|
Aviation Taxation And Subsidies
Aviation taxation and subsidies includes taxes and subsidies related to aviation. Taxation is one of several methods to mitigate the environmental impact of aviation. Types of taxes * Airport improvement fee, paid by passengers to the airport or government * Air passenger taxes, paid by passengers to the government for environmental reasons; may be variable by distance and includes domestic flights ** Departure tax, paid by passengers leaving the country to the government (sometimes also applies outside of aviation) * Jet fuel tax, paid by airline companies to the government for the jet fuel (kerosene) they burn * Landing fee, paid by airline companies to the airports they land on * Solidarity tax on airplane tickets (Chirac Tax), paid by passengers to Unitaid, a global health initiative against HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis Fuel taxes According to the Amsterdam-based international environmental organisation Friends of the Earth (2005), aviation does not pay t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore Airlines Airbus A380 Woah!
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country, island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor to the north. The country's territory is composed of one Singapore Island, main island, List of islands of Singapore, 63 satellite islands and islets, and Pedra Branca, Singapore, one outlying islet; the combined area of these has increased by 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects. It has the List of countries and dependencies by population density, third highest population density in the world. With a multicultural population and recognising the need to respect cultural identities of the major ethnic groups within the nation, Singapore has four La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The Commission is divided into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or ministries each headed by a Director-General who is responsible to a Commissioner. There is one member per member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the general interest of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. The Commission President (currently Ursula von der Leyen) is proposed by the European Council (the 27 heads of state/governments) and elected by the European Parliament. The Council of the European Union then nominates the other members of the Commission in agreement with the nominated President, and the 27 members as a team are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Carrier
A flag carrier is a transport company, such as an airline or shipping company, that, being locally registered in a given sovereign state, enjoys preferential rights or privileges accorded by the government for international operations. Historically, the term was used to refer to airlines owned by the government of their home country and associated with the national identity of that country. Such an airline may also be known as a national airline or a national carrier, although this can have different legal meanings in some countries. Today, it is any international airline with a strong connection to its home country or that represents its home country internationally, regardless of whether it is government-owned. Flag carriers may also be known as such due to laws requiring aircraft or ships to display the state flag of the country of their registry. For example, under the law of the United States, a U.S. flag air carrier is any airline that holds a certificate under Sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Greens – The Green Alternative
The Greens – The Green Alternative (german: Die Grünen – Die Grüne Alternative, ) is a green political party in Austria. The party was founded in 1986 under the name "Green Alternative" (''Grüne Alternative''), following the merger of the more conservative Green party ''Vereinte Grüne Österreichs'' (United Greens of Austria VGÖ, founded 1982) and the more progressive party ''Alternative Liste Österreichs'' (Alternative List Austria, ALÖ, founded 1982). Since 1993, the party has carried the official name ''Die Grünen – Die Grüne Alternative (Grüne)'', but refers to itself in English as "Austrian Greens". There are still differences between the former members of the old Alternative and VGÖ factions within the party, reflected in the differing approaches of the national and state parties. Apart from ecological issues such as environmental protection, the Greens also campaign for the rights of minorities and advocate a socio-ecological (''ökosozial'') tax reform. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonore Gewessler
Leonore Gewessler (; born 15 September 1977) is an Austrian Green politician serving as Minister of Climate Action, Environment, Energy, Mobility, Innovation and Technology in the government of Chancellor Sebastian Kurz and later Alexander Schallenberg since January 2020. Early life Education Gewessler earned her political science degree (BA) from the University of Vienna. Political career From 2014 until 2019, Gewessler served as head of Austria's largest environmental charity and lobbying group Global 2000. In this capacity, she championed a popular campaign against the expansion of the ageing Soviet-era Mochovce nuclear power plant in neighbouring Slovakia, just 100 km from the Austrian border.Sam Jones (March 2, 2020)Austrian Greens’ ‘super minister’ takes the reins''Financial Times''. In the negotiations on a coalition government following the 2019 national elections, Gewessler was a member of the Green Party’s delegation. References External links Leonore G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Ministry For Climate Action, Environment, Energy, Mobility, Innovation And Technology
The Ministry of Climate Action and Energy () is the government ministry of Austria in charge of traffic, research, innovation, energy, and environmental protection. Overview First established in 1896, its exact name and portfolio have undergone changes numerous times throughout the years. From 2000 to 2020, the ministry was officially called the Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology (''Bundesministerium für Verkehr, Innovation und Technologie'' or ''BMVIT''). It is tasked, in addition to its core regulatory and infrastructure responsibilities, with the promotion of scientific research and technological progress. The ministry regulates motor vehicles, railways, waterways, aviation safety, air traffic control, air weather services, public transport, the postal system, and the telecommunications sector. It maintains the autobahns and other national highways. The Ministry also owns and supervises the via donau, a corporation charged with the maintenance of the Danube a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe, immigrant environmental activists from the United States. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth to nurture life in all its diversity" and focuses its campaigning on worldwide issues such as climate change, deforestation, overfishing, commercial whaling, genetic engineering, and anti-nuclear issues. It uses direct action, lobbying, research, and ecotage to achieve its goals. The network comprises 26 independent national/regional organisations in over 55 countries across Europe, the Americas, Africa, Asia and the Pacific, as well as a co-ordinating body, Greenpeace International, based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. The global network does not accept funding from governments, corporations, or political parties, relying on three million individual supporters and foundation grants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Federation For Transport And Environment
The European Federation for Transport and Environment, commonly referred to as Transport & Environment (T&E), is a European umbrella for non-governmental organisations working in the field of transport and the environment, promoting sustainable transport in Europe; which means an approach to transport that is environmentally responsible, economically sound and socially just. History Since it was founded 30 years ago, T&E has shaped some of Europe's most important environmental laws. It played a key role in getting the EU to set the world's most ambitious standards for cars and trucks and also helped uncover the dieselgate scandal; it campaigned successfully to end palm oil diesel; secured a global ban on dirty shipping fuels and the creation of the world's biggest carbon market for aviation, to name a few. In 2020 T&E's campaigninledUber to commit to electrifying much of its European operations. T&E's research findings are regularly cited in major publications across the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
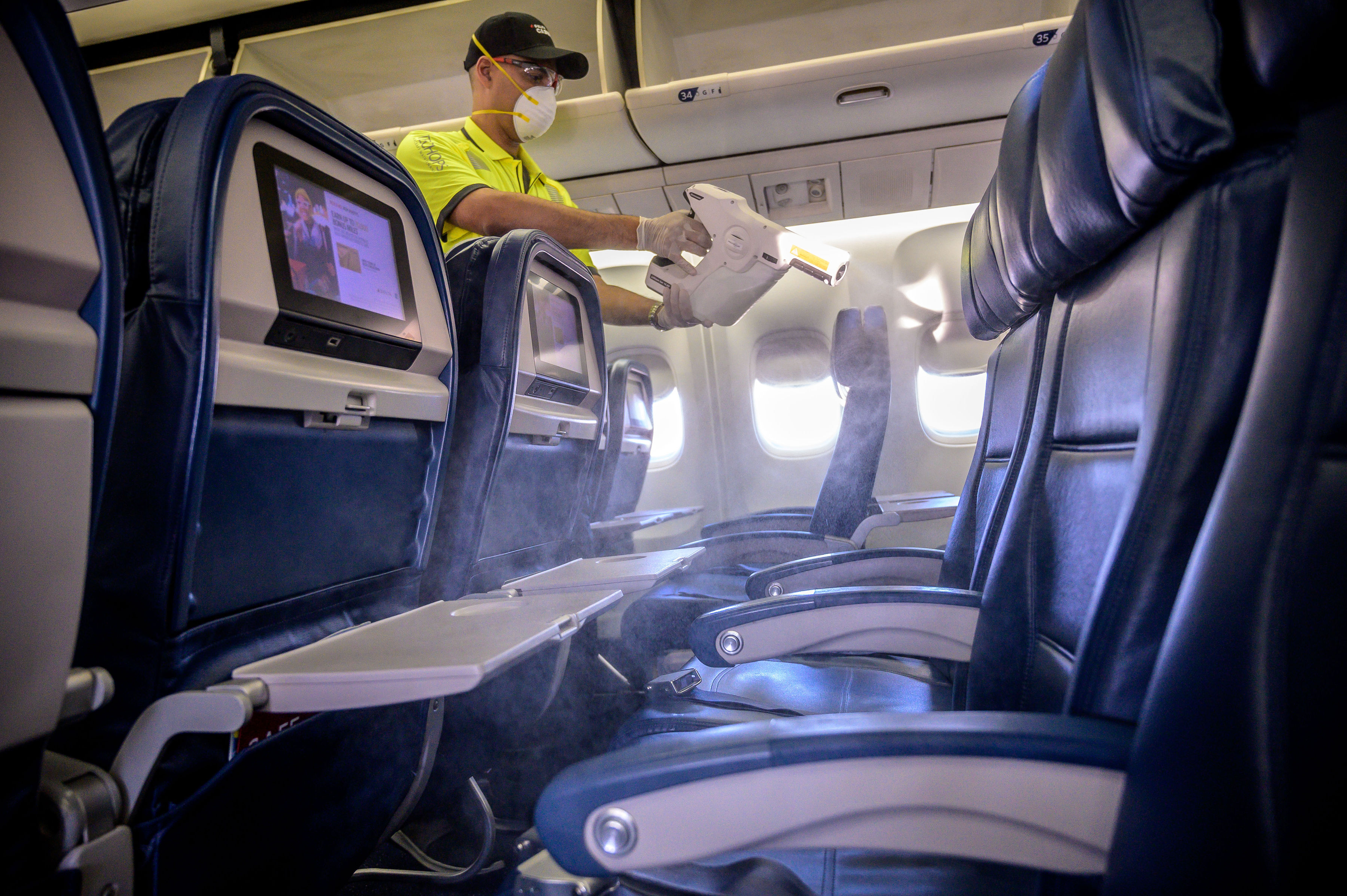
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Aviation
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the airline industry due to travel restrictions and a decimation in demand among travelers. Significant reductions in passenger numbers have resulted in flights being cancelled or planes flying empty between airports, which in turn massively reduced revenues for airlines and forced many airlines to lay off employees or declare bankruptcy. Some have attempted to avoid refunding cancelled trips to diminish their losses. Airliner manufacturers and airport operators have also laid off employees. Only several months into the pandemic, the crisis was already the worst in the aviation industry's history, according to statements made in early 2020 by Airbus' Guillaume Faury, EasyJet's Johan Lundgren, United Airlines' Oscar Munoz, Qantas' Alan Joyce, and media outlets: the ''Financial Times'', ''The New York Times'', and ''The Independent''. Flight cancellations Government regulations in Europe and the United States mandated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified in an outbreak in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread to other areas of Asia and later COVID-19 pandemic by country and territory, worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of , the pandemic had caused COVID-19 pandemic cases, more than cases and COVID-19 pandemic deaths, confirmed deaths, making it one of the deadliest pandemics in history, deadliest in history. COVID-19 symptoms range from Asymptomatic, undetectable to deadly, but most commonly include fever, Nocturnal cough, dry cough, and fatigue. Severe illness is more likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigajoule
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule can also be defined by any of the following: * The work required to move an electric charge of one coulomb through an electrical potential difference of one volt, or one coulomb-volt (C⋅V). This relationship can be used to define the volt. * The work required to produce one watt of power for one second, or one watt-second (W⋅s) (compare kilowatt-hour, which is 3.6 megajoules). This relationship can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |