|
Application Account
A service account or application account is a digital identity used by an application software or service to interact with other applications or the operating system. They are often used for machine to machine communication (M2M), for example for application programming interfaces (API). The service account may be a privileged identity within the context of the application. Updating passwords Local service accounts can interact with various components of the operating system, which makes coordination of password changes difficult. In practice this causes passwords for service accounts to rarely be changed, which poses a considerable security risk for an organization. Some types of service accounts do not have a password.{{Cite web , title=Best practices for working with service accounts {{! IAM Documentation , url=https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/best-practices-service-accounts , access-date=2023-01-05 , language=en Wide access Service accounts are often used by applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity (philosophy)
In philosophy, identity (from , "sameness") is the relation each thing bears only to itself. The notion of identity gives rise to List of unsolved problems in philosophy, many philosophical problems, including the identity of indiscernibles (if ''x'' and ''y'' share all their properties, are they one and the same thing?), and questions about change and personal identity over time (what has to be the case for a person ''x'' at one time and a person ''y'' at a later time to be one and the same person?). It is important to distinguish between ''qualitative identity'' and ''numerical identity''. For example, consider two children with identical bicycles engaged in a race while their mother is watching. The two children have the ''same'' bicycle in one sense (''qualitative identity'') and the ''same'' mother in another sense (''numerical identity''). This article is mainly concerned with ''numerical identity'', which is the stricter notion. The philosophical concept of identity is dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
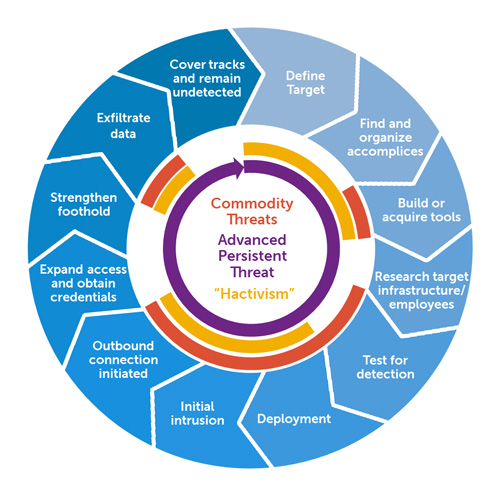
Advanced Persistent Threat
An advanced persistent threat (APT) is a stealthy threat actor, typically a nation state or state-sponsored group, which gains unauthorized access to a computer network and remains undetected for an extended period. In recent times, the term may also refer to non-state-sponsored groups conducting large-scale targeted intrusions for specific goals. Such threat actors' motivations are typically political or economic. Every major business sector has recorded instances of cyberattacks by advanced actors with specific goals, whether to steal, spy, or disrupt. These targeted sectors include government, defense, financial services, legal services, industrial, telecoms, consumer goods and many more. Some groups utilize traditional espionage vectors, including social engineering, human intelligence and infiltration to gain access to a physical location to enable network attacks. The purpose of these attacks is to install custom malware (malicious software). The median "dwell-time", the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a form of business process automation technology based on metaphorical software robots (bots) or on artificial intelligence (AI)/digital workers. It is sometimes referred to as ''software robotics'' (not to be confused with robot software). In traditional workflow automation tools, a software developer produces a list of actions to automate a task and interface to the back end system using internal application programming interfaces (APIs) or dedicated scripting language. In contrast, RPA systems develop the action list by watching the user perform that task in the application's graphical user interface (GUI), and then perform the automation by repeating those tasks directly in the GUI. This can lower the barrier to the use of automation in products that might not otherwise feature APIs for this purpose. RPA tools have strong technical similarities to graphical user interface testing tools. These tools also automate interactions with the GUI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Managed Services
Managed services is the practice of outsourcing the responsibility for maintaining, and anticipating need for, a range of processes and functions, ostensibly for the purpose of improved operations and reduced budgetary expenditures through the reduction of directly-employed staff. It is an alternative to the break/fix or on-demand outsourcing model where the service provider performs on-demand services and bills the customer only for the work done. Under this subscription model, the client or customer is the entity that owns or has direct oversight of the organization or system being managed, whereas the managed services provider (MSP) is the service provider delivering the managed services. The client and the MSP are bound by a contractual, service-level agreement that states the performance and quality metrics of their relationship. Advantages and challenges Adopting managed services is intended to be an efficient way to stay up-to-date on technology, have access to skills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerberos (protocol)
Kerberos () is a computer-network authentication protocol that works on the basis of ''tickets'' to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. Its designers aimed it primarily at a client–server model, and it provides mutual authentication—both the user and the server verify each other's identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks. Kerberos builds on symmetric-key cryptography and requires a trusted third party, and optionally may use public-key cryptography during certain phases of authentication.RFC 4556, abstract. Kerberos uses UDP port 88 by default. The protocol was named after the character '' Kerberos'' (or ''Cerberus'') from Greek mythology, the ferocious three-headed guard dog of Hades. History and development Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) developed Kerberos in 1988 to protect network services provided by Project Athena. The protocol is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Disclosure
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random, and any observable pattern in any medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analog signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning that may be derived from a representation through interpretation. Information is often processed iteratively: Data available at one step are processed into information to be interpreted and processed at the next step. For example, in written text each symbol or letter conveys information relevant to the word it is part of, each word conveys information relevan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation refers to a situation where a statement's author cannot successfully dispute its authorship or the validity of an associated contract. The term is often seen in a legal setting when the authenticity of a signature is being challenged. In such an instance, the authenticity is being "repudiated". For example, Mallory buys a cell phone for $100, writes a paper cheque as payment, and signs the cheque with a pen. Later, she finds that she can't afford it, and claims that the cheque is a forgery. The signature guarantees that only Mallory could have signed the cheque, and so Mallory's bank must pay the cheque. This is non-repudiation; Mallory cannot repudiate the cheque. In practice, pen-and-paper signatures aren't hard to forge, but digital signatures can be very hard to break. In security In general, ''non-repudiation'' involves associating actions or changes with a unique individual. For example, a secure area may use a key card access system where non-repudiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoofing Attack
In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage. Internet Spoofing and TCP/IP Many of the protocols in the TCP/IP suite do not provide mechanisms for authenticating the source or destination of a message, leaving them vulnerable to spoofing attacks when extra precautions are not taken by applications to verify the identity of the sending or receiving host. IP spoofing and ARP spoofing in particular may be used to leverage man-in-the-middle attacks against hosts on a computer network. Spoofing attacks which take advantage of TCP/IP suite protocols may be mitigated with the use of firewalls capable of deep packet inspection or by taking measures to verify the identity of the sender or recipient of a message. Domain name spoofing The term 'Domain name spoofing' (or simply though less accurately, 'Domain spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privilege Escalation
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, a design flaw, or a configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions. Background Most computer systems are designed for use with multiple user accounts, each of which has abilities known as privileges. Common privileges include viewing and editing files or modifying system files. Privilege escalation means users receive privileges they are not entitled to. These privileges can be used to delete files, view private information, or install unwanted programs such as viruses. It usually occurs when a system has a bug that allows security to be bypassed or, alternatively, has flawed design assumptions about how it will be used. Privilege escalation occurs in two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Identity
A digital identity is information used by computer systems to represent an external agent – a person, organization, application, or device. Digital identities allow access to services provided with computers to be automated and make it possible for computers to mediate relationships. The use of digital identities is so widespread that many discussions refer to the ''entire'' collection of information generated by a person's online activity as a "digital identity". This includes usernames, passwords, Search engine, search history, birthdate, social security number, and purchase history, especially where that information is publicly available and not anonymized and so can be used by others to discover that person's civil identity. In this broader sense, a digital identity is a facet of a person's social identity and is also referred to as ''online identity''. An individual's digital identity is often linked to their civil or national identity and many countries have instituted n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the severity of the failure, as compared to a naively designed system, in which even a small failure can cause total breakdown. Fault tolerance is particularly sought after in high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems. The ability of maintaining functionality when portions of a system break down is referred to as graceful degradation. A fault-tolerant design enables a system to continue its intended operation, possibly at a reduced level, rather than failing completely, when some part of the system fails. The term is most commonly used to describe computer systems designed to continue more or less fully operational with, perhaps, a reduction in throughput or an increase in response time in the event of some partial fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)