|
Anorthositic
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic minerals most commonly present. Anorthosites are of enormous geologic interest, because it is still not fully understood how they form. Most models involve separating plagioclase crystals based on their density. Plagioclase crystals are usually less dense than magma; so, as plagioclase crystallizes in a magma chamber, the plagioclase crystals float to the top, concentrating there. Anorthosite on Earth can be divided into five types: # Archean-age anorthosites # Proterozoic anorthosite (also known as massif or massif-type anorthosite) – the most abundant type of anorthosite on Earth # Layers within Layered Intrusions (e.g., Bushveld and Stillwater intrusions) # Mid-ocean ridge and transform fault anorthosites # Anorthosite xenoliths in other rocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Moon
The geology of the Moon (sometimes called selenology, although the latter term can refer more generally to "lunar science") is quite different from that of Earth. The Moon lacks a true atmosphere, which eliminates erosion due to weather. It does not have any known form of plate tectonics, it has a lower gravity, and because of its small size, it cooled faster. The complex geomorphology of the lunar surface has been formed by a combination of processes, especially impact cratering and volcanism. The Moon is a differentiated body, with a crust, mantle, and core. Geological studies of the Moon are based on a combination of Earth-based telescope observations, measurements from orbiting spacecraft, lunar samples, and geophysical data. Six locations were sampled directly during the crewed Apollo program landings from 1969 to 1972, which returned of lunar rock and lunar soil to Earth In addition, three robotic Soviet Luna spacecraft returned another of samples, and the Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salem District
Salem District is one of the 38 districts of Tamil Nadu state in southern India. The district is now divided into Dharmapuri, Krishnagiri, Namakkal as individual districts. Salem is the district headquarters and other major towns in the district include Mettur, Thammampatti, Attur, Omalur, Sankagiri and Edappadi. That Salem dates to at least two thousand years ago is evident from the discovery of silver coins from the Roman Emperor Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (37–68 CE) found by Koneripatti of Salem in 1987. It was ruled by Mazhavar King Kolli Mazhavan and kings Adhiyaman and Valvil Ori of Sangam age. It is part of Mazhanadu, a vast region that dates to the second century BCE. Salem was the largest district of Tamil Nadu. It was bifurcated into Salem and Dharmapuri districts in 1965 and Namakkal district in 1997. Now Salem has been developed a lot by building many bridges and is considered to be the smart city. Salem is famous for cultivating mangoes. Politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students. Located about south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg. Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar, Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region. Heidelberg University, founded in 1386, is Germany's oldest and one of Europe's most reputable universities. Heidelberg is a Science, scientific hub in Germany and home to several internationally renowned #Research, research facilities adjacent to its university, including the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and four Max Planck Society, Max Planck Institutes. The city has also been a hub for the arts, especially literature, throughout the centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such as granite, quartz monzonite, or diorite (see also ''granite dome''). Formation Although they may appear uniform, batholiths are in fact structures with complex histories and compositions. They are composed of multiple masses, or ''plutons'', bodies of igneous rock of irregular dimensions (typically at least several kilometers) that can be distinguished from adjacent igneous rock by some combination of criteria including age, composition, texture, or mappable structures. Individual plutons are solidified from magma that traveled toward the surface from a zone of partial melting near the base of the Earth's crust. Traditionally, these plutons have been considered to form by ascent of relatively buoyant magma in large masses called ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock (geology)
In geology, a stock is an igneous intrusion that has a surface exposure of less than ,Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, p. 513. . differing from batholiths only in being smaller. A stock has a discordant relationship with the rocks that it intrudes. Many stocks are cupolas of hidden batholiths. Some circular or elliptical stocks may be volcanic plugs, which fill the vents of now extinct volcanoes. A boss is a small stock. Examples * the Alta and Clayton Peak stocks (composed of granodiorite), near Park City, Utah * the Hellroaring Creek and Salal Creek stocks (of granite-granodiorite and quartz monzonite, respectively) in British Columbia, Canada * the Céret stock (of gabbro and diorite) in Pyrénées-Orientales, France * the Parashi stock (of tonalite) in La Guajira Department, Colombia * stocks of syenite in the Caldera de Tejeda on Gran Canaria * Ailsa Craig Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annum
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution. The geological time scale (GTS), as defined by international convention, depicts the large spans of time from the beginning of the Earth to the present, and its divisions chronicle some definitive events of Earth history. (In the graphic, Ma means "million years ago".) Earth formed around 4.54 billion years ago, approximately one-third the age of the universe, by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere and then the ocean, but the early atmosphere contained almost no oxygen. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. While the Earth was in its earliest stage (Early Earth), a gia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment (country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in igneous rock entrained during magma ascent, emplacement and eruption. Xenoliths may be engulfed along the margins of a magma chamber, torn loose from the walls of an erupting lava conduit or explosive diatreme or picked up along the base of a flowing body of lava on the Earth's surface. A xenocryst is an individual foreign crystal included within an igneous body. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. Xenoliths can be non-uniform within individual locations, even in areas which are spatially limited, e.g. rhyolite-dominated lava of Niijima volcano (Japan) contains two types of gabbroic xenoliths which are of different origin - they were formed in different temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillwater Igneous Complex
The Stillwater igneous complex is a large layered mafic intrusion (LMI) located in southern Montana in Stillwater, Sweet Grass and Park Counties. The complex is exposed across 30 miles (48 km) of the north flank of the Beartooth Mountain Range. The complex has extensive reserves of chromium ore and has a history of being mined for chromium. More recent mining activity has produced palladium and other platinum group elements.The Stillwater Complex: A review of the geology by I. S. McCallum http://serc.carleton.edu/files/NAGTWorkshops/petrology03/McCallum.Stillwater.doc Geology The Stillwater complex is a large layered intrusion with many similarities to the Bushveld igneous complex of South Africa. The complex was intruded into existing gneisses during the Archean at about 2700 Ma. Host rocks on the northern side are Archean sedimentary rocks while the southern boundary includes Precambrian rocks of granite, granite gneiss and schist. The Precambrian rock on its southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
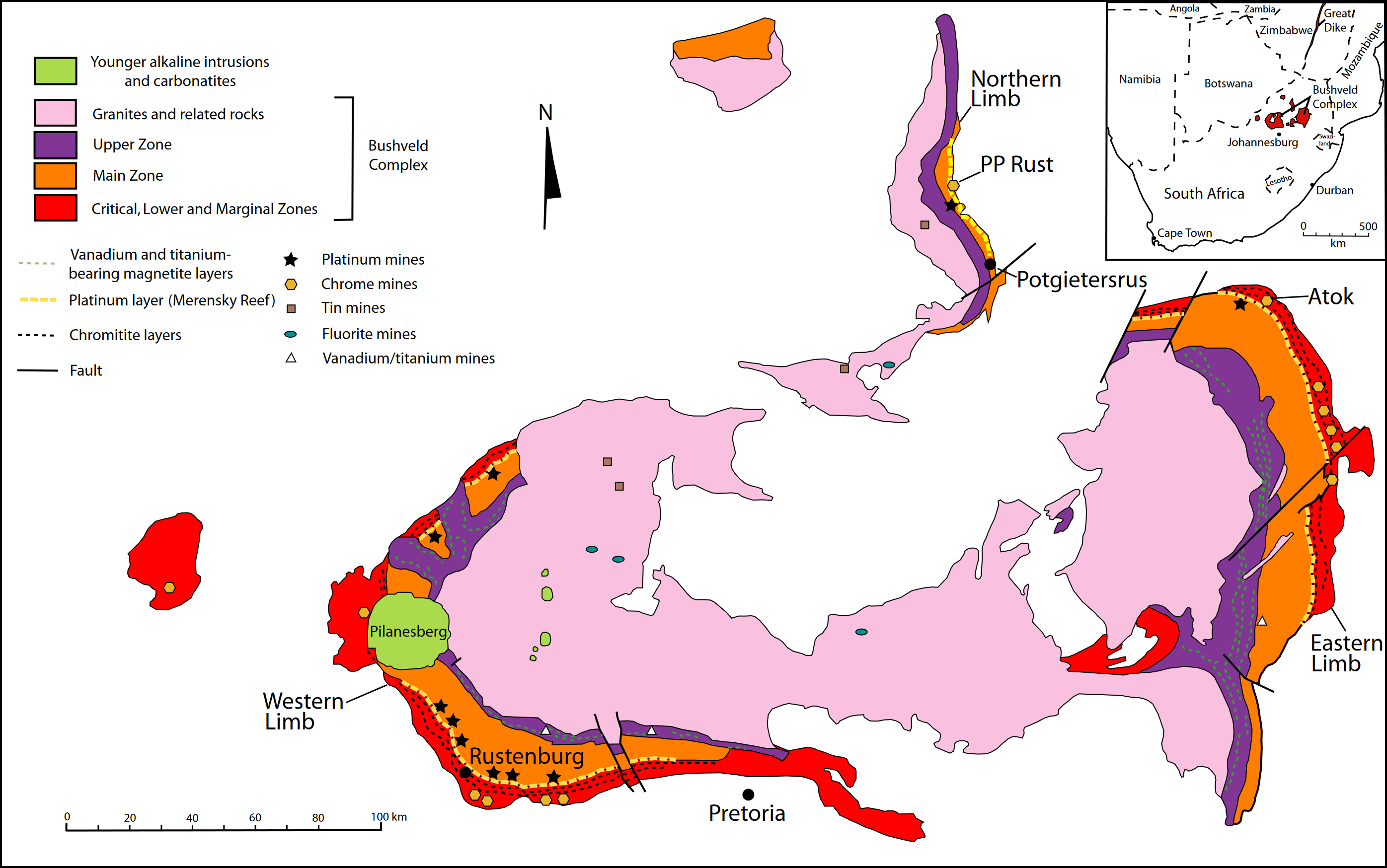
Bushveld Igneous Complex
The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion within the Earth's crust. It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately 2 billion years old and is divided into four different limbs: the northern, southern, eastern, and western limbs. The Bushveld Complex comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments. The site was first discovered around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff. Located in South Africa, the BIC contains some of the richest ore deposits on Earth. The complex contains the world's largest reserves of platinum-group metals (PGMs) or platinum group elements (PGEs)—platinum, palladium, osmium, iridium, rhodium, and ruthenium along with vast quantities of iron, tin, chromium, titanium and vanadium. These are used in, but not limited to, jewellery, automobiles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Labrador.jpg)