|
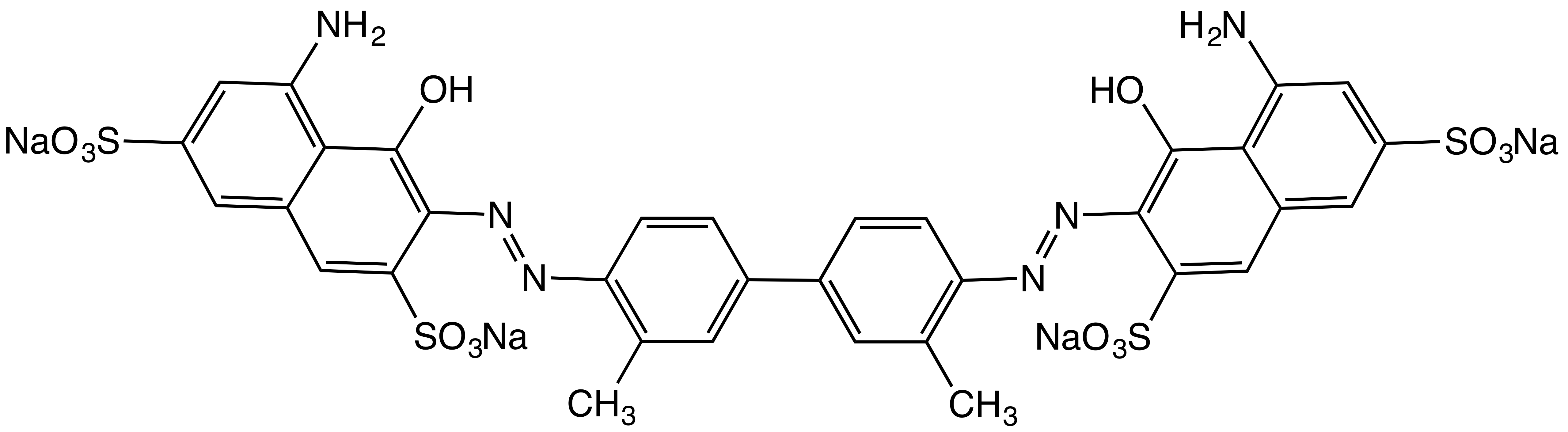
Azorubine
Azorubine is an azo dye consisting of two naphthalene subunits. It is a red solid. It is mainly used in foods that are heat-treated after fermentation. It has E number E122. Uses In the US, this color was listed in 1939 as FD&C Red No. 10 for use in externally applied drugs and cosmetics. It was delisted in 1963 because no party was interested in supporting the studies needed to establish safety. It was not used in food in the US.FDABackground Document for the Food Advisory Committee: Certified Color Additives in Food and Possible Association with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children: March 30-31, 2011/ref>FDA. 9 November 2008Food and Drug Administration, Compliance Program Guidance Manual, Chapter 03 - Foodborne Biological Hazardsp37 In the EU, azorubine is known as E number E122, and is authorized for use in certain foods and beverages, such as cheeses, dried fruit, and some alcoholic beverages, and is permitted for use as an excipient in medications. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is best known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two fused benzene rings was proposed by Emil Erlenmeye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Number
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today. Having a single unified list for food additives was first agreed upon in 1962 with food colouring. In 1964, the directives for preservatives were added, in 1970 antioxidants were added, in 1974 emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents were added as well. Numbering schemes The numbering scheme follows that of the International Numbering System (INS) as determined by the '' Codex Alimentarius'' committee, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excipient
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication, included for the purpose of long-term stabilization, bulking up solid formulations that contain potent active ingredients in small amounts (thus often referred to as "bulking agents", "fillers", or "diluents"), or to confer a therapeutic enhancement on the active ingredient in the final dosage form, such as facilitating drug absorption, reducing viscosity, or enhancing solubility. Excipients can also be useful in the manufacturing process, to aid in the handling of the active substance concerns such as by facilitating powder flowability or non-stick properties, in addition to aiding ''in vitro'' stability such as prevention of denaturation or aggregation over the expected shelf life. The selection of appropriate excipients also depends upon the route of administration and the dosage form, as well as the active ingredient and other factors. A comprehensive classification system based on structure- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Alimentarius
The Codex Alimentarius () is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations relating to food, food production, food labeling, and food safety. History and governance Its name is derived from the Codex Alimentarius Austriacus. Its texts are developed and maintained by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), a body established in early November 1961 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), was joined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in June 1962, and held its first session in Rome in October 1963. The Commission's main goals are to protect the health of consumers, to facilitate international trade, and ensure fair practices in the international food trade.Understanding Codex', World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (5th ed. Sept. 2018). The CAC is an intergov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceptable Daily Intake
Acceptable daily intake or ADI is a measure of the amount of a specific substance (originally applied for a food additive, later also for a residue of a veterinary drug or pesticide) in food or drinking water that can be ingested (orally) daily over a lifetime without an appreciable health risk. ADIs are expressed usually in milligrams (of the substance) per kilograms of body weight per day. History This concept was first introduced in 1961 by the Council of Europe and later, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), a committee maintained by two United Nations bodies: the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). Concept An ADI value is based on current research, with long-term studies on animals and observations of humans. First, a no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL), the amount of a substance that shows no toxic effects, is determined. Usually the studies are performed with several doses including high doses. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Intolerance
Food intolerance is a detrimental reaction, often delayed, to a food, beverage, food additive, or compound found in foods that produces symptoms in one or more body organs and systems, but generally refers to reactions other than food allergy. Food hypersensitivity is used to refer broadly to both food intolerances and food allergies. Food allergies are immune reactions, typically an IgE reaction caused by the release of histamine but also encompassing non-IgE immune responses. This mechanism causes allergies to typically give immediate reaction (a few minutes to a few hours) to foods. Food intolerances can be classified according to their mechanism. Intolerance can result from the absence of specific chemicals or enzymes needed to digest a food substance, as in hereditary fructose intolerance. It may be a result of an abnormality in the body's ability to absorb nutrients, as occurs in fructose malabsorption. Food intolerance reactions can occur to naturally occurring chemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction, and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society. Although people with ADHD struggle to focus on tasks they are not particularly interested in completing, they are often able to maintain an unusually prolonged and intense level of attention for tasks they do find interesting or rewarding; this is known as hyperfocus. The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases. Genetic factors play an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Colorings
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food production and domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in a variety of non-food applications, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices. Purpose of food coloring People associate certain colors with certain flavors, and the color of food can influence the perceived flavor in anything from candy to wine. Sometimes, the aim is to simulate a color that is perceived by the consumer as natural, such as adding red coloring to glacé cherries (which would otherwise be beige), but sometimes it is for effect, like the green ketchup that Heinz launched in 2000. Color additives are used in foods for many reasons including: * To make food more attractive, appealing, appetizing, and informative * Offset col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dyes
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Sodium Salts
Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product of decay, or is composed of organic compounds * Organic compound, a compound that contains carbon ** Organic chemistry, chemistry involving organic compounds Farming, certification and products * Organic farming, agriculture conducted according to certain standards, especially the use of stated methods of fertilization and pest control * Organic certification, accreditation process for producers of organically-farmed products * Organic horticulture, the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture * Organic products, "organics": ** Organic food, food produced from organic farming methods and often certified organic according to organic farming stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalenesulfonates
Naphthalenesulfonates are derivatives of sulfonic acid which contain a naphthalene functional unit. A related family of compounds are the aminonaphthalenesulfonic acids. Of commercial importance are the alkylnaphthalene sulfonates, which are used as superplasticizers in concrete. They are produced on a large scale by condensation of naphthalenesulfonate or alkylnaphthalenesulfonates with formaldehyde. Examples include: * amaranth dye * amido black * armstrong's acid * congo red * Evans blue * suramin * trypan blue Trypan blue is an azo dye. It is a direct dye for cotton textiles. In biosciences, it is used as a vital stain to selectively colour dead tissues or cells blue. Live cells or tissues with intact cell membranes are not coloured. Since cells ... References External links * Naphthalenesulfonates {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |