|
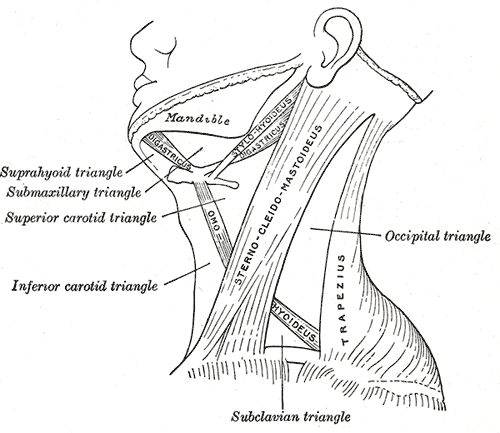
Anterior Triangle
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck. Structure The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin. Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor. Anatomy Muscles: * Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and Post Belly), mylohyoid, geniohyoid and Stylohyoid. * Infrahyoid muscles - Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, Sternothyroid, and Thyrohyoid. Nerve supply 2 Bellies of Digastric * Anterior: Mylohyoid nerve * Posterior: Facial nerve Stylohyoid: by the facial nerve, by a branch from that to the posterior belly of digastric. Mylohyoid: by its own nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar ( from the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve), which arises just before the parent nerve enters the mandibular foramen, pierces the sphenomandibular ligament, and runs forward on the inferior surface of the mylohyoid, supplying it and the anterior belly of the digastric. Geniohyoid: by a branch from the hypoglossal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches. In the human embryo, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of development. They appear as a series of outpouchings of mesoderm on both sides of the developing pharynx. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches is known as the aortic arches. In fish, the branchial arches support the gills. Structure In vertebrates, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three germ layers (the primary layers of cells that form during embryogenesis). Neural crest cells enter these arches where they contribute to features of the skull and facial skeleton such as bone and cartilage. However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existence of neural crest-independent mechanisms of phary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck
Posterior may refer to: * Posterior (anatomy), the end of an organism opposite to its head ** Buttocks, as a euphemism * Posterior horn (other) * Posterior probability The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior p ..., the conditional probability that is assigned when the relevant evidence is taken into account * Posterior tense, a relative future tense {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the manub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submental Triangle
The submental triangle (or suprahyoid triangle) is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck. Boundaries It is limited to: * Lateral (away from the midline), formed by the anterior belly of the digastricus * Medial (towards the midline), formed by the midline of the neck between the mandible and the hyoid bone * Inferior Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton *Inferior (book), ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The ... (below), formed by the body of the hyoid bone *Floor is formed by the mylohyoideus *Roof is formed by Investing layer of deep cervical fascia Contents It contains one or two lymph glands, the submental lymph nodes (three or four in number) and Submental veins and commencement of anterior jugular veins. (The contents of the triangle actually lie in the superficial fascia over the roof of submental t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submandibular Triangle
The submandibular triangle (or submaxillary or digastric triangle) corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible. Boundaries and coverings It is bounded: * ''above'', by the lower border of the body of the mandible, and a line drawn from its angle to the mastoid process; * ''below'', by the posterior belly of the Digastricus; in front, by the anterior belly of the Digastricus. It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, Platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are branches of the facial nerve and ascending filaments of the cutaneous cervical nerve. Its floor is formed by the Mylohyoideus anteriorly, and by the hyoglossus posteriorly. Triangles * Beclard Triangle * Lesser Triangle * Pirogoff Triangle Divisions It is divided into an anterior and a posterior part by the stylomandibular ligament. Anterior part The anterior part contains the submandibular gland, superficial to which is the anterior facial vein, while imbedde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Triangle
The carotid triangle (or superior carotid triangle) is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck. Coverings and boundaries It is bounded: * Posteriorly by the anterior border of the Sternocleidomastoid; * Anteroinferiorly, by the superior belly of the Omohyoid muscle. * Superiorly by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is (covered) by the integument, superficial fascia, Platysma and deep fascia; ramifying in which are branches of the facial and cutaneous cervical nerves. Its floor is formed by parts of the * Thyrohyoid membrane, *Hyoglossus, and the *Constrictores pharyngis medius and inferior. Arteries The external and internal carotids lie side by side, the external being the more anterior of the two. The following branches of the external carotid are also met with in this space: * the superior thyroid artery, running forward and downward; * the lingual artery, directly forward; * the facial artery, forward and upward; * the occipital artery, backward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Triangle
The inferior carotid triangle (or muscular triangle), is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid. It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are some of the branches of the supraclavicular nerves. Beneath these superficial structures are the sternohyoid and sternothyroid, which, together with the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid, conceal the lower part of the common carotid artery. This vessel is enclosed within its sheath, together with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve; the vein lies lateral to the artery on the right side of the neck, but overlaps it below on the left side; the nerve lies between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both. In front of the sheath are a few descending filaments from the ansa cervicalis; behind the sheath are the infe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omohyoideus
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck, and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. The omohyoid muscle is proximally attached to the scapula and distally attached to the hyoid bone, stabilising it. Its superior belly serves as the most lateral member of the infrahyoid muscles, located lateral to both the sternothyroid muscles and the thyrohyoid muscles.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 102 Structure The omohyoid muscle arises from the upper border of the scapula, inserting into the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone. It has two separate bellies, superior and inferior: * The ''inferior belly'' forms a flat, narrow fasciculus, which inclines forward and slightly upward across the lower part of the neck, being bound down to the clavicle by a fibrous expansion; it then passes behind the sternocleidomastoid, becomes tendinous and changes its dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digastricus
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis. It lies below the body of the mandible, and extends, in a curved form, from the mastoid notch to the mandibular symphysis. It belongs to the suprahyoid muscles group. A broad aponeurotic layer is given off from the tendon of the digastric muscle on either side, to be attached to the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone; this is termed the suprahyoid aponeurosis. Structure The digastricus (digastric muscle) consists of two muscular bellies united by an intermediate rounded tendon. The two bellies of the digastric muscle have different embryological origins, and are supplied by different cranial nerves. Each person has a right and left digastric muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve) and anterior to cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). The facial nerve also supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to several head and neck ganglia. The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis. The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: # intracranial (cisternal) segment # meatal (canalicular) segment (within the internal auditory canal) # labyrinthine segmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular Notch
The suprasternal notch, also known as the fossa jugularis sternalis, jugular notch, or Plender gap, is a large, visible dip in between the neck in humans, between the clavicles, and above the manubrium of the sternum. Structure The suprasternal notch is a visible dip in between the neck, between the clavicles, and above the manubrium of the sternum. It is at the level of the T2 and T3 vertebrae. The trachea lies just behind it, rising about 5 cm above it in adults. Clinical significance Intrathoracic pressure is measured by using a transducer held in such a way over the body that an actuator engages the soft tissue that is located above the suprasternal notch. Arcot J. Chandrasekhar, MD of Loyola University, Chicago, is the author of an evaluative test for the aorta using the suprasternal notch. - Evaluative tests using the suprasternal notch The test can help recognize the following conditions: * Aneurysm * Dissecting aneurysm * Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |