|
Atomic Veteran
An atomic veteran is a veteran who was exposed to ionizing radiation while present in the site of a nuclear explosion during their active duty. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs defines an atomic veteran "who, as part of his or her military service: Participated in an above-ground nuclear test, 1945–1962; or was part of the U.S. military occupation forces in/around Hiroshima/Nagasaki before 1946; or was held as a POW in or near Hiroshima or Nagasaki (certain cases)." Atomic veterans also includes service personnel from other nations, including the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, France, China, and Russia who were similarly exposed during their active service. United States Recognition On July 15, 2021, President Joe Biden declared July 16, 2021 as "National Atomic Veterans Day" via presidential proclamation. Affected veterans The Defense Threat Reduction Agency's Nuclear Test Personnel Review has maintained a database of participants and radiation dos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military. A military veteran that has served directly in combat in a war is further defined as a war veteran (although not all military conflicts, or areas in which armed combat took place, are necessarily referred to as ''wars''). Military veterans are unique as a group as their lived experience is so strongly connected to the conduct of war in general and application of professional violence in particular. Therefore, there are a large body of knowledge developed through centuries of scholarly studies that seek to describe, understand and explain their lived experience in and out of service. Griffith with colleagues provides an overview of this research field that addresses veterans general health, transition from military service to civilian life, homelessness, veteran empl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stone (director)
Robert Stone is a British-American documentary filmmaker. His work has been screened at dozens of film festivals and televised around the world, notably seven of his films have appeared on PBS's ''American Experience'' series and four of his films have premiered at the Sundance Film Festival (including Closing Night Film in 2009). He is an Oscar nominee for Best Feature Documentary and a three-time Emmy nominee for Exceptional Merit in Documentary Filmmaking. Life and career Stone was born in England and educated in the United States. His father Lawrence Stone was a noted historian and chair of the History Department at Princeton University in Princeton, New Jersey where Robert grew up, graduating Princeton High School in 1976. He was later educated at the University of Wisconsin at Madison, did a brief stint at Sorbonne University in Paris and at the Lee Strasberg Theatre and Film Institute in New York. Known in large part for his innovative use of archival material in histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montebello Islands
The Montebello Islands, also rendered as the Monte Bello Islands, are an archipelago of around 174 small islands (about 92 of which are named) lying north of Barrow Island (Western Australia), Barrow Island and off the Pilbara region of Western Australia, Pilbara coast of north-western Australia. The islands form a marine conservation reserve of administered by the Western Australian Department of Environment and Conservation (Western Australia), Department of Environment and Conservation. The islands were the site of three British atmospheric nuclear weapons tests in 1952 and 1956. Description The islands of the archipelago have a collective land area of about . The largest islands, Hermite and Trimouille, have areas of and respectively. They consist of limestone rock and sand. The rocky parts are dominated by ''Triodia (grass), Triodia'' hummock grassland with scattered shrubs, while the sandy areas support grasses, Cyperaceae, sedges and shrubs, mainly ''Acacia''. Pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maralinga
Maralinga, in the remote western areas of South Australia, was the site, measuring about in area, of British nuclear tests in the mid-1950s. In January 1985 native title was granted to the Maralinga Tjarutja, a southern Pitjantjatjara Aboriginal Australian people, over some land, but around the same time, the McClelland Royal Commission identified significant residual nuclear contamination at some sites. Under an agreement between the governments of the United Kingdom and Australia, efforts were made to clean up the site before the Maralinga people resettled on the land in 1995. The main community, which includes a school, is Oak Valley. There are still concerns that some of the ground is still contaminated, despite two attempts at cleanup. History Nuclear tests and cleanup Maralinga was the scene of UK nuclear testing and was contaminated with radioactive waste in the 1950s and early 1960s. Maralinga was surveyed by Len Beadell in the early 1950s. It followed the survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emu Field, South Australia
Emu Field is located in the desert of South Australia, at (ground zero Totem I test). Variously known as Emu Field, Emu Junction or Emu, it was the site of the Operation Totem pair of nuclear tests conducted by the British government in October 1953. The site was surveyed by Len Beadell in 1952. A village and airstrip were constructed for the subsequent testing program. The site was supported from the RAAF Woomera Range Complex. Two British nuclear weapon tests were conducted at the site. ''Totem I'' was detonated on 15 October 1953 and ''Totem II'' was detonated on 27 October 1953. The devices were both sited on towers and yielded 9 kilotons and 7 kilotons respectively. The site was also used in September–October 1953 for some of the Kitten series of tests, which were conventional (rather than nuclear) explosions used to evaluate neutron initiators. It was later found that the radioactive cloud from the first detonation did not disperse as expected, and travelled north-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
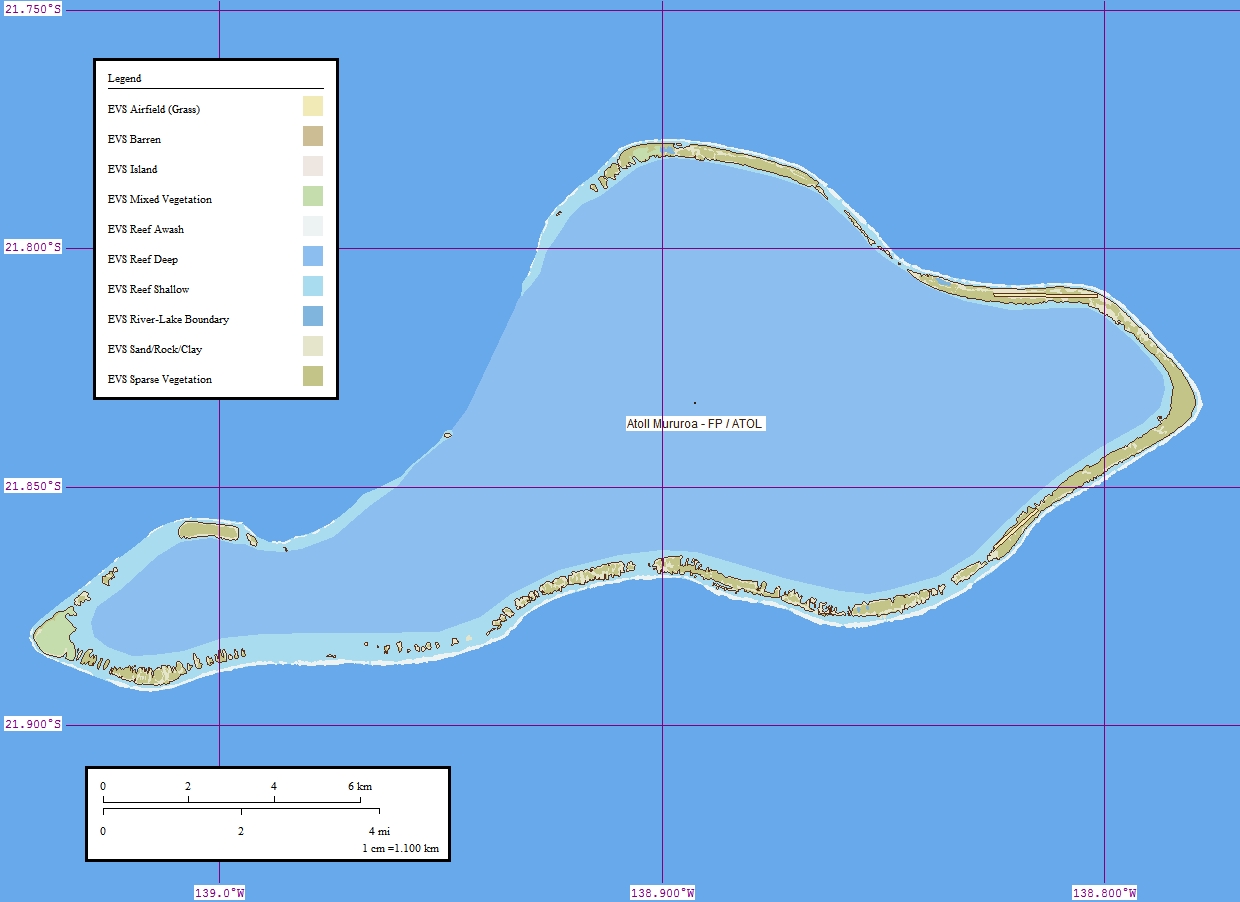
Moruroa Atoll
Moruroa (Mururoa, Mururura), also historically known as Aopuni, is an atoll which forms part of the Tuamotu Archipelago in French Polynesia in the southern Pacific Ocean. It is located about southeast of Tahiti. Administratively Moruroa Atoll is part of the commune of Tureia, which includes the atolls of Tureia, Fangataufa, Tematangi and Vanavana. France undertook nuclear weapon tests between 1966 and 1996 at Moruroa and Fangataufa, causing international protests, notably in 1974 and 1995. The number of tests performed on Moruroa has been variously reported as 175 and 181. History Ancient Polynesians knew Mururoa Atoll by the ancestral name of Hiti-Tautau-Mai. The first recorded European to visit this atoll was Commander Philip Carteret on HMS ''Swallow'' in 1767, just a few days after he had discovered Pitcairn Island. Carteret named Mururoa "Bishop of Osnaburgh Island". In 1792, the British whaler was wrecked here, and it became known as Matilda's Rocks. Frederick William Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Employees Occupational Illness Compensation Program
The Energy Employees Occupational Illness Compensation Program Act (EEOICPA) was passed by Congress in 2000 and is designed to compensate individuals who worked in nuclear weapons production and as a result of occupational exposures contracted certain illnesses. EEOICPA was signed into law by President Bill Clinton on October 30, 2000. Executive Order 13179 Executive Order 13179 states the following: Program administration The program is administered by four Federal agencies, and the Department of Labor (DOL) has the primary responsibility for administering the compensation program. EEOICPA, as amended, has four sections:Department of LaboEEOICP/ref> * Part A establishes the compensation program. * Part B covers individuals, or certain survivors of individuals, who worked at a covered facility and have developed beryllium sensitivity, chronic beryllium disease, chronic silicosis, or a radiogenic cancer. Compensation under Part B is a lump sum payment of $150,000, except for el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George H
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Day. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the two-year term of a Congress. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 establishes that there be 435 representatives and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Exposure Compensation Act
The United States Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) is a federal statute providing for the monetary compensation of people, including atomic veterans, who contracted cancer and a number of other specified diseases as a direct result of their exposure to atmospheric nuclear testing undertaken by the United States during the Cold War, or their exposure to radon gas and other radioactive isotopes while undertaking uranium mining, milling or the transportation of ore. The Act provides the following remunerations: *$50,000 to individuals residing or working "downwind" of the Nevada Test Site *$75,000 for workers participating in atmospheric nuclear weapons tests *$100,000 for uranium miners, millers, and ore transporters In all cases there are additional requirements which must be satisfied (proof of exposure, establishment of duration of employment, establishment of certain medical conditions, etc.). Origins Attempts to enact the legislation can be traced back to the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the United States government tasked with the enforcement of federal law and administration of justice in the United States. It is equivalent to the justice or interior ministries of other countries. The department is headed by the U.S. attorney general, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current attorney general is Merrick Garland, who was sworn in on March 11, 2021. The modern incarnation of the Justice Department was formed in 1870 during the Ulysses S. Grant presidency. The department comprises federal law enforcement agencies, including the Federal Bureau of Investigation, the U.S. Marshals Service, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, the Drug Enforcement Administration, and the Federal Bureau of Prisons. It also has eight major divisions of lawyers who rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care Services
The healthcare industry (also called the medical industry or health economy) is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, and palliative care. It includes the generation and commercialization of goods and services lending themselves to maintaining and re-establishing health. The modern healthcare industry includes three essential branches which are services, products, and finance and may be divided into many sectors and categories and depends on the interdisciplinary teams of trained professionals and paraprofessionals to meet health needs of individuals and populations.HEALTH PROFESSIONS [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |