|
Astrogeodetic
Geodetic astronomy or astronomical geodesy (astro-geodesy) is the application of astronomical methods into geodetic networks and other technical projects of geodesy. Applications The most important applications are: * Establishment of geodetic datum systems (e.g. ED50) or at expeditions * apparent places of stars, and their proper motions * precise astronomical navigation * astro-geodetic geoid determination * modelling the rock densities of the topography and of geological layers in the subsurface * Monitoring of the Earth rotation and polar wandering * Contribution to the time system of physics and geosciences Measuring techniques Important measuring techniques are: * Latitude determination and longitude determination, by theodolites, tacheometers, astrolabes or zenith cameras * time and star positions by observation of star transits, e.g. by meridian circles (visual, photographic or CCD) * Azimuth determination ** for the exact orientation of geodetic networks ** for mutua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
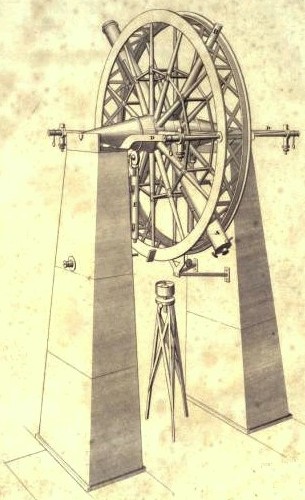
Theodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building and infrastructure construction, and some specialized applications such as meteorology and rocket launching. It consists of a moveable telescope mounted so it can rotate around horizontal and vertical axes and provide angular readouts. These indicate the orientation of the telescope, and are used to relate the first point sighted through the telescope to subsequent sightings of other points from the same theodolite position. These angles can be measured with accuracies down to microradians or seconds of arc. From these readings a plan can be drawn, or objects can be positioned in accordance with an existing plan. The modern theodolite has evolved into what is known as a total station where angles and distances are measured electronically, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduction (mathematics)
In mathematics, reduction refers to the rewriting of an expression into a simpler form. For example, the process of rewriting a fraction into one with the smallest whole-number denominator possible (while keeping the numerator a whole number) is called " reducing a fraction". Rewriting a radical (or "root") expression with the smallest possible whole number under the radical symbol is called "reducing a radical". Minimizing the number of radicals that appear underneath other radicals in an expression is called denesting radicals. Algebra In linear algebra, ''reduction'' refers to applying simple rules to a series of equations or matrices to change them into a simpler form. In the case of matrices, the process involves manipulating either the rows or the columns of the matrix and so is usually referred to as ''row-reduction'' or ''column-reduction'', respectively. Often the aim of reduction is to transform a matrix into its "row-reduced echelon form" or "row-echelon form"; thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
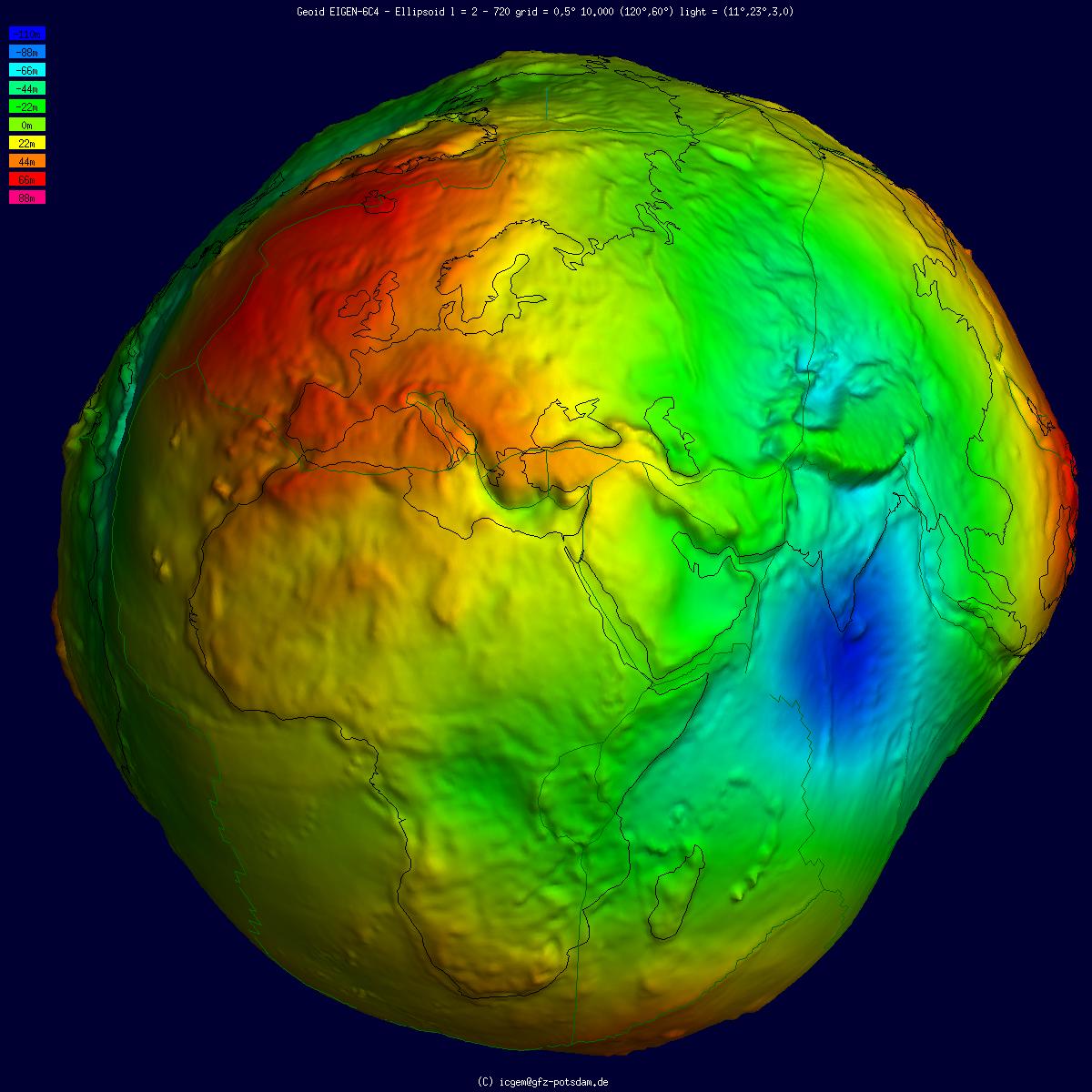
Geoid Determination
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational potential energy and centrifugal potential energy). The force of gravity acts everywhere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Deflection Determination
The vertical deflection (VD) or deflection of the vertical (DoV), also known as deflection of the plumb line and astro-geodetic deflection, is a measure of how far the gravity direction at a given point of interest is rotated by local mass anomalies such as nearby mountains. They are widely used in geodesy, for surveying networks and for geophysical purposes. The vertical deflection are the angular components between the true zenith–nadir curve (plumb line) tangent line and the normal vector to the surface of the reference ellipsoid (chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface). VDs are caused by mountains and by underground geological irregularities and can amount to angles of 10 ″ in flat areas or 20–50″ in mountainous terrain). The deflection of the vertical has a north–south component ''ξ'' ( xi) and an east–west component ''η'' (eta). The value of ''ξ'' is the difference between the '' astronomic latitude'' and the ''geodetic latitude'' (taki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Point
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized and extended the work of his predecessors in his five-volume Traité de mécanique céleste, ''Mécanique céleste'' (''Celestial Mechanics'') (1799–1825). This work translated the geometric study of classical mechanics to one based on calculus, opening up a broader range of problems. In statistics, the Bayesian probability, Bayesian interpretation of probability was developed mainly by Laplace. Laplace formulated Laplace's equation, and pioneered the Laplace transform which appears in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (mathematics)
In mathematics, a transformation is a function ''f'', usually with some geometrical underpinning, that maps a set ''X'' to itself, i.e. . Examples include linear transformations of vector spaces and geometric transformations, which include projective transformations, affine transformations, and specific affine transformations, such as rotations, reflections and translations. Partial transformations While it is common to use the term transformation for any function of a set into itself (especially in terms like " transformation semigroup" and similar), there exists an alternative form of terminological convention in which the term "transformation" is reserved only for bijections. When such a narrow notion of transformation is generalized to partial functions, then a partial transformation is a function ''f'': ''A'' → ''B'', where both ''A'' and ''B'' are subsets of some set ''X''. Algebraic structures The set of all transformations on a given base set, together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer ( origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on planetary surface, Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane In astronomy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital camera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian Circle
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis. The similar transit instrument, transit circle, or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east–west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Transit
A star transit is the passage of a star across the field of view of a telescope eyepiece. The precise observation of star transits is the basis of many methods in astronomy and in geodesy. The measurements can be done in different ways: # visually (mostly up to 1990): accuracy 0,1" to 2" (depending on the instrument); timing with digital clocks about 0,05–0,2 seconds # by CCD and other electro-optical sensors: as above, time often better # semi automatic instruments: Photography or " impersonal micrometer", ca. 2 times better than No.1 # by Scanning methods: Astrometry satellites like Hipparcos about 0,01". See also * Accuracy and precision * Instrument error * Meridian circle * Minute and second of arc * Theodolite * Transit instrument Literature * Karl Ramsayer, 1969: '' Geodätische Astronomie'', Vol.2a of Handbuch der Vermessungskunde, 900 p., J.B. Metzler-Verlag Stuttgart. * Ivan I. Mueller, 1969: Spherical and Practical Astronomy as applied to Geodesy, 610 p., Fred.Ungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Position
Star position is the apparent angular position of any given star in the sky, which seems fixed onto an arbitrary sphere centered on Earth. The location is defined by a pair of angular coordinates relative to the celestial equator: right ascension () and declination (). This pair based the equatorial coordinate system. While is given in degrees (from +90° at the north celestial pole to −90° at the south), is usually given in hour angles (0 to 24 h). This is due to the observation technique of star transits, which cross the field of view of telescope eyepieces due to Earth's rotation. The observation techniques are topics of positional astronomy and of astrogeodesy. Ideally, the Cartesian coordinate system refers to an inertial frame of reference. The third coordinate is the star's distance, which is normally used as an attribute of the individual star. The following factors change star positions over time: #axial precession and nutation – slow tilts of Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)