|
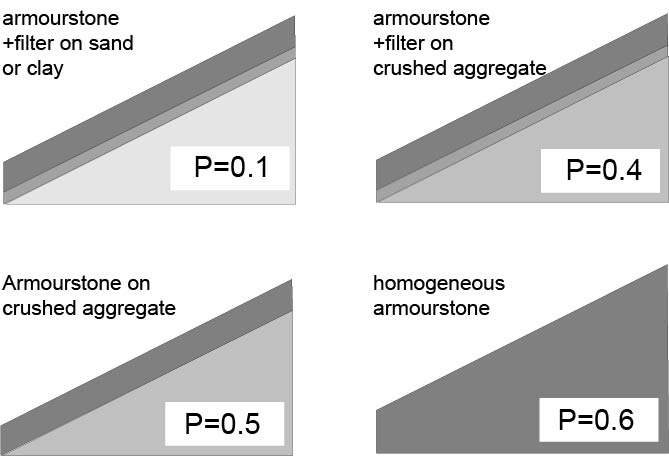
Armourstone
Armourstone is a generic term for broken stone with stone masses between (very coarse Construction aggregate, aggregate) that is suitable for use in hydraulic engineering. Dimensions and characteristics for armourstone are laid down in European Standard EN13383. In the United States, there are a number of different standards and publications setting out different methodologies for classifying armourstone, ranging from weight-based classifications to gradation curves and size-based classifications. Stone Classes European Practice to EN13383 Armourstone is available in standardised stone classes, defined by both a lower and upper value of the stone mass within these classes. For instance, Class 60-300 signifies that up to 10% of the stones weigh less than and up to 30% weigh more than . The standard also mentions values which shouldn't be exceeded by 5% or 3%. For particular applications like a top layer for a breakwater (structure), breakwater or bank protection, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Meer Formula
The Van der Meer formula is a formula for calculating the required stone weight for armourstone under the influence of (wind) waves. This is necessary for the design of breakwaters and shoreline protection. Around 1985 it was found that the Hudson formula in use at that time had considerable limitations (only valid for permeable breakwaters and steep (storm) waves). That is why the Dutch government agency Rijkswaterstaat commissioned Deltares to start research for a more complete formula. This research, conducted by Jentsje van der Meer, resulted in the Van der Meer formula in 1988, as described in his dissertation. This formula reads :\frac= \begin c_ P^ \left (\frac \right)^ \xi_m^ & \mbox \xi_m < \xi \quad lunging\\ c_ P^ \left (\frac \right)^ \xi_m^ \sqrt & \mbox \xi_m \ge \xi \quad urging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Formula (armourstone)
Hudson's equation, also known as Hudson formula, is an equation used by coastal engineers to calculate the minimum size of riprap (armourstone) required to provide ''satisfactory'' stability characteristics for rubble structures such as breakwaters under attack from storm wave conditions. The equation was developed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station (WES), following extensive investigations by Hudson (1953, 1959, 1961a, 1961b) Initial equation The equation itself is: :W =\frac where: *''W'' is the design weight of the riprap armor (Newton) *''\gamma_r'' is the specific weight of the armor blocks (N/m3) *''H'' is the design wave height at the toe of the structure (m) *''K''''D'' is a dimensionless stability coefficient, deduced from laboratory experiments for different kinds of armour blocks and for very small damage (a few blocks removed from the armour layer) (-): :* ''K''''D'' = around 3 for natural quarry rock :* ''K''''D'' = aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Wall And Rip-rap South Of Dawlish Warren - Geograph
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, as well as certain large, entirely landlocked, saltwater lakes, such as the Caspian Sea. The sea moderates Earth's climate and has important roles in the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles. Humans harnessing and studying the sea have been recorded since ancient times, and evidenced well into prehistory, while its modern scientific study is called oceanography. The most abundant solid dissolved in seawater is sodium chloride. The water also contains salts of magnesium, calcium, potassium, and mercury, amongst many other elements, some in minute concentrations. Salinity varies widely, being lower near the surface and the mouths of large rivers and higher in the depths of the ocean; however, the relative proportions of dissolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |