|
Axlebox
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axle Box
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axlebox
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Box
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
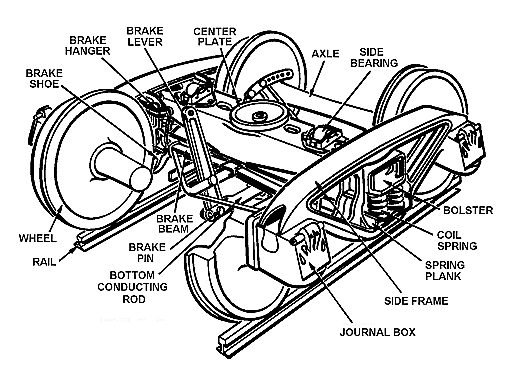
List Of Railroad Truck Parts
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Garratt
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Garratt was a class of Garratt 2-6-0+0-6-2 steam locomotive designed for heavy freight. A total of 33 were built from 1927, making them the most numerous class of Garratt in Britain. Overview After Grouping, the LMS initially continued the Midland Railway's "small engine policy" of hauling trains using two or three locomotives of moderate power coupled together. This led to most of the Toton (Nottinghamshire)- Brent (London) coal trains being double-headed by 0-6-0 locomotives. It was realised that double heading was uneconomical so a Garratt locomotive, designed by Fowler, was ordered from Beyer, Peacock and Company to haul 1450 long tons at 25 mph. However, the LMS Derby design office insisted on, amongst other changes, the fitting of their standard axleboxes to the design. These axleboxes were barely adequate for the LMS Fowler Class 4F locomotives, on which they frequently overheated, and were a major weakness on the LMS Garratts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Bearing
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe. Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity. Design The design of a plain bearing depends on the type of motion the bearing must provide. The three types of motions possible are: * ''Journal'' (''friction'', ''radial'' or ''rotary'') ''bearing'': This is the most common type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain Bearing
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe. Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity. Design The design of a plain bearing depends on the type of motion the bearing must provide. The three types of motions possible are: * ''Journal'' (''friction'', ''radial'' or ''rotary'') ''bearing'': This is the most common type of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain Bearing
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe. Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity. Design The design of a plain bearing depends on the type of motion the bearing must provide. The three types of motions possible are: * ''Journal'' (''friction'', ''radial'' or ''rotary'') ''bearing'': This is the most common type of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transport. A bogie may remain normally attached (as on many railroad cars and semi-trailers) or be quickly detachable (as the dolly in a road train or in railway bogie exchange); it may contain a suspension within it (as most rail and trucking bogies do), or be solid and in turn be suspended (as most bogies of tracked vehicles are); it may be mounted on a swivel, as traditionally on a railway carriage or locomotive, additionally jointed and sprung (as in the landing gear of an airliner), or held in place by other means (centreless bogies). In Scotland, the term is used for a child’s (usually home-made) wooden cart. While ''bogie'' is the preferred spelling and first-listed variant in various dictionaries, bogey and bogy are also used. Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GCR Class 1
The GCR Class 1 was a class of steam locomotives designed by John G. Robinson for the Great Central Railway, and introduced to service between December 1912 and 1913. In the 1923 grouping, they all passed to the London and North Eastern Railway which placed them in class B2. Their classification was changed to B19 in 1945, and all had been retired by the end of 1947. Service Although commonly believed that they were intended as express passenger locomotives, the Great Central actually classified and used them as mixed traffic locomotives. The minutes of the Locomotive Committee show that they were ordered as a superheated version of the 8F (''Immingham'') class mixed traffic locomotives. They were described as mixed traffic locomotives in the contemporary Great Central publication ''Per Rail'', which promoted the company's goods services. When new, three of the class – 423, 425 and 428 – were painted in GCR's standard green passenger livery, while the other three – 424, 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transport. A bogie may remain normally attached (as on many railroad cars and semi-trailers) or be quickly detachable (as the dolly in a road train or in railway bogie exchange); it may contain a suspension within it (as most rail and trucking bogies do), or be solid and in turn be suspended (as most bogies of tracked vehicles are); it may be mounted on a swivel, as traditionally on a railway carriage or locomotive, additionally jointed and sprung (as in the landing gear of an airliner), or held in place by other means (centreless bogies). In Scotland, the term is used for a child’s (usually home-made) wooden cart. While ''bogie'' is the preferred spelling and first-listed variant in various dictionaries, bogey and bogy are also used. Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |