|
Alpha-glucosidase
α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20, maltase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, α-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, α-D-glucosidase, α-glucoside hydrolase, α-1,4-glucosidase, α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; systematic name α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase located in the brush border of the small intestine that acts upon α(1→4) bonds: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose This is in contrast to β-glucosidase. α-Glucosidase breaks down starch and disaccharides to glucose. Other glucosidases include: * Cellulase * Beta-glucosidase * Debranching enzyme Mechanism α-Glucosidase hydrolyzes terminal non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-glucose residues to release a single α-glucose molecule. α-Glucosidase is a carbohydrate-hydrolase that releases α-glucose as opposed to β-glucose. β-Glucose residues can be released by glucoamylase, a functionally similar enzyme. The sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) are oral anti-diabetic drugs used for diabetes mellitus type 2 that work by preventing the digestion of carbohydrates (such as starch and table sugar). Carbohydrates are normally converted into simple sugars (monosaccharides) by alpha-glucosidase enzymes present on cells lining the intestine, enabling monosaccharides to be absorbed through the intestine. Hence, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors reduce the impact of dietary carbohydrates on blood sugar. Examples and differences Examples of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors include: * Acarbose- Precose or Glucobay * Miglitol – Glyset * Voglibose Even though the drugs have a similar mechanism of action, there are subtle differences between acarbose and miglitol. Acarbose is an oligosaccharide, whereas miglitol resembles a monosaccharide. Miglitol is fairly well absorbed by the body, as opposed to acarbose. Moreover, acarbose inhibits pancreatic alpha-amylase in addition to alpha-glucosidase, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosidase
Glucosidases are the glycoside hydrolase enzymes categorized under the EC number 3.2.1. Function Alpha-glucosidases are enzymes involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into their monomers. They catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates including alpha- or beta-linked polymers of glucose. This enzyme convert complex sugars into simpler ones. Members Different sources include different members in this class. Members marked with a "#" are considered by MeSH to be glucosidases. Clinical significance Alpha-glucosidases are targeted by alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose and miglitol to control diabetes mellitus type 2. See also * DNA glycosylases * Mucopolysaccharidoses Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
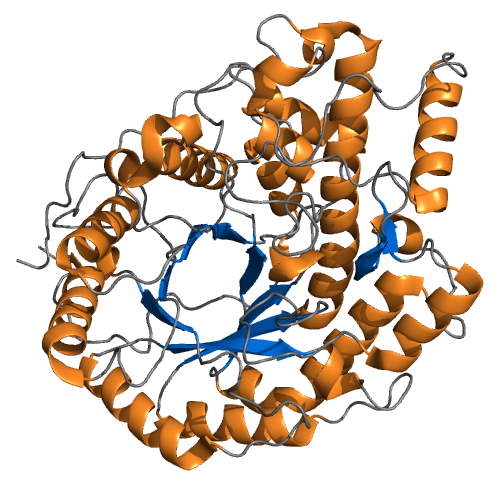
Alpha-glucosidase In Complex With Maltose And NAD+
α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20, maltase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, α-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, α-D-glucosidase, α-glucoside hydrolase, α-1,4-glucosidase, α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; systematic name α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase located in the brush border of the small intestine that acts upon α(1→4) bonds: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose This is in contrast to β-glucosidase. α-Glucosidase breaks down starch and disaccharides to glucose. Other glucosidases include: * Cellulase * Beta-glucosidase * Debranching enzyme Mechanism α-Glucosidase hydrolyzes terminal non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-glucose residues to release a single α-glucose molecule. α-Glucosidase is a carbohydrate-hydrolase that releases α-glucose as opposed to β-glucose. β-Glucose residues can be released by glucoamylase, a functionally similar enzyme. The substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltase
Maltase (, '' alpha-glucosidase'', ''glucoinvertase'', ''glucosidosucrase'', ''maltase-glucoamylase'', ''alpha-glucopyranosidase'', ''glucosidoinvertase'', ''alpha-D-glucosidase'', ''alpha-glucoside hydrolase'', ''alpha-1,4-glucosidase'', ''alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase'') is one type of alpha-glucosidase enzymes located in the brush border of the small intestine. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of disaccharide maltose into two simple sugars of glucose. Maltase is found in plants, bacteria, yeast, humans, and other vertebrates. It is thought to be synthesized by cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall. Digestion of starch requires six intestinal enzymes. Two of these enzymes are luminal endo-glucosidases named alpha-amylases. The other four enzymes have been identified as different maltases, exo-glucosidases bound to the luminal surface of enterocytes. Two of these maltase activities were associated with sucrase-isomaltase (maltase Ib, maltase Ia). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltase-glucoamylase
Maltase-glucoamylase, intestinal is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MGAM'' gene. Maltase-glucoamylase is an alpha-glucosidase digestive enzyme. It consists of two subunits with differing substrate specificity. Recombinant enzyme studies have shown that its N-terminal catalytic domain has highest activity against maltose, while the C-terminal domain has a broader substrate specificity and activity against glucose oligomers. In the small intestine, this enzyme works in synergy with sucrase-isomaltase and alpha-amylase to digest the full range of dietary starches. Gene The MGAM gene –– which is located on chromosome 7q34 –– codes for the protein Maltase-Glucoamylase. An alternative name for Maltase-Glucoamylase is glucan 1,4-alpha-glycosidase. Tissue distribution Maltase-glucoamylase is a membrane-bound enzyme located in the intestinal walls. This lining of the intestine forms brush border in which food has to pass in order for the intestines to absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acarbose
Acarbose (INN) is an anti-diabetic drug used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2 and, in some countries, prediabetes. It is a generic sold in Europe and China as Glucobay (Bayer AG), in North America as Precose ( Bayer Pharmaceuticals), and in Canada as Prandase (Bayer AG). It is cheap and popular in China, but not in the U.S. One physician explains the use in the U.S. is limited because it is not potent enough to justify the side effects of diarrhea and flatulence. However, a recent large study concludes "acarbose is effective, safe and well tolerated in a large cohort of Asian patients with type 2 diabetes." A possible explanation for the differing opinions is an observation that acarbose is significantly more effective in patients eating a relatively high carbohydrate Eastern diet. It is a starch blocker, and inhibits alpha glucosidase, an intestinal enzyme that releases glucose from larger carbohydrates. It is composed of an acarviosin moiety with a maltose at the reducing term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alglucosidase Alfa
Alglucosidase alfa, sold under the brand name Myozyme among others, is an enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) orphan drug for treatment of Pompe disease (Glycogen storage disease type II), a rare lysosomal storage disorder (LSD). Chemically speaking, the drug is an analog of the enzyme that is deficient in patients affected by Pompe disease, alpha-glucosidase. It is the first drug available to treat this disease. It was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2006, as Myozyme and in May 2010, as Lumizyme. Medical uses Alglucosidase alfa is indicated for people with Pompe disease (GAA deficiency). In 2014 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of alglucosidase alfa for treatment of people with infantile-onset Pompe disease, including people who are less than eight years of age. In addition, the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) is being eliminated. Side effects Common observed adverse reactions to alglucosidase alfa treatment are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azoospermia
Azoospermia is the medical condition of a man whose semen contains no sperm. It is associated with male infertility, but many forms are amenable to medical treatment. In humans, azoospermia affects about 1% of the male population and may be seen in up to 20% of male infertility situations in Canada. In a non-pathological context, azoospermia is also the intended result of a successful vasectomy. Classification Azoospermia can be classified into three major types as listed. Many conditions listed may also cause various degrees of oligospermia rather than azoospermia. Pretesticular and testicular azoospermia are known as non-obstructive azoospermia, whereas post-testicular azoospermia is considered obstructive. Pretesticular Pretesticular azoospermia is characterized by inadequate stimulation of otherwise normal testicles and genital tract. Typically, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are low (hypogonadotropic) commensurate with inadequate stimulation of the testes to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This technique is also called micropropagation. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions the need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases ( CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment ( pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavone, a type of flavonoid, with a yellow crystalline appearance. Luteolin is the principal yellow dye compound that is obtained from the plant ''Reseda luteola'', which has been used as a source of the dye since at least the first millennium B.C. Luteolin was first isolated in pure form, and named, in 1829 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. The luteolin empirical formula was determined by the Austrian chemists Heinrich Hlasiwetz and Leopold Pfaundler in 1864. In 1896, the English chemist Arthur George Perkin proposed the correct structure for luteolin. Perkin's proposed structure for luteolin was confirmed in 1900 when the Polish-Swiss chemist Stanislaw Kostanecki (1860–1910) and his students A. Różycki and J. Tambor synthesized luteolin. Natural occurrences Luteolin is most often found in leaves, but it is also seen in rinds, barks, clover blossom, and ragweed pollen. It has also been isolated from the aromatic flowering plant, ''Salvia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |