|
Arithmometer
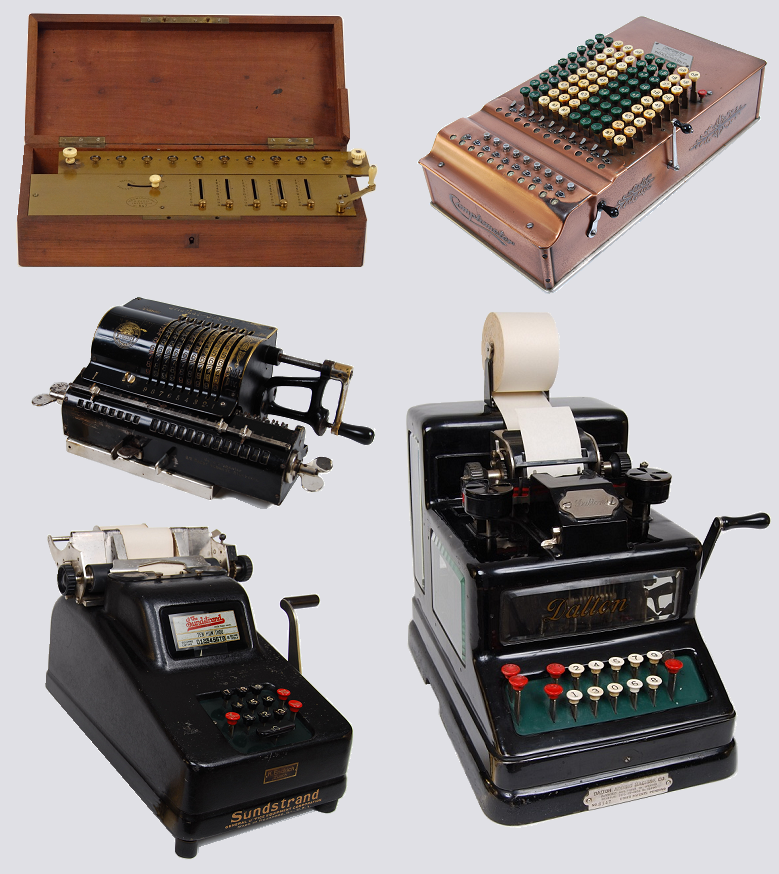
The arithmometer (french: arithmomètre) was the first digital mechanical calculator strong enough and reliable enough to be used daily in an office environment. This calculator could add and subtract two numbers directly and could perform long multiplications and divisions effectively by using a movable accumulator for the result. Patented in France by Thomas de Colmar in 1820 and manufactured from 1851 to 1915, it became the first commercially successful mechanical calculator.Chase G.C.: ''History of Mechanical Computing Machinery'', Vol. 2, Number 3, July 1980, page 204, IEEE Annals of the History of Computing https://archive.org/details/ChaseMechanicalComputingMachinery Its sturdy design gave it a strong reputation for reliability and accuracy and made it a key player in the move from to calculating machines that took place during the second half of the 19th century. Its production debut of 1851 launched the mechanical calculator industry which ultimately built millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmometre
The arithmometer (french: arithmomètre) was the first digital mechanical calculator strong enough and reliable enough to be used daily in an office environment. This calculator could add and subtract two numbers directly and could perform long multiplications and divisions effectively by using a movable accumulator for the result. Patented in France by Thomas de Colmar in 1820 and manufactured from 1851 to 1915, it became the first commercially successful mechanical calculator.Chase G.C.: ''History of Mechanical Computing Machinery'', Vol. 2, Number 3, July 1980, page 204, IEEE Annals of the History of Computing https://archive.org/details/ChaseMechanicalComputingMachinery Its sturdy design gave it a strong reputation for reliability and accuracy and made it a key player in the move from to calculating machines that took place during the second half of the 19th century. Its production debut of 1851 launched the mechanical calculator industry which ultimately built millions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Calculator
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or (historically) a simulation such as an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators were comparable in size to small desktop computers and have been rendered obsolete by the advent of the electronic calculator and the digital computer. Surviving notes from Wilhelm Schickard in 1623 reveal that he designed and had built the earliest of the modern attempts at mechanizing calculation. His machine was composed of two sets of technologies: first an abacus made of Napier's bones, to simplify multiplications and divisions first described six years earlier in 1617, and for the mechanical part, it had a dialed pedometer to perform additions and subtractions. A study of the surviving notes shows a machine that would have jammed after a few entries on the same dial, and that it could be damaged if a carry had to be propagated over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Xavier Thomas
Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar (May 5, 1785 – March 12, 1870) was a French inventor and entrepreneur best known for designing, patenting and manufacturing the first commercially successful mechanical calculator, the Arithmometer, and for founding the insurance companies ''Le Soleil'' and ''L'aigle'' which, under his leadership, became the number one insurance group in France at the beginning of the Second Empire. Biography Born Charles Xavier Thomas in Colmar, France, his father was a doctor and member of the town council. After a short employment in the French administration, Thomas joined the French army in 1809 eventually reaching the level of General Manager of the supply store of all of the armies located in Spain in 1813. Shortly thereafter he was promoted to Inspector of Supply for the entire French army. It was during that time that he conceived the idea of the Arithmometer to help him with the great deal of calculations that he had to perform. Back into civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
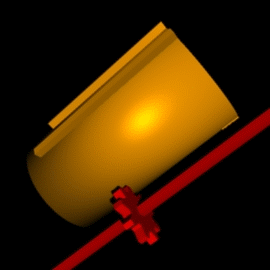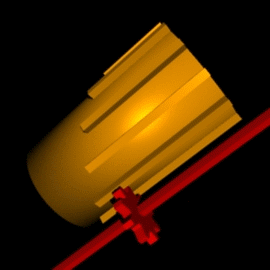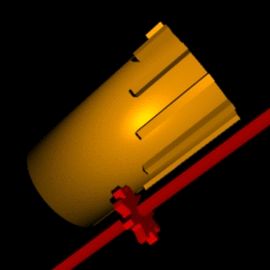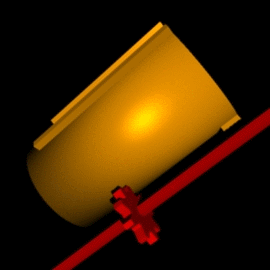
Leibniz Cylinder
A Leibniz wheel or stepped drum is a cylinder with a set of teeth of incremental lengths which, when coupled to a counting wheel, can be used in the calculating engine of a class of mechanical calculators. Invented by Leibniz in 1673, it was used for three centuries until the advent of the electronic calculator in the mid-1970s. Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz built a machine called the stepped reckoner based on the design of the stepped drum in 1694. It was made famous by Thomas de Colmar when he used it, a century and a half later, in his Arithmometer, the first mass-produced calculating machine. It was also used in the Curta calculator, a very popular portable calculator introduced in the second part of the 20th century. Concept By coupling a Leibniz wheel with a counting wheel free to move up and down its length, the counting wheel can mesh with any number of teeth. The animation on the side shows a nine-tooth Leibniz wheel coupled to a red counting wheel. It is set to mesh wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odhner Arithmometer
The Odhner Arithmometer was a very successful pinwheel calculator invented in Russia in 1873 by W. T. Odhner, a Swedish immigrant. Its industrial production officiallyTrogemann G., Nitussov A.: ''Computing in Russia'', page 39-45, GWV-Vieweg, 2001, started in 1890 in Odhner's Saint Petersburg workshop. Even though the machine was very popular, the production only lasted thirty years until the factory was nationalised and closed down during the Russian revolution of 1917. From 1892 to the middle of the 20th century, independent companies were set up all over the world to manufacture Odhner's clones and, by the 1960s, with millions sold, it became one of the most successful type of mechanical calculator ever designed. History Odhner thought of his machine in 1871 while repairing a Thomas' Arithmometer (which was the only mechanical calculator in production at the time) and decided to replace its heavy, bulky Leibniz cylinder by a lighter, smaller pinwheel disk. This is why ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burroughs Corporation
The Burroughs Corporation was a major American manufacturer of business equipment. The company was founded in 1886 as the American Arithmometer Company. In 1986, it merged with Sperry UNIVAC to form Unisys. The company's history paralleled many of the major developments in computing. At its start, it produced mechanical adding machines, and later moved into programmable ledgers and then computers. It was one of the largest producers of mainframe computers in the world, also producing related equipment including typewriters and printers. Early history In 1886, the American Arithmometer Company was established in St. Louis, Missouri, to produce and sell an adding machine invented by William Seward Burroughs (grandfather of Beat Generation author William S. Burroughs). In 1904, six years after Burroughs' death, the company moved to Detroit and changed its name to the Burroughs Adding Machine Company. It was soon the biggest adding machine company in America. Evolving pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinwheel Calculator
A pinwheel calculator is a class of mechanical calculator described as early as 1685, and popular in the 19th and 20th century, calculating via wheels whose number of teeth were adjustable. These wheels, also called pinwheels, could be set by using a side lever which could expose anywhere from 0 to 9 teeth, and therefore when coupled to a counter they could, at each rotation, add a number from 0 to 9 to the result. By linking these wheels with carry mechanisms a new kind of calculator engine was invented. Turn the wheels one way and one performs an addition, the other way a subtraction. As part of a redesign of the arithmometer, they reduced by an order of magnitude the cost and the size of mechanical calculators on which one could easily do the four basic operations (add, subtract, multiply and divide). Pinwheel calculators became extremely popular with the success of Thomas' Arithmometer (manufactured 1850s) and Odhner Arithmometer (manufactured 1890s). History * - In "M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comptometer
The Comptometer was the first commercially successful key-driven mechanical calculator, patented in the United States by Dorr Felt in 1887. A key-driven calculator is extremely fast because each key adds or subtracts its value to the accumulator as soon as it is pressed and a skilled operator can enter all of the digits of a number simultaneously, using as many fingers as required, making them sometimes faster to use than electronic calculators. Consequently, in specialized applications, comptometers remained in use in limited numbers into the early 1990s, but with the exception of museum pieces, they have all now been superseded by electronic calculators and computers. Manufactured without interruption from 1887 to the mid-1970s, it was constantly improved. The mechanical versions were made faster and more reliable, then a line of electro-mechanical models was added in the 1930s. It was the first mechanical calculator to receive an all-electronic calculator engine in 1961, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmaurel
The Arithmaurel was a mechanical calculator that had a very intuitive user interface, especially for multiplying and dividing numbers because the result was displayed as soon as the operands were entered. It was first patented in France by Timoleon Maurel, in 1842. It received a gold medal at the French national show in Paris in 1849. Unfortunately its complexity and the fragility of its design prevented it from being manufactured. Its name came from the concatenation of Arithmometer, the machine that inspired its design and of Maurel, the name of its inventor. The heart of the machine uses one Leibniz stepped cylinder driven by a set of differential gears. History Timoleon Maurel patented an early version of his machine in 1842,(f1842 patent- Document scanned by www.ami19.org he then improved its design with the help of Jean Jayet and patented it in 1846.(frpatent held by Maurel and Jayet 1846- Document scanned par www.ami19.org This is the design that won a gold medal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |