|
Ar (Unix)
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils. In the Linux Standard Base (LSB), ar has been deprecated and is expected to disappear in a future release of that standard. The rationale provided was that "the LSB does not include software development utilities nor does it specify .o and .a file formats." File format details The ar format has never been standardized; modern archives are based on a common format with two main variants, BSD and System V (initially known as COFF, and used as well by GNU, ELF, and Windows.) Historically there have been other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Thompson
Kenneth Lane Thompson (born February 4, 1943) is an American pioneer of computer science. Thompson worked at Bell Labs for most of his career where he designed and implemented the original Unix operating system. He also invented the B programming language, the direct predecessor to the C programming language, and was one of the creators and early developers of the Plan 9 operating system. Since 2006, Thompson has worked at Google, where he co-developed the Go programming language. Other notable contributions included his work on regular expressions and early computer text editors QED and ed, the definition of the UTF-8 encoding, and his work on computer chess that included the creation of endgame tablebases and the chess machine Belle. He won the Turing Award in 1983 with his long-term colleague Dennis Ritchie. Early life and education Thompson was born in New Orleans, Louisiana. When asked how he learned to program, Thompson stated, "I was always fascinated with logic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Library
In computer science, a static library or statically-linked library is a set of routines, external functions and variables which are resolved in a caller at compile-time and copied into a target application by a compiler, linker, or binder, producing an object file and a stand-alone executable. This executable and the process of compiling it are both known as a static build of the program. Historically, libraries could only be ''static''. Static libraries are either merged with other static libraries and object files during building/linking to form a single executable or loaded at run-time into the address space of their corresponding executable at a static memory offset determined at compile-time/link-time. Advantages and disadvantages There are several advantages to statically linking libraries with an executable instead of dynamically linking them. The most significant advantage is that the application can be certain that all its libraries are present and that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
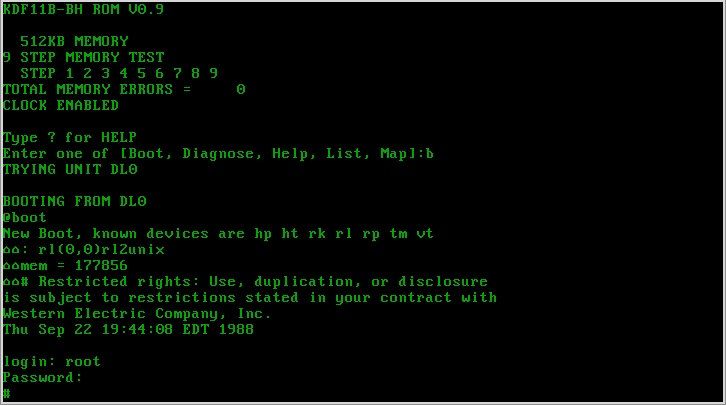
Version 7 Unix
Seventh Edition Unix, also called Version 7 Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 6 Unix
Sixth Edition Unix, also called Version 6 Unix or just V6, was the first version of the Unix operating system to see wide release outside Bell Labs. It was released in May 1975 and, like its direct predecessor, targeted the DEC PDP-11 family of minicomputers. It was superseded by Version 7 Unix in 1978/1979, although V6 systems remained in regular operation until at least 1985. AT&T Corporation licensed Version 5 Unix to educational institutions only, but licensed Version 6 also to commercial users for $20,000, and it remained the most widely used version into the 1980s. An enhanced V6 was the basis of the first ever commercially sold Unix version, INTERACTIVE's IS/1. Bell's own PWB/UNIX 1.0 was also based on V6, where earlier (unreleased) versions were based on V4 and V5. Whitesmiths produced and marketed a (binary-compatible) V6 clone under the name Idris. Source code V6 Unix was released as a distribution including the full source code. Since source code was availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Kaufmann
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers is a Burlington, Massachusetts (San Francisco, California until 2008) based publisher specializing in computer science and engineering content. Since 1984, Morgan Kaufmann has published content on information technology, computer architecture, data management, computer networking, computer systems, human computer interaction, computer graphics, multimedia information and systems, artificial intelligence, computer security, and software engineering. Morgan Kaufmann's audience includes the research and development communities, information technology (IS/IT) managers, and students in professional degree programs. The company was founded in 1984 by publishers Michael B. Morgan and William Kaufmann and computer scientist Nils Nilsson. It was held privately until 1998, when it was acquired by Harcourt General and became an imprint of the Academic Press, a subsidiary of Harcourt. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001; Morgan Kaufmann is now an impri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows API
The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is Microsoft's core set of application programming interfaces (APIs) available in the Microsoft Windows operating systems. The name Windows API collectively refers to several different platform implementations that are often referred to by their own names (for example, Win32 API); see the versions section. Almost all Windows programs interact with the Windows API. On the Windows NT line of operating systems, a small number (such as programs started early in the Windows startup process) use the Native API. Developer support is available in the form of a software development kit, Microsoft Windows SDK, providing documentation and tools needed to build software based on the Windows API and associated Windows interfaces. The Windows API (Win32) is focused mainly on the programming language C in that its exposed functions and data structures are described in that language in recent versions of its documentation. However, the API may be used by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executable And Linkable Format
In computing, the Executable and Linkable FormatTool Interface Standard (TIS) Portable Formats SpecificationVersion 1.1'' (October 1993) (ELF, formerly named Extensible Linking Format), is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps. First published in the specification for the application binary interface (ABI) of the Unix operating system version named System V Release 4 (SVR4), and later in the Tool Interface Standard,Tool Interface Standard (TIS) Executable and Linking Format (ELF) SpecificationVersion 1.2'' (May 1995) it was quickly accepted among different vendors of Unix systems. In 1999, it was chosen as the standard binary file format for Unix and Unix-like systems on x86 processors by the 86open project. By design, the ELF format is flexible, extensible, and cross-platform. For instance, it supports different endiannesses and address sizes so it does not exclude any particular central processing unit (CPU) or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COFF
The Common Object File Format (COFF) is a format for executable, object code, and shared library computer files used on Unix systems. It was introduced in Unix System V, replaced the previously used a.out format, and formed the basis for extended specifications such as XCOFF and ECOFF, before being largely replaced by ELF, introduced with SVR4. COFF and its variants continue to be used on some Unix-like systems, on Microsoft Windows (Portable Executable), in UEFI environments and in some embedded development systems. History The original Unix object file format a.out is unable to adequately support shared libraries, foreign format identification , or explicit address linkage . As development of Unix-like systems continued both inside and outside AT&T, different solutions to these and other issues emerged. COFF was introduced in 1983, in AT&T's UNIX System V for non-VAX 32-bit platforms such as the 3B20. Improvements over the existing AT&T ''a.out'' format included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System V
Unix System V (pronounced: "System Five") is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as ''Unix System Unification'', which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV. , the AT&T-derived Unix market is divided between four System V variants: IBM's AIX, Hewlett Packard Enterprise's HP-UX and Oracle's Solaris, plus the free-software illumos forked from OpenSolaris. Overview Introduction System V was the successor to 1982's UNIX System III. While AT&T developed and sold hardware that ran System V, most customers ran a version from a reseller, based on AT&T's reference implementation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deb File Structure
{{disambig ...
Deb or DEB may refer to: People * Deb (surname) * Deb (given name) * A débutante DEB * Dynamic energy budget theory, a metabolic theory * Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica * German Ice Hockey Federation (''Deutscher Eishockey Bund'') * Diepoxybutane, an industrial chemical * Distant Education Bureau, India * New South Wales 900/800 class railcar, Australia Other uses * deb (file format), Debian * Debrecen International Airport IATA airport code * Deb Shops, a former US clothing chain * ''Deb'' (album), 2005, by Souad Massi See also * Debs (other) * Debra (other) * Debbie (other) * Deborah (other) Deborah is a major character in the Book of Judges. Deborah may also refer to: Given name * Deborah (given name) or Devorah, a female given name * Deborah (Genesis), the nurse of Rebecca, a minor character in the Book of Genesis Music * ''Deb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Standard Base
The Linux Standard Base (LSB) was a joint project by several Linux distributions under the organizational structure of the Linux Foundation to standardize the software system structure, including the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard used in the Linux kernel. LSB was based on the POSIX specification, the Single UNIX Specification (SUS), and several other open standards, but extended them in certain areas. According to LSB: The goal of the LSB is to develop and promote a set of open standards that will increase compatibility among Linux distributions and enable software applications to run on any compliant system even in binary form. In addition, the LSB will help coordinate efforts to recruit software vendors to port and write products for Linux Operating Systems. LSB compliance might be certified for a product by a certification procedure. LSB specified standard libraries (centered around the ), a number of commands and utilities that extend the POSIX standard, the layout of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Binutils
The GNU Binary Utilities, or , are a set of programming tools for creating and managing binary programs, object files, libraries, profile data, and assembly source code. Tools They were originally written by programmers at Cygnus Solutions. The GNU Binutils are typically used in conjunction with compilers such as the GNU Compiler Collection (), build tools like , and the GNU Debugger (). Through the use of the Binary File Descriptor library (), most tools support the various object file formats supported by . Commands The include the following commands: elfutils Ulrich Drepper wrote , to partially replace GNU Binutils, purely for Linux and with support only for ELF and DWARF. It distributes three libraries with it for programmatic access. See also * GNU Core Utilities * GNU Debugger * ldd (Unix), list symbols imported by the object file; similar to * List of Unix commands *llvm LLVM is a set of compiler and toolchain technologies that can be used to develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |