|
Azaspirodecanedione
Azaspirodecanedione is a chemical compound. It is a component of the chemical structures of several of the azapirones. See also * Azapirone * Azaspirodecane * Glutarimide * Ketone In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ... * Spirodecanedione Azapirones Imides Cyclopentanes Spiro compounds {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azaspirodecane
Azaspirodecane is a chemical compound. It is the core structure of the azaspirodecanedione moiety found in some of the azapirones. See also * Azaspirodecanedione * Azapirone Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Medical uses Azapirones have shown ... {{organic-compound-stub Azapirones Cyclopentanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
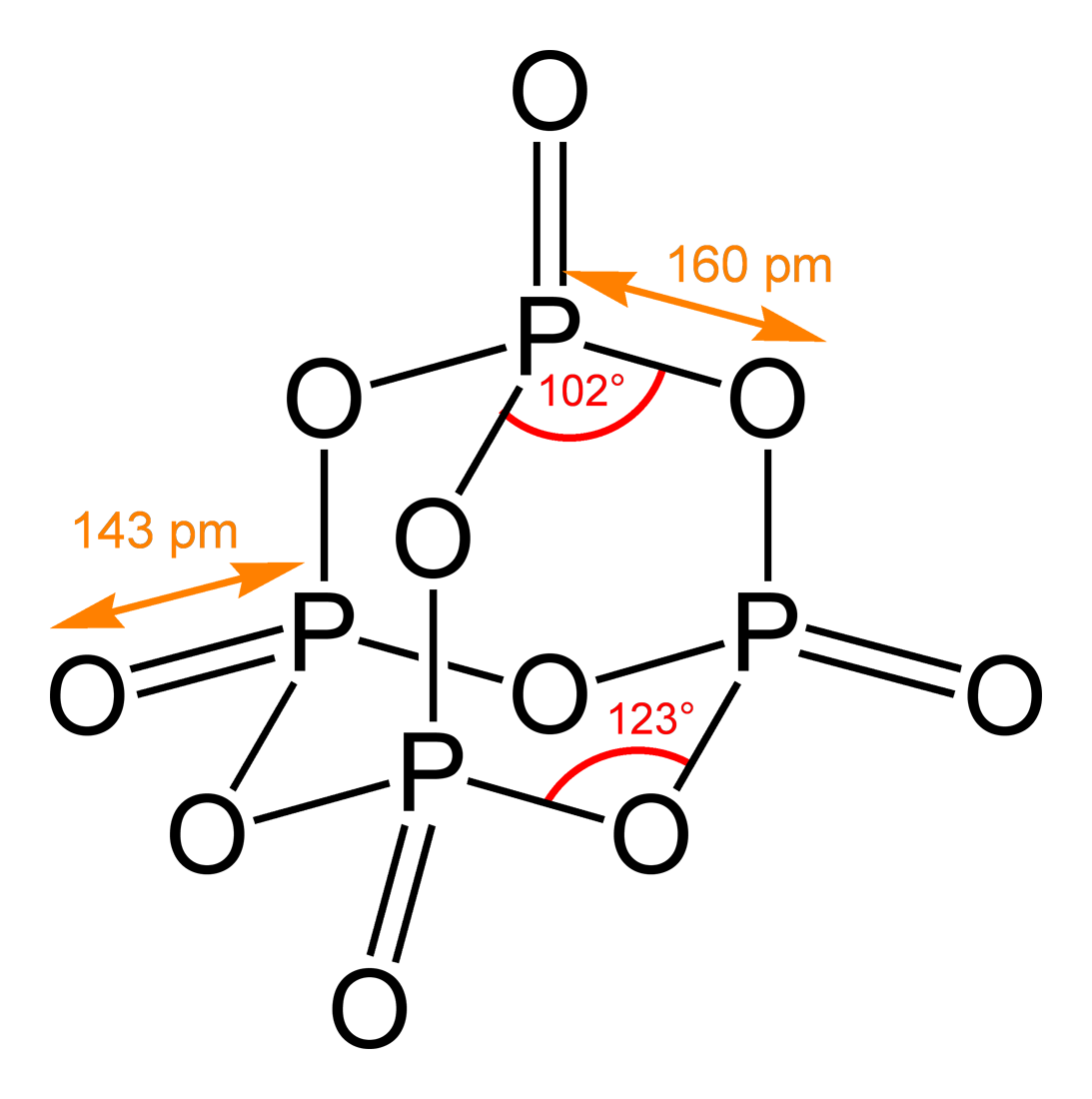
Spirodecanedione
Spirodecanedione is a chemical compound. It features spirodecane with two ketones attached. See also * Spirodecane * Azaspirodecanedione * Glutarimide * Ketone In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ... References {{ketone-stub Diketones Spiro compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azapirone
Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Medical uses Azapirones have shown benefit in general anxiety and augmenting SSRIs in social anxiety and depression. Evidence is not clear for panic disorder and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Tandospirone has also been used to augment antipsychotics in Japan as it improves cognitive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Buspirone is being investigated for this purpose as well. Gepirone was abandoned after FDA rejection. Side effects Side effects of azapirones may include dizziness, headaches, restlessness, nausea, and diarrhea. Azapirones have more tolerable adverse effects than many other available anxiolytics, such as benzodiazepines or SSRIs. Unlike benzodiazepines, azapirones lack abuse potential and are not addictive, do not cause cognitive/memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azapirone
Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Medical uses Azapirones have shown benefit in general anxiety and augmenting SSRIs in social anxiety and depression. Evidence is not clear for panic disorder and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Tandospirone has also been used to augment antipsychotics in Japan as it improves cognitive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Buspirone is being investigated for this purpose as well. Gepirone was abandoned after FDA rejection. Side effects Side effects of azapirones may include dizziness, headaches, restlessness, nausea, and diarrhea. Azapirones have more tolerable adverse effects than many other available anxiolytics, such as benzodiazepines or SSRIs. Unlike benzodiazepines, azapirones lack abuse potential and are not addictive, do not cause cognitive/memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutarimide
Glutarimide is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(CO)2NH. It is a white solid. The compound forms upon dehydration of the amide of glutaric acid. Glutarimide is sometimes called 2,6-piperidinedione. It is the core of a variety of medication, drugs, including thalidomide, a medication used to treat multiple myeloma and leprosy, and cycloheximide, a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. References Glutarimides, {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imides
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called polyimides. Inorganic imides are also known as solid state or gaseous compounds, and the imido group (=NH) can also act as a ligand. Nomenclature Most imides are cyclic compounds derived from dicarboxylic acids, and their names reflect the parent acid. Examples are succinimide, derived from succinic acid, and phthalimide, derived from phthalic acid. For imides derived from amines (as opposed to ammonia), the ''N''-substituent is indicated by a prefix. For example, N-ethylsuccinimide is derived from succinic acid and ethylamine. Isoimides are isomeric with normal imides and have the formula RC(O)OC(NR′)R″. They are often intermediates that convert to the more symmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentanes
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occurs as a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its melting point is −94 °C and its boiling point is 49 °C. Cyclopentane is in the class of cycloalkanes, being alkanes that have one or more rings of carbon atoms. It is formed by cracking cyclohexane in the presence of alumina at a high temperature and pressure. It was first prepared in 1893 by the German chemist Johannes Wislicenus. Production, occurrence and use Cycloalkanes are formed by catalytic reforming. For example, when passed over a hot platinum surfact, 2-methylbutane converts into cyclopentane. Cyclopentane has no particular use. No commercial products are made from cyclopentane itself. As a volatile hydrocarbon it is an incidental component of some fuels and blowing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |