|
Anti-Shakerism
Anti-Shakerism refers to negative attitudes concerning the Shakers. At their peak in popularity in the first half of the 19th century in the United States, the Shakers had approximately 4,000 to 6,000 members. , the Shakers currently have at least three active members; few to no extant religious or ethnic groups have fewer members than the Shakers. Issues Perhaps most significant to the hostility towards Shakers concerned their celibacy, millenarianism, and views on race and gender. The main current writer on anti-Shakerism compares allegations against them as similar to other celibate religious groups like Roman Catholic monks and nuns, although there are also similarities with hostility to Mormons or Masons. People who formerly resided in Shaker communities even wrote anti-Shaker tracts as some former, or allegedly former, nuns did. Their millenarian views drew ire. Under Joseph Meachem, beliefs concerning God coming to destroy the Anti-Christ and create a better world grew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Shakerism
Anti-Shakerism refers to negative attitudes concerning the Shakers. At their peak in popularity in the first half of the 19th century in the United States, the Shakers had approximately 4,000 to 6,000 members. , the Shakers currently have at least three active members; few to no extant religious or ethnic groups have fewer members than the Shakers. Issues Perhaps most significant to the hostility towards Shakers concerned their celibacy, millenarianism, and views on race and gender. The main current writer on anti-Shakerism compares allegations against them as similar to other celibate religious groups like Roman Catholic monks and nuns, although there are also similarities with hostility to Mormons or Masons. People who formerly resided in Shaker communities even wrote anti-Shaker tracts as some former, or allegedly former, nuns did. Their millenarian views drew ire. Under Joseph Meachem, beliefs concerning God coming to destroy the Anti-Christ and create a better world grew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Marshall Dyer
Mary Marshall Dyer (1780–1867) was a voice for the largely forgotten anti-Shakerism sentiment in rural New Hampshire, United States. In 1813 she joined the Shakers of Enfield, New Hampshire. Disappointed in her lack of a leadership role and frustrated by the constraints of Shaker life, Dyer left the community in 1815. Her husband, Joseph, remained, as did all five of the Dyer children. Mary Dyer accused the Shakers of alienating her from her children. Fearing for her children's safety and left without any means of financial support, she gave public talks and wrote tracts against the Shakers in an attempt to gain public, and legislative, support for her cause. Her principal writings included ''A Brief Statement of the Sufferings of Mary Dyer'' and ''A Portraiture of Shakerism'' in 1822. In 1819, she attempted to raise a mob to storm the Enfield Shaker Community to take her children back, but this effort failed. Joseph Dyer remained devoted to the community and criticized her in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
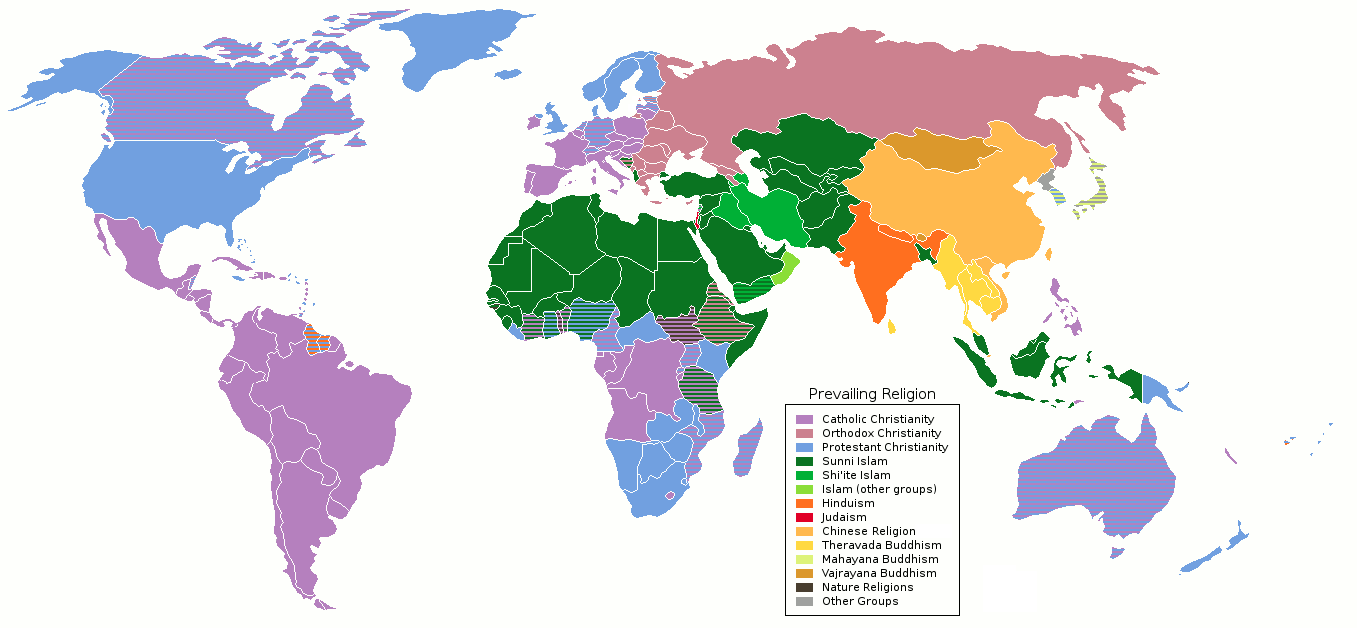
Religious Denomination
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name and tradition among other activities. The term refers to the various Christian denominations (for example, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and the many varieties of Protestantism). It is also used to describe the five major branches of Judaism (Karaite Judaism, Orthodox, Conservative, Reform, and Reconstructionist). Within Islam, it can refer to the branches or sects (such as Sunni, Shia), as well as their various subdivisions such as sub-sects, schools of jurisprudence, schools of theology and religious movements. The world's largest religious denominations are Sunni Islam and Catholic Church. Christianity A Christian denomination is a generic term for a distinct religious body identified by traits such as a common name, structure, leadership and doctrine. Individual bodies, however, may use alternative terms to describe themselves, such as church or fellowship. Divisions between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaker Quarterly
''The Shaker Quarterly'' was a periodical published by the Sabbathday Lake Shaker Village from 1961 to 1996. It served as a journal and newsletter about the Shakers The United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing, more commonly known as the Shakers, are a Millenarianism, millenarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian sect founded in England and then organized in the Unit ..., and at times also doubled as a mail order catalog advertising products created by the Shaker community at Sabbathday Lake. It was the first regular Shaker publication since the ''Manifesto'' ceased publication in 1899. The ''Quarterly'' was launched in 1961 by Theodore E. Johnson and Mildred Barker. An attempt to keep Shaker doctrine alive, its founding marked the beginning of a renewed interest in the Shakers during the 1960s. Several Shaker industries were revived, including the Shaker herb industry, at Sabbathday Lake. In 1971, the Shaker community began stocking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
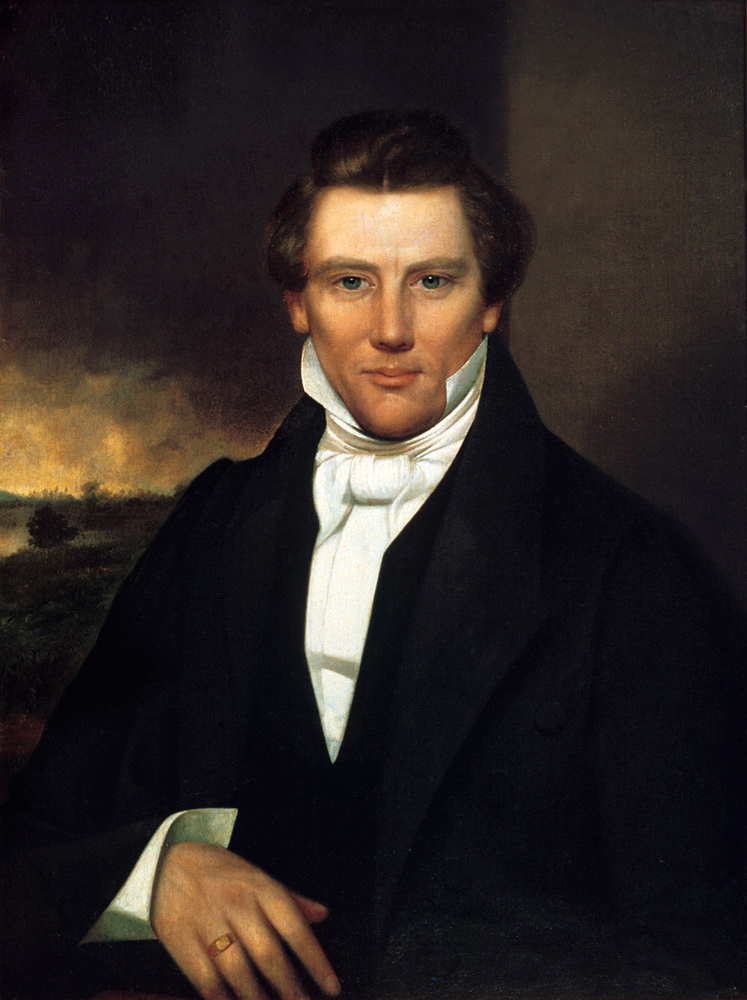
Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, he had attracted tens of thousands of followers and founded a religion that continues to the present with millions of global adherents. Smith was born in Sharon, Vermont. By 1817, he had moved with his family to Western New York, the site of intense religious revivalism during the Second Great Awakening. Smith said he experienced a series of visions, including one in 1820 during which he saw "two personages" (whom he eventually described as God the Father and Jesus Christ), and another in 1823 in which an angel directed him to a buried book of golden plates inscribed with a Judeo-Christian history of an ancient American civilization. In 1830, Smith published what he said was an English translation of these plates called the ''Book of Mormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revelation In Mormonism
In Mormonism, revelation is communication from God to man. Latter Day Saints teach that the Latter Day Saint movement began with a revelation from God, which began a process of restoring the gospel of Jesus Christ to the earth. Latter Day Saints also teach that revelation is the foundation of the church established by Jesus Christ and that it remains an essential element of his true church today. Continuous revelation provides individual Latter Day Saints with a "testimony", described by Richard Bushman as "one of the most potent words in the Mormon lexicon". In response to an inquiry on the beliefs of the church, Joseph Smith wrote what came to be called the Wentworth Letter, the last section of which was canonized as the Articles of Faith. The fifth, sixth, seventh and ninth articles state the essence of Latter Day Saint belief concerning revelation: : 5 We believe that a man must be called of God, by prophecy, and by the laying on of hands by those who are in authority, to pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Church Of Jesus Christ Of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the One true church#Latter Day Saint movement, original church founded by Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. The church is headquartered in the United States in Salt Lake City, Salt Lake City, Utah, and has established congregations and built Temple (LDS Church), temples worldwide. According to the church, it has over 16.8 million the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints membership statistics, members and 54,539 Missionary (LDS Church), full-time volunteer missionaries. The church is the Christianity in the United States, fourth-largest Christian denomination in the United States, with over 6.7 million US members . It is the List of denominations in the Latter Day Saint movement, largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctrine And Covenants
The Doctrine and Covenants (sometimes abbreviated and cited as D&C or D. and C.) is a part of the open scriptural canon of several denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement. Originally published in 1835 as Doctrine and Covenants of the Church of the Latter Day Saints: Carefully Selected from the Revelations of God, editions of the book continue to be printed mainly by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and the Community of Christ (formerly the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints LDS Church. The book originally contained two parts: a sequence of lectures setting forth basic church doctrine, followed by a compilation of revelations, or "covenants" of the church: thus the name "Doctrine and Covenants". The "doctrine" portion of the book, however, has been removed by both the LDS Church and Community of Christ. The remaining portion of the book contains revelations on numerous topics, most of which were dictated by the movement's fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult
In modern English, ''cult'' is usually a pejorative term for a social group that is defined by its unusual religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals, or its common interest in a particular personality, object, or goal. This sense of the term is controversial and weakly defined—having divergent definitions both in popular culture and academia—and has also been an ongoing source of contention among scholars across several fields of study. Richardson, James T. 1993. "Definitions of Cult: From Sociological-Technical to Popular-Negative." ''Review of Religious Research'' 34(4):348–56. . . An older sense of the word involves a set of religious devotional practices that are conventional within their culture, related to a particular figure, and often associated with a particular place. References to the "cult" of a particular Catholic saint, or the imperial cult of ancient Rome, for example, use this sense of the word. While the literal and original sense of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Countercult Movement
The Christian countercult movement or the Christian anti-cult movement is a social movement among certain Protestant evangelical and fundamentalist and other Christian ministries ("discernment ministries") and individual activists who oppose religious sects that they consider cults. Overview Christian countercult activism mainly stems from evangelicalism or fundamentalism. The countercult movement asserts that particular Christian sects are erroneous because their beliefs are not in accordance with the teachings of the Bible. It also states that a religious sect can be considered a cult if its beliefs involve a denial of any of the essential Christian teachings (such as salvation, the Trinity, Jesus himself as a person, the ministry and miracles of Jesus, his crucifixion, his resurrection, the Second Coming and the Rapture). Countercult ministries often concern themselves with religious sects that consider themselves Christian but hold beliefs that are thought to contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
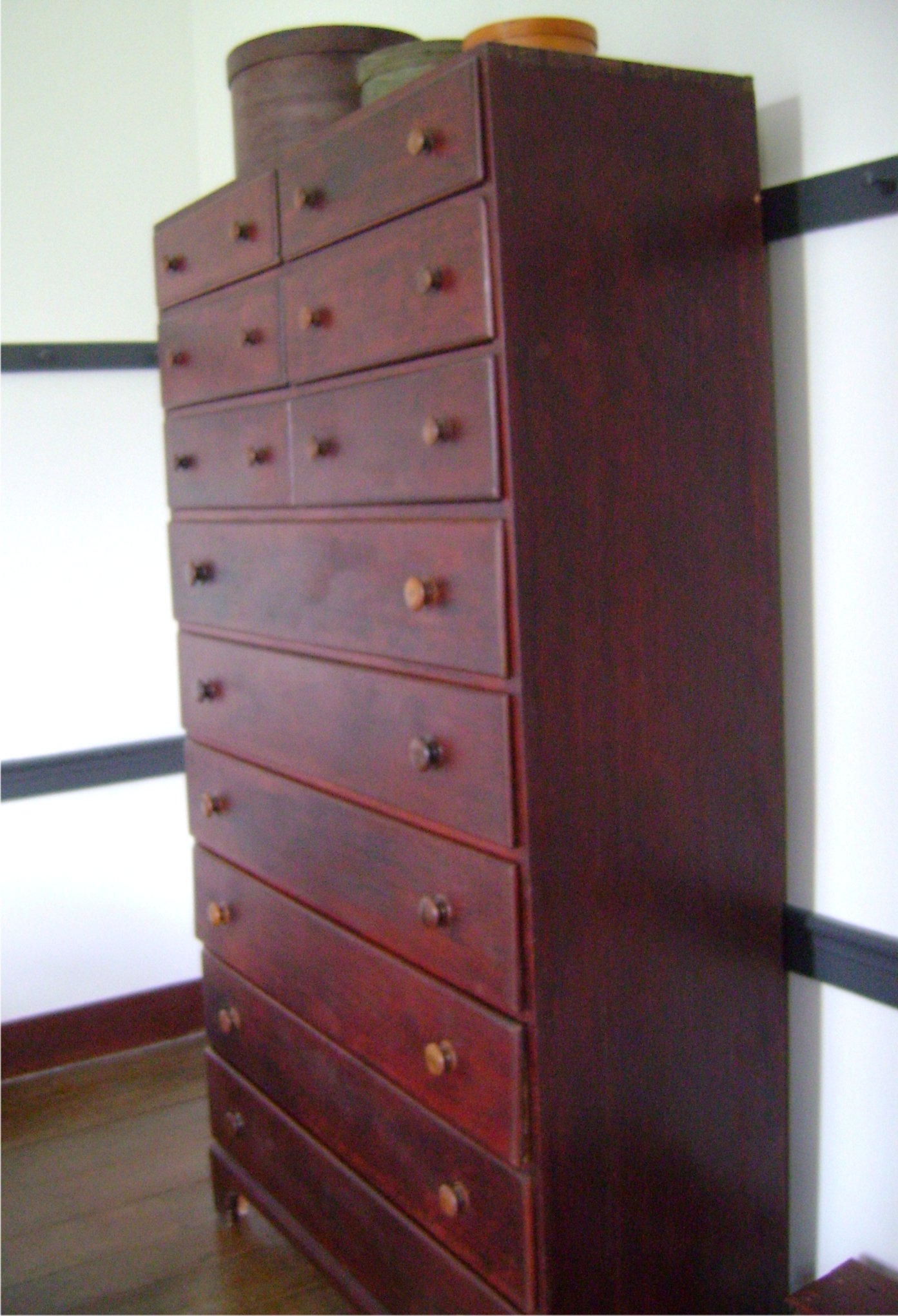
Shaker Furniture
__NOTOC__ Shaker furniture is a distinctive style of furniture developed by the United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing, commonly known as Shakers, a religious sect that had guiding principles of simplicity, utility and honesty. Their beliefs were reflected in the well-made furniture of minimalist designs. History Shaker communities were largely self-sufficient: in their attempt to separate themselves from the outside world and to create a heaven-on-earth, members grew their own food, constructed their own buildings, and manufactured their own tools and household furnishings.—Metropolitan Museum of Art''Shaker furniture''. Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved March 23, 2014. Overview Furniture was made thoughtfully, with functional form and proportion. Rather than using o ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |