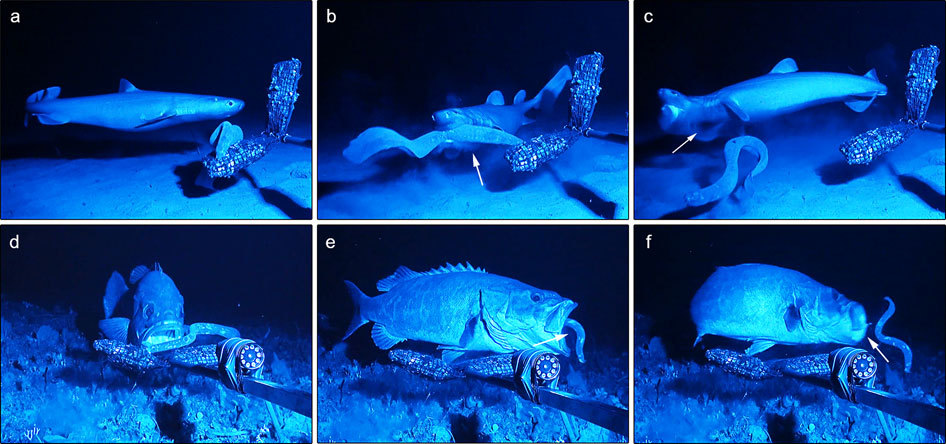
|
Autothysis
Autothysis (from the Greek roots ''autos-'' "self" and ''thysia'' "sacrifice") or suicidal altruism is the process where an animal destroys itself via an internal rupturing or explosion of an organ which ruptures the skin. The term was proposed by Ulrich Maschwitz and Eleonore Maschwitz in 1974 to describe the defensive mechanism of ''Colobopsis saundersi'', a species of ant. It is caused by a contraction of muscles around a large gland that leads to the breaking of the gland wall. Some termites (such as the soldiers of ''Globitermes sulphureus'') release a sticky secretion by rupturing a gland near the skin of their neck, producing a tar effect in defense against ants. Termites Groups of termite whose soldiers have been found to use autothysis to defend their colonies include: '' Serritermes serrifer'', '' Dentispicotermes'', '' Genuotermes'', and '' Orthognathotermes''. Several species of the soldierless Apicotermitinae, for example those of the '' Grigiotermes'' and '' Rupti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploding Animals
The explosion of animals is an uncommon event arising through natural causes or human activity. Among the best known examples are the post-mortem Exploding whale, explosion of whales, either as a result of natural decomposition or deliberate attempts at Carrion, carcass disposal.Steven HackstadtThe Evidence TheExplodingWhale.com Accessed November 7, 2005The Infamous Exploding Whale perp.com, Accessed June 6, 2005 Other instances of exploding animals are defensive in nature or the result of human intervention. Causes of explosions Natural explosions can occur for a variety of reasons. Post-mortem explosions, like that of a beached whale, are the result of the build-up of natural gases created by methane-producing bacteria inside the carcass during the decomposition process. Natural explosions which occur while an animal is living may be defense-related. A number of toads in Germany and Denmark exploding toad, exploded in April 2005. The ''Los Angeles Herald'' in 1910 reported a du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipredator Adaptations
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by avoiding detection, warding off attack, fighting back, or escaping when caught. The first line of defence consists in avoiding detection, through mechanisms such as camouflage, masquerade, apostatic selection, living underground, or nocturnality. Alternatively, prey animals may ward off attack, whether by advertising the presence of strong defences in aposematism, by mimicking animals which do possess such defences, by startling the attacker, by signalling to the predator that pursuit is not worthwhile, by distraction, by using defensive structures such as spines, and by living in a group. Members of groups are at reduced risk of predation, despite the increased conspicuousness of a group, through improved vigilance, predator confusion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colobopsis Saundersi
''Colobopsis saundersi'', synonym ''Camponotus saundersi'', is a species of ant found in Malaysia and Brunei, belonging to the genus ''Colobopsis''. A worker can explode suicidally and aggressively as an ultimate act of defense, an ability it has in common with several other species in this genus and a few other insects. The ant has an enormously enlarged mandibular (jaw) gland, many times the size of a normal ant, which produces defense adhesive secretions. According to a 2018 study, this species forms a species complex and is probably related to '' C. explodens'', which is part of the '' C. cylindrica'' group. Defenses Its defensive behaviours include self-destruction by autothysis, a term coined by Maschwitz and Maschwitz (1974). Two oversized, poison-filled mandibular glands run the entire length of the ant's body. When combat takes a turn for the worse, the worker ant violently contracts its abdominal muscles to rupture its gaster at the intersegmental fold, which also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-destruct
A self-destruct is a mechanism that can cause an object to destroy itself or render itself inoperable after a predefined set of circumstances has occurred. Self-destruct mechanisms are typically found on devices and systems where malfunction could endanger large numbers of people. Uses Land mines Some types of modern land mines are designed to self-destruct, or chemically render themselves inert after a period of weeks or months to reduce the likelihood of friendly casualties during the conflict or civilian casualties after the conflict's end. The Amended Protocol II to the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW), amended in 1996, requires that anti-personnel land mines deactivate and self-destruct, and sets standards for both. Landmines currently used by the United States military are designed to self-destruct after between 4 hours and 15 days depending upon the type. The landmines have a battery and when the battery dies, the land mine self-destructs. The self-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploding Animal
The explosion of animals is an uncommon event arising through natural causes or human activity. Among the best known examples are the post-mortem explosion of whales, either as a result of natural decomposition or deliberate attempts at carcass disposal.Steven HackstadtThe Evidence TheExplodingWhale.com Accessed November 7, 2005The Infamous Exploding Whale perp.com, Accessed June 6, 2005 Other instances of exploding animals are defensive in nature or the result of human intervention. Causes of explosions Natural explosions can occur for a variety of reasons. Post-mortem explosions, like that of a beached whale, are the result of the build-up of natural gases created by methane-producing bacteria inside the carcass during the decomposition process. Natural explosions which occur while an animal is living may be defense-related. A number of toads in Germany and Denmark exploded in April 2005. The ''Los Angeles Herald'' in 1910 reported a duck which exploded after consuming yeast. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autohaemorrhaging
Autohaemorrhaging, or reflex bleeding, is the action of animals deliberately ejecting blood from their bodies. Autohaemorrhaging has been observed as occurring in two variations. In the first form, blood is squirted toward a predator. The blood of these animals usually contains toxic compounds, making the behaviour an effective chemical defence mechanism. In the second form, blood is not squirted, but is slowly emitted from the animal's body. This form appears to serve a deterrent effect, and is used by animals whose blood does not seem to be toxic. Most animals that autohaemorrhage are insects, but some reptiles also display this behaviour. Some organisms have shown an ability to tailor their autohaemorrhaging response. Armoured crickets will projectile autohaemorrhage over longer distances when attacked from the side, compared to being attacked from an overhead predator. Insects Six orders of insects have been observed to utilize this defence mechanism. *Beetles **Meloidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaster (insect Anatomy)
The gaster is the bulbous posterior portion of the metasoma found in hymenopterans of the suborder Apocrita (bees, wasps and ants). This begins with abdominal segment III on most ants, but some make a constricted postpetiole out of segment III, in which case the gaster begins with abdominal segment IV. Certain ants in the genus ''Cataglyphis'', specifically '' Cataglyphis bicolor'' and '' Cataglyphis fortis'', have a cubiform petiole that allows them to decrease their inertia Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law o ... (and therefore increase their speed) by raising their gaster into an upright position. References Insect anatomy {{insect-anatomy-stub de:Gaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropods
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colobopsis
''Colobopsis'' is a genus of ant in the subfamily Formicinae. This genus was first described in 1861 by Mayr and contains 95 species. The type species is '' Colobopsis truncata''. Description As part of Camponotini, ''Colobopsis'' workers have distinctive mandibular dentition (5-8 teeth with the 3rd tooth from the apex not being reduced), antennae 12-segmented and antennal separations well separated from the posterior clypeal margin. ''Colobopsis'' workers are dimorphic, being divided into major workers and minor workers. The major workers generally have phragmotic heads that are truncate to varying extents. This may cause them to be confused for '' Camponotus'' and vice versa, since some ''Camponotus'' also have phragmotic heads. Pupae of ''Colobopsis'' are always naked. This is unlike pupae of ''Camponotus'', which are enclosed in cocoons. Phylogeny For a period of time, ''Colobopsis'' was considered a subgenus of ''Camponotus''. A 2015 phylogenomic study found it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |