|
Apochromatic
An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens that has better correction of chromatic and spherical aberration than the much more common achromat lenses. Explanation Chromatic aberration is the phenomenon of different colors focusing at different distances from a lens. In photography, chromatic aberration produces soft overall images, and color fringing at high-contrast edges, like an edge between black and white. Astronomers face similar problems, particularly with telescopes that use lenses rather than mirrors. ''Achromatic'' lenses are corrected to bring ''two'' wavelengths into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.590 µm) and blue (~0.495 µm). ''Apo''chromatic lenses are designed to bring ''three'' colors into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.620 µm), green (~0.530 µm), and blue (~0.465 µm). The residual color error (secondary spectrum) can be up to an order of magnitude less than for an ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apochromat
An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens that has better correction of chromatic and spherical aberration than the much more common achromat lenses. Explanation Chromatic aberration is the phenomenon of different colors focusing at different distances from a lens. In photography, chromatic aberration produces soft overall images, and color fringing at high-contrast edges, like an edge between black and white. Astronomers face similar problems, particularly with telescopes that use lenses rather than mirrors. ''Achromatic'' lenses are corrected to bring ''two'' wavelengths into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.590 µm) and blue (~0.495 µm). ''Apo''chromatic lenses are designed to bring ''three'' colors into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.620 µm), green (~0.530 µm), and blue (~0.465 µm). The residual color error (secondary spectrum) can be up to an order of magnitude less than for an achromat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apochromatic Focal Curve
An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens that has better correction of chromatic and spherical aberration than the much more common achromat lenses. Explanation Chromatic aberration is the phenomenon of different colors focusing at different distances from a lens. In photography, chromatic aberration produces soft overall images, and color fringing at high-contrast edges, like an edge between black and white. Astronomers face similar problems, particularly with telescopes that use lenses rather than mirrors. ''Achromatic'' lenses are corrected to bring ''two'' wavelengths into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.590 µm) and blue (~0.495 µm). ''Apo''chromatic lenses are designed to bring ''three'' colors into focus in the same plane – typically red (~0.620 µm), green (~0.530 µm), and blue (~0.465 µm). The residual color error (secondary spectrum) can be up to an order of magnitude less than for an achr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Aberration Lens Diagram
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the twelve-note chromatic scale, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek music theory to a particular tuning of the tetrachord, and to a rhythmic notational convention in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
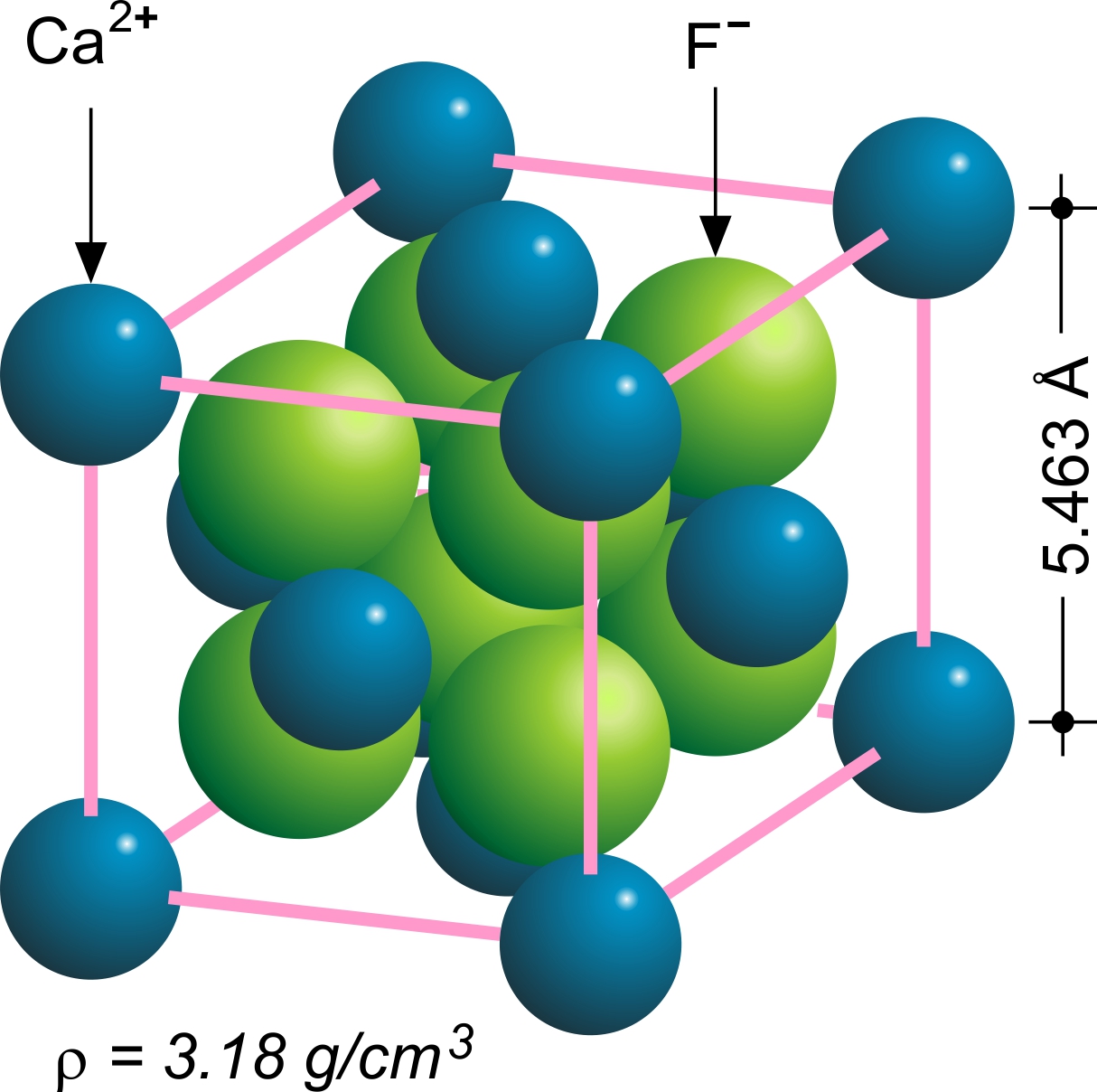
Fluorite Lens
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superachromat
The superachromat or superachromatic lens was first conceived and developed by Maximilian Herzberger as the ultimate well-corrected lens. The color shift curve of a superachromat is a quartic, meaning that in theory four separate colors can be brought to focus in the same plane, while simultaneously correcting spherical aberration and field aberrations. This near-perfect correction of chromatic aberration is highly beneficial in film and digital multi-spectral photography, as a superachromat can focus near-infrared energy in the 0.7 to 1.0 micrometer wavelength band in the same focal plane as visible light, eliminating the need for refocusing. Unfortunately, due to the limited selection of optical glasses and partial dispersion properties, superachromats must be manufactured with costly fluorite glasses and to very tight tolerances. {{clear, left See also *Photographic lens *Achromat *Apochromat An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoom Lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length (and thus angle of view) can be varied, as opposed to a fixed-focal-length (FFL) lens (see prime lens). A true zoom lens, also called a parfocal lens, is one that maintains focus when its focal length changes. Most consumer zoom lenses do not maintain perfect focus, but are still parfocal designs. Most camera phones that are advertised as having optical zoom actually use a few cameras of different but fixed focal length, combined with digital zoom to make a hybrid system. The convenience of variable focal length comes at the cost of complexity – and some compromises on image quality, weight, dimensions, aperture, autofocus performance, and cost. For example, all zoom lenses suffer from at least slight, if not considerable, loss of image resolution at their maximum aperture, especially at the extremes of their focal length range. This effect is evident in the corners of the image, when display ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Lens
In film and photography, a prime lens is a fixed focal length photographic lens (as opposed to a zoom lens), typically with a maximum aperture from f2.8 to f1.2. The term can also mean the primary lens in a combination lens system. Confusion between these two meanings can occur without clarifying context. Alternate terms, such as ''primary focal length'', ''fixed focal length'', or ''FFL'' are sometimes used to avoid ambiguity. As alternative to zoom lens The term ''prime'' has come to mean the opposite of ''zoom''—a fixed-focal-length, or unifocal lens. While a prime lens of a given focal length is less versatile than a zoom lens, it is often of superior optical quality, wider maximum aperture, lighter weight, and smaller size. These advantages stem from having fewer moving parts, optical elements optimized for one particular focal length, and a less complicated lens formula that creates fewer optical aberration issues. Larger maximum aperture (smaller f-number) facilita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''λ''0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint Glass
Flint glass is optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number (high dispersion). Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45 and 2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is commonly combined with a convex lens of crown glass to produce an achromatic doublet lens because of their compensating optical properties, which reduces chromatic aberration (colour defects). With respect to glass, the term ''flint'' derives from the flint nodules found in the chalk deposits of southeast England that were used as a source of high purity silica by George Ravenscroft, c. 1662, to produce a potash lead glass that was the precursor to English lead crystal. Traditionally, flint glasses were lead glasses containing around 4–60% lead(II) oxide; however, the manufacture and disposal of these glasses were sources of pollution. In many modern flint gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Glass (optics)
Crown glass is a type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. It has relatively low refractive index (≈1.52) and low dispersion (with Abbe numbers around 60). Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide and is one of the earliest low dispersion glasses. As well as the specific material named ''crown glass'', there are other optical glasses with similar properties that are also called crown glasses. Generally, this is any glass with Abbe numbers in the range 50 to 85. For example, the borosilicate glass Schott BK7 (Schott designates it as 517642. The first three digits tell you its refractive index (1.517) and the last three tell you its Abbé number (64.2))The crown/flint distinction is so important to optical glass technology that many glass names, notably Schott glasses, incorporate it. A ''K'' in a Schott name indicates a crown glass (''Krone'' in German — Schott is a German company). The ''B'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |