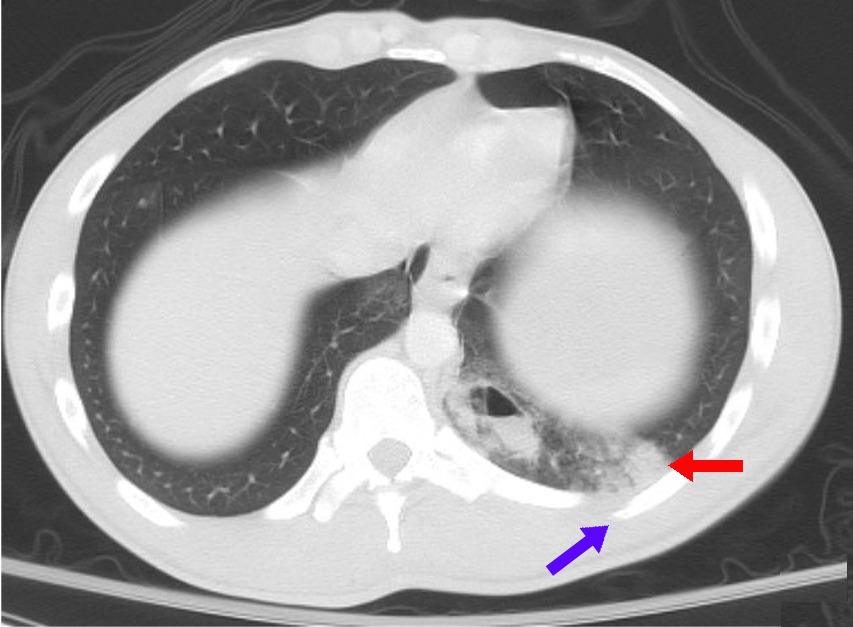
Tuberculosis Radiology
Radiology (X-rays) is used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Abnormalities on chest radiographs may be suggestive of, but are never diagnostic of TB, but can be used to rule out pulmonary TB. Chest X-ray A posterior-anterior (PA) chest X-ray is the standard view used; other views (lateral or lordotic) or CT scans may be necessary. In active pulmonary TB, infiltrates or consolidations and/or cavities are often seen in the upper lungs with or without mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007). ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 516-522 However, lesions may appear anywhere in the lungs. In HIV and other immunosuppressed persons, any abnormality may indicate TB or the chest X-ray may even appear entirely normal. Old healed tuberculosis usually presents as pulmonary nodules in the hilar area or upper lobes, with or without fibrotic scars and volume loss. Bronchiectasis and pleural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Radiography
Digital radiography is a form of radiography that uses x-ray–sensitive plates to directly capture data during the patient examination, immediately transferring it to a computer system without the use of an intermediate cassette. Advantages include time efficiency through bypassing chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images. Also, less radiation can be used to produce an image of similar contrast to conventional radiography. Instead of X-ray film, digital radiography uses a digital image capture device. This gives advantages of immediate image preview and availability; elimination of costly film processing steps; a wider dynamic range, which makes it more forgiving for over- and under-exposure; as well as the ability to apply special image processing techniques that enhance overall display quality of the image. Detectors Flat panel detectors 250px, Flat panel detector used in digital radiography Flat panel detectors (FPDs) are the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Drug
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or Subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous location). Intravenous therapy, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. , there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries. A wide variety of drugs are injected, often opioids: these may include legally prescribed medicines and medication such as morphine, as well as stronger compounds often favored in recreational drug use, which are often illegal. Although there are various methods of taking drugs, injection is favoured by some people as the full effects of the drug are experienced very quickly, typically in five to ten seconds. It also bypasses first pass effect, first-pass metabolism in the liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to people of the same sex. It "also refers to a person's sense of identity based on those attractions, related behaviors, and membership in a community of others who share those attractions." Along with bisexuality and heterosexuality, homosexuality is one of the three main categories of sexual orientation within the heterosexual–homosexual continuum. Scientists do not yet know the exact cause of sexual orientation, but they theorize that it is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental influences and do not view it as a choice. Although no single theory on the cause of sexual orientation has yet gained widespread support, scientists favor biologically based theories. There is considerably more evidence supportin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
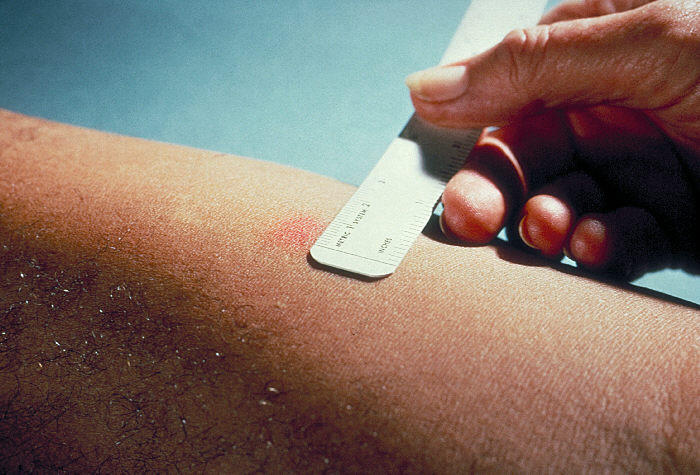
Tuberculin Skin Test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states. History Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules obtained from filtrates of sterilized, concentrated cultures. The tuberculin reaction was first described by Robert Koch in 1890. The test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |